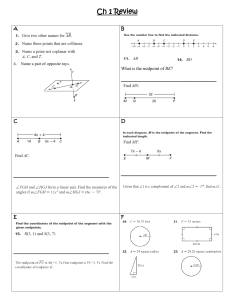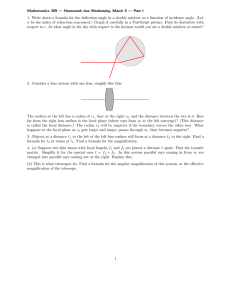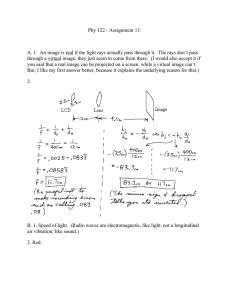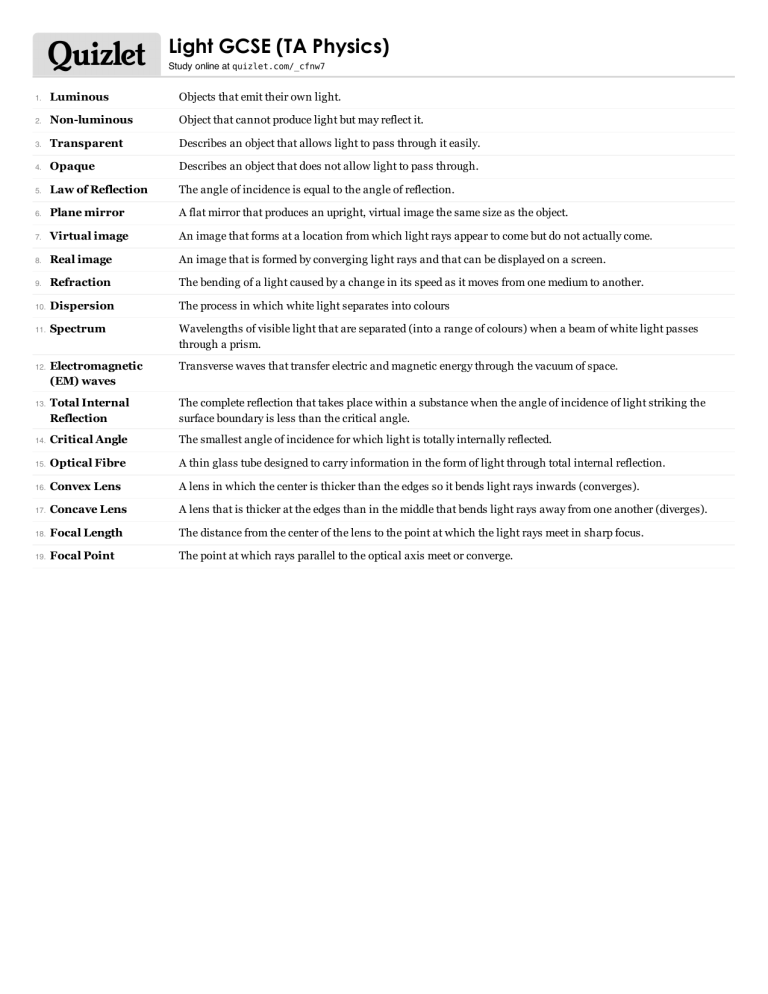
Light GCSE (TA Physics) Study online at quizlet.com/_cfnw7 1. Luminous Objects that emit their own light. 2. Non-luminous Object that cannot produce light but may reflect it. 3. Transparent Describes an object that allows light to pass through it easily. 4. Opaque Describes an object that does not allow light to pass through. 5. Law of Reflection The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. 6. Plane mirror A flat mirror that produces an upright, virtual image the same size as the object. 7. Virtual image An image that forms at a location from which light rays appear to come but do not actually come. 8. Real image An image that is formed by converging light rays and that can be displayed on a screen. 9. Refraction The bending of a light caused by a change in its speed as it moves from one medium to another. 10. Dispersion The process in which white light separates into colours 11. Spectrum Wavelengths of visible light that are separated (into a range of colours) when a beam of white light passes through a prism. Electromagnetic (EM) waves Transverse waves that transfer electric and magnetic energy through the vacuum of space. Total Internal Reflection The complete reflection that takes place within a substance when the angle of incidence of light striking the surface boundary is less than the critical angle. 14. Critical Angle The smallest angle of incidence for which light is totally internally reflected. 15. Optical Fibre A thin glass tube designed to carry information in the form of light through total internal reflection. 16. Convex Lens A lens in which the center is thicker than the edges so it bends light rays inwards (converges). 17. Concave Lens A lens that is thicker at the edges than in the middle that bends light rays away from one another (diverges). 18. Focal Length The distance from the center of the lens to the point at which the light rays meet in sharp focus. 19. Focal Point The point at which rays parallel to the optical axis meet or converge. 12. 13. Luminous Objects that emit their own light. Non-luminous Object that cannot produce light but may reflect it. Transparent Describes an object that allows light to pass through it easily. Opaque Describes an object that does not allow light to pass through. Law of Reflection The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Plane mirror A flat mirror that produces an upright, virtual image the same size as the object. Virtual image An image that forms at a location from which light rays appear to come but do not actually come. Real image An image that is formed by converging light rays and that can be displayed on a screen. Refraction The bending of a light caused by a change in its speed as it moves from one medium to another. Dispersion The process in which white light separates into colours Spectrum Wavelengths of visible light that are separated (into a range of colours) when a beam of white light passes through a prism. Electromagnetic (EM) waves Transverse waves that transfer electric and magnetic energy through the vacuum of space. Total Internal Reflection The complete reflection that takes place within a substance when the angle of incidence of light striking the surface boundary is less than the critical angle. Critical Angle The smallest angle of incidence for which light is totally internally reflected. Optical Fibre A thin glass tube designed to carry information in the form of light through total internal reflection. Convex Lens A lens in which the center is thicker than the edges so it bends light rays inwards (converges). Concave Lens A lens that is thicker at the edges than in the middle that bends light rays away from one another (diverges). Focal Length The distance from the center of the lens to the point at which the light rays meet in sharp focus. Focal Point The point at which rays parallel to the optical axis meet or converge. Light GCSE (TA Physics) NAME: ________________________ 7 Written Questions 1. Electromagnetic (EM) waves 2. Optical Fibre 3. Convex Lens 4. Non-luminous 5. Total Internal Reflection 6. Law of Reflection 7. Luminous 6 Multiple Choice Questions 1. Virtual image a. An image that is formed by converging light rays and that can be displayed on a screen. b. The smallest angle of incidence for which light is totally internally reflected. c. The process in which white light separates into colours d. An image that forms at a location from which light rays appear to come but do not actually come. 2. Concave Lens a. The distance from the center of the lens to the point at which the light rays meet in sharp focus. b. A lens in which the center is thicker than the edges so it bends light rays inwards (converges). c. A lens that is thicker at the edges than in the middle that bends light rays away from one another (diverges). d. Describes an object that does not allow light to pass through. 3. Spectrum a. Describes an object that allows light to pass through it easily. b. The process in which white light separates into colours c. The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. d. Wavelengths of visible light that are separated (into a range of colours) when a beam of white light passes through a prism. 4. Dispersion a. Objects that emit their own light. b. The point at which rays parallel to the optical axis meet or converge. c. The process in which white light separates into colours d. The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. 5. Opaque a. Objects that emit their own light. b. Describes an object that does not allow light to pass through. c. Object that cannot produce light but may reflect it. d. Describes an object that allows light to pass through it easily. 6. Real image a. An image that forms at a location from which light rays appear to come but do not actually come. b. Object that cannot produce light but may reflect it. c. The smallest angle of incidence for which light is totally internally reflected. d. An image that is formed by converging light rays and that can be displayed on a screen. 6 True/False Questions 1. The smallest angle of incidence for which light is totally internally reflected. → Critical Angle True False 2. The bending of a light caused by a change in its speed as it moves from one medium to another. → Focal Point True False 3. The distance from the center of the lens to the point at which the light rays meet in sharp focus. → Focal Length True False 4. The point at which rays parallel to the optical axis meet or converge. → Focal Point True False 5. Describes an object that allows light to pass through it easily. → Opaque True False 6. A flat mirror that produces an upright, virtual image the same size as the object. → Plane mirror True False