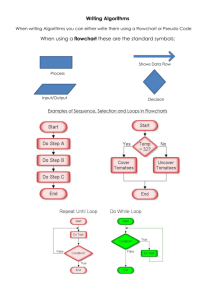
Introduction to Computer Programming Engr Asma Ali • Course Code: • Credit Hours: • Pre-requisite(s): • Email Address: CS-1301 2+1 None asma.ali@kiet.edu.pk Books: • Text Book: Problem solving and program design in C by Jeri R. Hanly, Elliot B. Koffman. (7th edition) • Reference Books: C - How To Program By Deitel Content : 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. What is Flowchart Flowchart Building Block Decimal-to-Binary Conversion What is Algorithm Tips to Write Good Pseudo Code Machine Language versus HLL FLOWCHART WHAT IS A FLOWCHART? • A flowchart is simply a graphical representation of steps. It shows steps in sequential order and is widely used in presenting the flow of algorithms, workflow or processes. WHEN TO USE A FLOWCHART? • To develop understanding of how a process is done • To study a process for improvement • To communicate to others how a process is done • To document a process • When planning a project Flowchart Symbols • Different flowchart shapes have different conventional meanings. The meanings of some of the more common shapes are as follows: Example: Write a program calculating the sum of two numbers: Example: Find the largest among three different numbers entered by the user. Decimal-to-Binary Conversion • Convert the following decimals into binary : 1. 2. 3. 4. 23 26 29 28.125 What is Algorithm • A set of step to accomplish a task. • An algorithm describes the step by step action to solve a problem. • An algorithm has a well defined sequence of steps, it gives you an output, and it will eventually terminate • List of steps for solving a problem. • There are many models supporting the development of the code: • Pseudo code • Structure Diagram • Flowcharts Example • Write an algorithm and draw a flow chart to compute the average of three numbers. Declare a variable a,b,c and avg as int; Read two numbers a,b and c; avg=(a+b+c)/3; Print avg; Assignment: • Write an algorithm and flow chart to find the area of rectangle. • Write an algorithm and flow chart of square of number. • Write algorithm and draw flowchart to find largest number among two numbers. Pseudo Code • An algorithm is a systematic logical approach used to solve problems in a computer while Pseudo code is the statement in plain English which may be translated later into a programming language (program). • Pseudo-code is just a syntax of the communication about solving a problem. This means that the algorithm is an actual way a problem is solved while the pseudo-code is just a way of expressing that way. Pseudo Code: • Uses phrases to outline the task • Easy to read and write • Allow the programmer to concentrate on the logic of the problem • Structured in English language • Pseudo code is "halfway" between English and a programming language. • It is a description of a process in detail, though not necessarily in full sentences. • The key is to provide enough information so that anyone could follow the instructions Pseudocode Write a program calculating the sum of two numbers: Pseudocode are English-like statements that follow a loosely defined syntax and are used to convey the design of an algorithm. Version 1: Version 2: PROGRAM Add Two Numbers READ two numbers ADD the numbers WRITE the sum END PROGRAM PROGRAM Add Two Numbers READ First READ Second Sum = First + Second WRITE Sum END PROGRAM Programming Languages: • Various programming languages enable people to tell computers what to do • Foundation for developing applications The Language Translation Process: • How are Programs Understood by the Computer? Program written in programming language (source code) Translator program Assembler Compiler Interpreter Program written in machine language (object code) Processed By CPU Programming Languages • Machine Language (first generation of programming languages) • The computer’s ‘natural language’ • Composed of binary digits (0s, 1s) • The only language that computers understand • Assembly Language (second generation of programming languages) • One-to-one correspondence to machine language • Somewhat more user-friendly than machine language (mnemonic rather than binary digits) • Assembler – program that translates an assembly language program into machine language Programming Languages: • Procedural Languages (High Level Languages) (third generation languages) • • • • • • One instruction translates into many machine language instructions Programs describe the computer’s processing step-by-step Closer to natural language; uses common words rather than abbreviated mnemonics Examples: C, Fortran, QuickBasic Compiler - translates the entire program into machine language Interpreter - translates and executes one source program statement at a time Programming Languages: • Nonprocedural Language (fourth generation languages) • Allows the user to specify the desired result without having to specify the detailed procedures needed for achieving the result • Example: data base query language - SQL • Can be used by non technical users • Natural Language Programming Languages (fifth generation (intelligent) languages) • Translates natural languages into a structured, machine-readable form • Are extremely complex and experimental Processing A High Level Language Program: Steps to execute a program written in C: 1. Use an editor to create a program. (source program) 2. Compiler translate the program in to an equivalent machine language. (object program) 3. The programs that you write in a high-level language are developed using a software development kit (SDK), which contains many programs that are useful in creating your program. This prewritten code resides in a place called the library. 4. Linking programs: The linker assembles all of functions (source and system’s) into final executable program. 5. The next step is to load the executable program into the main memory for execution and a program called loader accomplishes this. 6. The final step is to execute the program. THANK YOU