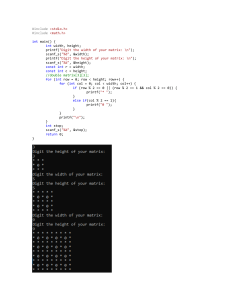
C Programming
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
..
..
return 0;
}
Ex:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf(“Hello world”);
return 0;
}
Output:
Hello world
For input: scanf(“format”, variable list)
For output: printf(“format”, variable list)
Format:
%d
integer
%c
character
%f
float
%lf double
Ex: Display a rectangle on the screen
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf(“**********”);
printf(“*
*”);
printf(“*
*”);
printf(“*
*”);
printf(“**********”);
return 0;
}
Output
**********
*
*
*
*
*
*
**********
Variables
a,var1,n,i…
Type
int
float, double
char
long, short
integer
real numbers
characters
Ex: Read a number from keyboard and display its square.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a, square;
printf(“Enter the number”);
scanf(“%d”, &a);
square=a*a;
printf(“%d”, square);
return 0;
}
a
5
Ex: Read two numbers from keyboard and display their sum.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n1, n2, sum;
printf(“Enter 2 numbers”);
scanf(“%d %d”, &n1, &n2);
n1
n2
sum
3
5
8
sum=n1+n2;
printf(“The sum of %d and %d is %d”, n1, n2, sum);
return 0;
}
Input:
3 5
Output:
The sum of 3 and 5 is 8
Ex: User enters initials and birth year. The program must calculate
and display the age.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char name, lastname;
int birthyear, age;
name
A
lastname
birthyear
2000
S
age
22
printf(“Enter initials and birth year”);
scanf(“%c %c %d”, &name, &lastname, &birthyear);
age=2022-birthyear;
printf(“Hello %c %c! you are %d years old”, name, lastname, age);
return 0;
}
Input:
A S 2000
Output:
Hello A S! you are 22 years old
Ex: Read three values and calculate their average.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
double a,b,c, aver;
a
2.0
printf(“Enter 3 values”);
scanf(“%lf %lf %lf”, &a, &b, &c);
aver=(a+b+c)/3;
printf(“average is %5.2lf”, aver);
b
3.0
c
aver
4.0
3.0
return 0;
}
Input:
200.0 300.0 400.0
Output:
average is 300.0
3.00
----300.00
-----300.457
300.46
.--
(round)
Arithmetic Operations
+
*
/
%
addition
subtraction
multiplication
division
remainder
Type conversion
Ex: Integers
15/3
17/3
3/15
0/4
4/0
5
5 5.6666..
0
0
undefined
int op int int
double op double double
double op int
double
int op double
double
Ex:
(double)16/3
16.0/3 5.3333
Ex: Read 3 integer numbers from keyboard and calculate their average.
int main()
{
int a,b,c, sum;
double aver;
a
b
printf(“Enter 3 values”);
scanf(“%d %d %d”, &a, &b, &c);
sum=a+b+c;
aver=(double)sum/3;
// or
aver=sum/3.0;
printf(“average is %5.2lf”, aver);
return 0;
}
Rules for Evaluating Expressions
1. Paranthesis rule
a=(b+c)*(d-3);
2. Operator Presedence
Unary +, *, /, %
+, a= -b;
a=b+c*d-3;
a= -b*c;
Ex:
a=πr2
PI=3.14;
area=PI*r*r;
unary 𝑎 = 𝑏 + (𝑐. 𝑑) − 3
c
aver
Ex: 𝑣 =
𝑝2−𝑝1
𝑡2−𝑡1
V = (p2-p1)/(t2-t1);
Functions
Ex: Function without parameters
#include <stdio.h>
void hello();
function prototype
int main()
{
hello();
return 0;
}
function call
void hello()
{
printf(“Hello world\n”);
}
function body
OR
#include <stdio.h>
void hello()
{
printf(“Hello world\n”);
}
int main()
{
hello();
return 0;
}
Functions
function body
function call
Ex: Function with input parameters
#include <stdio.h>
void square(double x);
function prototype
int main()
{
parameter/argument
square(5.0);
function call
return 0;
}
void square(double x)
{
printf(“x=%lf x square= %lf \n”, x, x*x); function body
}
x
5.0
Output:
x=5.0
x square= 25.0
Ex: Function with input parameters and a single result
#include <stdio.h>
double square(double x);
function prototype
int main()
{
parameter/argument
double a;
a=square(5.0);
printf(“5 square= %lf \n”, a);
return 0;
}
double square(double x)
{
double y;
y=x*x;
return y;
}
Output:
5 square= 25.0
5.0
y
x
5.0
25.
0
Ex: Function with Multiple input parameters and a single result
Y=10a+b
#include <stdio.h>
double addmult(double k, double l);
int main()
{
double a=5.0, b=7.0, y;
y= addmult (a,b);
printf(“result= %lf \n”, y);
return 0;
}
double addmult(double k, double l)
{
double w;
w=k*10+l;
//5*10+7
return w;
}
Output:
result= 57.0
b
a
7.0
5.0
l
k
7.0
5.0
w
57.
0
Library Functions
Math library
#include <math.h>
sin(x)
cos()
tan(x)
…
pow(x,y)
sqrt(x)
exp(x)
log(x)
log10(x)
fabs(x)
ceil(x)
floor(x)
x must be in radians
xy
Ex: pow(2.0, 3.0) 8.0
square root of x
Ex: sqrt(4.0) 2.0
ex
e=2.71828…
logex
log10x
|x| absolute value
ceiling
ceil(45.67) 46.0
ceil(45.23) 46.0
floor
floor(45.67) 45.0
Ex: ax2+by+c=0
Roots x1, x2
Discriminant b2-4ac
int main()
{
double a, b, c, discr, x1,x2;
…
//read the numbers here
discr=pow(b,2.0)-4*a*c;
x1= (-b + sqrt(discr))/(2.0*a);
x2= (-b - sqrt(discr))/(2.0*a);
// print…
}
Ex: a2=b2+c2-2bc.cos(t)
Calculate a.
#define PI 3.1415
a= sqrt(pow(b, 2.0) + pow(c, 2.0) – 2*b*c*cos(t*PI/180.0) );
Ex: Calculate (x2+2x)+(y2+2y)+(z2+2z)
double myfunc(double x);
int main()
{
double a,b,c, result;
scanf(“%d %d %d “, &a,&b,&c);
result=myfunc(a)+myfunc(b)+myfunc(c);
printf(“%lf”, result);
return 0;
}
double myfunc(double x)
{
double f;
f=pow(x,2.0)+2*x;
return f;
}
Ex: Write a function to calculate the maximum of two numbers and
return the maximum. Call this function to find the maximum of the
numbers entered from keyboard.
#include <stdio.h>
int maximum(int x, int y)
{
int max;
if (x>y)
{
max=x;
}
else
{
max=y;
}
return max;
}
int main()
{
int a,b;
printf (“enter a,b”);
scanf(“%d %d”, &a, &b);
printf(“the max of %d and %d is %d”, a, b, maximum(a,b));
return 0;
}
Ex: Maximum of 3 numbers
#include <stdio.h>
int maximum(int x, int y)
{
if (x>y)
return x;
else
return y;
}
int main()
{
int a,b,c,mx;
printf (“enter a,b,c”);
scanf(“%d %d %d”, &a, &b, &c);
mx=maximum(a,b);
mx=maximum(mx,c);
printf(“the max of %d %d %d is %d”, a, b, c, mx);
return 0;
}
if Statements
if (condition)
{
….
}
if (condition)
{
….
}
else
{
….
}
Variable or constant or expression
Operators
==
!=
>
>=
<
<=
equal
not equal
Logical operators
&&
||
!
AND
OR
NOT
Ex:
a>5 && a<=10
a= 6,7,8,9,10
Ex:
!(n>100)
(n<=100)
n=100,99,…
Ex:
!(0<=n && n<=100)
n=… -2,-1,101,102,…
Ex:
(0>n && n>100)
always False
(pq)’= p’q’
Ex:
x+y/2 >= a-3 && a>5
opearator
Variable or constant or expression
precedence:
1. arithmetic expressions
2. arithmetic operators
3. logical operators
Ex: Read a number from keyboard and decide if it is positive, negative
or zero.
int main()
{
int n;
printf (“enter n”);
scanf(“%d”, &n);
if (n==0)
{
printf(“zero”);
)
else
{
if(n>0)
{
printf(“positive”);
}
else
{
printf(“negative”);
}
}
return 0;
}
Ex: Find the letter grade:
80-100
60-80
40-60
<40
A
B
C
F
int main()
{
int grade;
printf (“enter grade”);
scanf(“%d”, &grade);
if(grade>=80 && grade <=100)
printf(“A”);
else
{
if(grade >=60 && grade <80)
printf(“B”);
else
{
if(grade >=40 && grade <60)
printf(“C”);
else
{
if(grade<40)
printf(“F”);
else
printf(“wrong grade”);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
Assume all data is between 0-100
if(grade>=80)
printf(“A”);
else
{
if(grade >=60)
printf(“B”);
else
{
if(grade >=40)
printf(“C”);
else
{
printf(“F”);
}
}
}
Ex:
Read two values: number of attempts (n) and score (s).
n=1
n=1
n>1
n>1
s>=50
s<50
s>=50
s<50
excellent
good
can be improved
try harder
if (n==1)
{
if(s>=50)
printf(“excellent”);
else
printf(“good”);
}
else
{
if(s>=50)
printf(“can be improved”);
else
printf(“try harder”);
}
else belongs to the last if
Ex:
if (a==5)
if(b==6)
printf(“ 5 & 6”);
else
printf(“xx”);
if (a==5)
if(b==6)
printf(“ 5 & 6”);
else
printf(“xx”);
if (a==5)
{
if(b==6)
printf(“ 5 & 6”);
else
printf(“xx”);
}
input
5 6
5 7
output
5 & 6
xx
if (a==5)
{
if(b==6)
printf(“ 5 & 6”);
}
else
printf(“xx”);
input
5 6
5 7
output
5 & 6
Ex:
char letter;
switch (letter)
{
case ‘A’: grade=100;
break;
case ‘B’: grade=80;
break;
case ‘C’: grade=60;
break;
case ‘F’: grade=0;
break;
default:
printf(“unknown grade”);
}
printf(“grade is %d”, grade);
Ex:
Write a function to calculate b2-4ac
−𝑏±√𝑏22 −4𝑎𝑐
If b2-4ac is positive calculate
2𝑎
Otherwise print “cannot be calculated”
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
double discr(double a, double b, double c)
{
return pow(b,2.0)-4*a*c;
}
int main()
{
double a,b,c, x1,x2;
printf(“enter a,b,c”);
scanf(“%lf %lf %lf”, &a, &b, &c);
if (discr(a,b,c)>0)
{
printf(“%lf %lf”,
( -b+sqrt(discr(a,b,c)) )/(2*a),
( -b-sqrt(discr(a,b,c)) )/(2*a));
}
else
printf(“cannot be calculated”);
return 0;
}
Ex: Interest calculation
Currency type:
$
‘d’
€
‘e’
TL
‘t’
Interest rates (x):
$
%1
€
%2 if amount<100
TL
%8
3% if amount>=100
Write a function to calculate a+ax
Input: amount (a), currency type
double new_amount(double a, double x)
{
return a+a*x;
}
int main();
{
double amount;
char curr;
printf(“enter amount and currency type”);
scanf(“%lf %c”, &amount, &curr);
if (curr==’d’)
printf(“%lf”, new_amount(amount, 0.01));
else
{
if (curr==’e’)
{
if( amount <100)
printf(“%lf”, new_amount(amount, 0.02));
else
printf(“%lf”, new_amount(amount, 0.03));
}
else
{
if (curr==’t’)
printf(“%lf”, new_amount(amount, 0.08));
else
printf(“%c invalid currency”, curr);
}
}
return 0;
}
switch (curr)
{
case ‘d’:
case ‘e’:
case ‘t’:
default:
}
printf(“%lf”, new_amount(amount, 0.01));
break;
if( amount <100)
printf(“%lf”, new_amount(amount, 0.02));
else
printf(“%lf”, new_amount(amount, 0.03));
break;
printf(“%lf”, new_amount(amount, 0.08));
break;
printf(“invalid currency”);
Loops
while(condition)
{
Statements
}
Ex: Print the square of 5 numbers that are entered from the keyboard.
int main()
{
int n, i;
i=0;
//counter 0,1,2,3,4
while(i<5)
{
printf(“enter n”);
scanf(“%d”, &n);
printf(“square= %d”, n*n);
i++;
//i=i+1; increment counter
}
return 0;
}
Ex: Compute the sum of 5 numbers that are entered from the keyboard.
int main()
{
int n, i, sum;
sum=0;
i=0;
//counter 0,1,2,3,4
while(i<5)
{
printf(“enter n”);
scanf(“%d”, &n);
sum=sum+n;
i++;
//i=i+1;
}
printf(“sum= %d”, sum);
return 0;
increment counter
}
Ex: Print the even numbers from 12 to 20.
int main()
{
int n;
n=12;
while(n<=20)
{
printf(“%d”, n);
n=n+2;
}
return 0;
}
n
output
12
12
14
14
16
16
18
18
20
20
22
Ex: Print the even numbers from 20 to 12.
int main()
{
int n;
n=20;
while(n>=12)
{
printf(“%d”, n);
n=n-2;
}
return 0;
}
n . . . 14 12 10
output …16 14 12
Ex: Sentinel controlled loops
Sum all numbers entered from the keyboard until -1 is entered.
-1 is the sentinel value.
int main()
{
int n, sum;
sum=0;
printf(“enter n”);
scanf(“%d”, &n);
// get data
while(n!= -1)
{
sum=sum+n;
//process data
printf(“enter n”);
scanf(“%d”, &n); //get another data
}
return 0;
}
Get data
while(sentinel value has not been encountered)
{
Process data
Get another data
}
Ex: Conditional loop
Stock contains 100 cars. Read the number of cars sold and subtract it
from the stock. If stock is less than 10, print the message “ lower
than min. stock”
int main()
{
int stock=100, n;
printf(“enter n”);
scanf(“%d”, &n);
// get data
stock=stock-n;
while(stock >= 10)
{
printf(“enter n”);
scanf(“%d”, &n);
// get data
stock=stock-n;
}
printf(“ lower than min. stock”);
return 0;
}
Ex: Flags
Read 10 numbers and sum them. If the numbers contain a negative value,
display a warning.
int main()
{
int n, i, sum, flag;
sum=0;
i=0;
flag=0;
// false
while(i<10)
{
printf(“enter n”);
scanf(“%d”, &n);
if (n<0)
flag=1;
// true
sum+=n;
// sum=sum+n;
i++;
// i=i+1;
}
if (flag==1)
printf(“ sum=%d
warning! Negative value”, sum);
else
printf(“sum=%d”, sum);
return 0;
}
Nested Loops
Ex: Find the factorial of the numbers entered from the keyboard. Exit
if a negative number is given.
int main()
{
int n, fact, i;
printf(“enter a number”);
scanf(“%d”, &n);
while(n>=0)
{
//find factorial
fact=1;
i=1;
while(i<=n)
{
fact *= i;
//fact=fact*i;
i++;
// i=i+1;
}
printf(“%d factorial is %d”, n, fact);
printf(“enter a number”);
scanf(“%d”, &n);
}
return 0;
}
Ex:
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
2
2 3
2 3 4
2 3 4 5
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int row, col;
row=0;
while(row<=5)
{
col=0;
while(col<=row)
{
printf("%d ", col);
col=col+1;
}
row=row+1;
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
Ex:
0
0 1
0 1 2
0 1 2 3
0
1
2
3
4
0
1
2
3
4
5
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int row, col, nblanks, i;
row=0;
nblanks=10;
while(row<=5)
{
i=0;
while(i<nblanks)
{
printf(" ");
i++;
}
col=0;
while(col<=row)
{
printf("%d ", col);
col=col+1;
}
row=row+1;
printf("\n");
nblanks=nblanks-2;
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
Ex:
*
* *
* * *
* * * *
* * * * *
* * * * * *
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int row, col, nblanks, i;
row=0;
nblanks=5;
while(row<=5)
{
i=0;
while(i<nblanks)
{
printf(" ");
i++;
}
col=0;
while(col<=row)
{
printf("* ");
col=col+1;
}
row=row+1;
printf("\n");
nblanks=nblanks-1;
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}