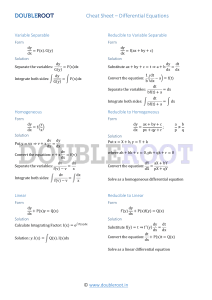
Enzyme Kinetics I Biological Catalysts • enzyme-catalysed reaction – reaction rate depends on [S] Initial Velocity or V0 – rate affected – equilibrium never affected Substrate concentration or [S] Michaelis-Menten equation • enzymes combines reversibly with substrate – form ES complex. • ES complex breaks downs substrate yielding free enzyme and product – rate limiting step E+S ES E+P Michaelis-Menten equation Initial Velocity or V0 Michaelis-Menten equation Vmax [ S ] Vo Km [ S ] Substrate concentration or [S] Linear Plots double-reciprocal plot or Lineweaver-Burk plot 1 V0 Slope Km 1 Vmax 1 1 [S ] Km Vmax 1 Km [ S ] V0 Vmax [ S ] Velocity (umol/min) [S] (M) Velocity (1/umol/min) [S] (1/M) 130 6.5 * 10-4 0.00769 1.539 * 103 116 2.3 * 10-4 0.00862 4.35 * 103 87 7.9 * 10-5 0.0115 1.27 * 104 63 3.9 * 10-5 0.0159 2.56 * 104 30 1.3 * 10-5 0.0330 7.69 * 104 10 3.7 * 10-6 0.1000 2.7 * 105 Reciprocal data 0.12000 y = 3E-07x + 0.0071 0.10000 0.08000 0.06000 0.04000 0.02000 0.00000 -50000.0 0.0 50000.0 100000.0 150000.0 200000.0 250000.0 300000.0 Reversible Inhibition • Competitive inhibition – Inhibitor competes with the substrate for the active site of an enzyme 1 V0 [I] 1 Vmax 1 [S ] • Uncompetitive inhibition – Inhibitor binds at a site distinct from the substrate active site AND only to ES complex 1 V0 [I] 1 [S ] • Mixed inhibition – Inhibitor binds at a site distinct from the substrate active site AND either E or ES 1 V0 [I] 1 [S ]