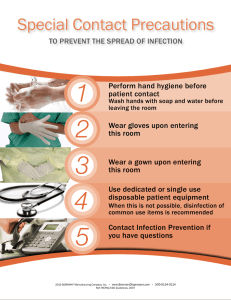
ENVIRONMENTAL SANITATION (HEALTHCARE) SANITATION o The word sanitation is derived from the Latin word “sanitas” meaning “health”. “All precautions and measures which are necessary in production, processing, storage and distribution, in order to assure an unobjectionable, sound and palatable product which is suited for human consumption”-(WHO). ENVIRONMENTAL SANITATION o Means the art and science of applying sanitary, biological and physical science principles and knowledge to improve and control the environment and factors therein for the protection of the health and welfare of the public. PATHOLOGIC ORGANISM o Any microscopic life form, from a virus to a nematode that has the potential to cause disease. Are of five main types: Viruses bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and worms. HOSPITAL-ACQUIRED INFECTION A hospital-acquired infection (HAI), also known as a nosocomial infection, is an infection that is acquired in a hospital or other health care facility. Such an infection can be acquired in: MAIN ROUTES OF TRANSMISSION 1. CONTACT TRANSMISSION o The most important and frequent mode of transmission of nosocomial infections is by direct contact. Divided into two subgroups: DIRECT-CONTACT: This involves a direct body surface-to-body surface contact and physical transfer of microorganisms between a susceptible host and an infected or colonized person. INDIRECT-CONTACT: This involves contact of a susceptible host with a contaminated intermediate object, usually inanimate, such as contaminated instruments, needles, or dressings, or contaminated gloves that are not changed between patients. 2. DROPLET TRANSMISSION o Transmission occurs when droplets containing microbes from the infected person are propelled a short distance through the air and deposited on the patient's body; droplets are generated from the source person mainly by coughing, sneezing, and talking, and during the performance of certain procedures. 3. AIRBORNE TRANSMISSION o Microorganisms carried in this manner can be dispersed widely by air currents and may become inhaled by a susceptible host within the same room or over a longer distance from the source patient, depending on environmental factors. 4. COMMON VEHICLE TRANSMISSION o This applies to microorganisms transmitted to the host by contaminated items, such as food, water, medications, devices, and equipment. 5. VECTOR BORNE TRANSMISSION o This occurs when vectors such as mosquitoes, flies, rats, and other vermin transmit microorganisms. Prevention WHO IS AT RISK OF HAI (HEALTHCARE-ASSOCIATED INFECTIONS)? DISINFECTION o Disinfection is the process, which involves the elimination of most pathogenic microorganisms (excluding bacterial spores) on inanimate objects. o The method of disinfection is used internationally for the safety of humans, to decrease the scale of transmission of diseases. HOSPITAL DISINFECTION o Hospital disinfection is a critical topic in infection control. o Without the standards of disinfection from hand washing to scrubs to proper ventilation -- hospitals would be the dens of illness and disease that they once were. UV LIGHT HOSPITAL DISINFECTION o Are used to kill pathogens associated with infectious disease and infections. o These devices work primarily through the use of lamps that produce high-intensity ultraviolet C (UV-C) light; UV-C is germicidal; o It destroys the DNA of bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms, preventing them from multiplying, repairing the damaged DNA, and causing infections and disease. STERILIZATION o Sterilization refers to any process that eliminates, removes, kills, or deactivates all forms of life and other biological agents (such as fungi, bacteria, viruses, spore forms, prions, unicellular eukaryotic organisms) present in a specified region, such as a surface, a volume of fluid, medication, or in a compound such as biological culture media. Environmental Health Hazard An environmental health hazard is a substance, state or event which has the potential to threaten the surrounding natural environment and/or adversely affect human's health. Three Fundamental Sets of Components: PURPOSE OR IMPORTANCE OF ENVIRONMENTAL SANITATION: To provide a healthy living environment for everyone either patient or health worker; To reduce the risk of diseases/infections spreading; and To provide safety, security and protection of both patients’ and health workers’ health. Color Coding Scheme for Health Care Waste Color of container/bag Black Green Yellow Yellow w/ black band Orange Red Type of waste Non-infectious dry waste Non-infectious wet waste (kitchen, dietary etc.) Infectious and pathological waste Chemical waste including those w/ heavy metals Radioactive waste Sharps and pressurized containers Basic steps in health care waste handling