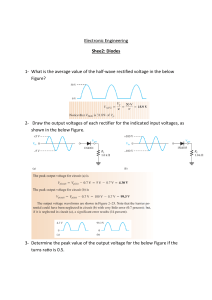
NAME: MA. THEREZA R. ZAMORA Design Activity 1 Using the Multisim, make the following circuits according to the given block diagram. Measure the voltages in test points 1 & 2 using the voltmeter. Connect the virtual oscilloscope, draw the waveforms in test points 1 & 2. 1 Transformer Vrms = 12 V Freq = 60 Hz Rectifier 2 1N4001 1. half-wave rectifier circuit 2. full-wave rectifier circuit (with two diodes) 3. bridge-type rectifier circuit (with four diodes) 1. HALF-WAVE RECTIFIER CIRCUIT Diagram: The 12-Vrms, 60-Hz voltage In a similar fashion, we can source simulates the power line. The calculate default turns ratio is 10:1, which means secondary current can be determined by the primary has ten times more windings Ohm’s law. than the secondary. Using the ideal transformer relationship to determine the 𝐼𝑠 = the primary current. The 𝑉𝑠 1.2𝑉𝑟𝑚𝑠 = = 1.2𝑚𝐴𝑟𝑚𝑠 𝑅𝐿 1000𝑜ℎ𝑚𝑠 secondary voltage. 𝐼𝑝 𝑁𝑠 = 𝐼𝑠 𝑁𝑝 𝑉𝑠 𝑁𝑠 1 = = 𝑉𝑝 𝑁𝑝 10 𝑁𝑠 1 (12𝑉𝑟𝑚𝑠) = 1.2𝑉𝑟𝑚𝑠 𝑉𝑠 = (𝑉𝑝 ) = 𝑁𝑝 10 𝐼𝑝 = 𝑉𝑠 1 (1.2𝑚𝐴𝑟𝑚𝑠 ) = 0.12𝑚𝐴 (𝐼𝑠 ) = 𝑅𝐿 10 AC supply is given to the primary winding, the step-down transformer, and the secondary winding, the low voltage output from the secondary winding of the transformer is given to the half wave rectifier circuit. Here, T1 is a step-down transformer, which provides the secondary voltage, Vout. When the top of the transformer secondary voltage is positive, D1 is forward-biased, producing current flow in the load, R1 which is the resistive load the half wave rectifier used to convert alternating voltage or current into pulsating voltage or current for one half cycle period of the input cycle. When the top of the secondary is negative, D1 is reverse-biased and acts like an open switch. This results in zero current in the load, R1. As a result of this action, the output voltage is a series of positive pulses. The output waveform for the half-wave rectifier shown above that in anytime the secondary voltage is positive, D1 conducts and produces current flow in the load, R1. The input signal, the rectifier and the output signal are shown above. A single diode acts as a half wave rectifier the AC supply to be rectified is applied in series with the diode and load resistance R1. Generally, AC supply is given through a transformer the use of transformer permits two advantages: it allows us to step up or step down the AC input voltage as the situation demands and the transformer isolates the rectifier circuit from power line reducing the risk of electric shock. 2. FULL-WAVE RECTIFIER CIRCUIT (2- DIODES) Diagram: A full wave rectifier is an electronic circuit which converts AC voltage into pulsating DC voltage using both half cycles of the applied AC input voltage. It consists of a transformer two semiconductor diodes and a load resistor R1. The secondary windings of a transformer is center-tapped the two voltages V1 and V2 fed to the two diodes are equal in magnitude but opposite in 180 degrees phase difference one ND terminal a of the transformer secondary is connected to the anode of diode D1 and the other end terminal b is connected to the anode of diode D2. the load resistor RL is connected between the center tap c of the secondary winding and inter junction of two cathodes of diode D1 and D2. Whenever the secondary voltage, V1, is positive, D2 conducts and provides the output waveform. Likewise, whenever the secondary voltage, V2 becomes positive, D2 conducts and provides the output waveform in. Notice that D1 and D2 conduct on opposite half-cycles of the secondary voltage, VS. When V1 is positive, D2 is off. Likewise, when V2 is positive, D1 is off. Each diode provides a half-wave rectified waveform for the load, R1. The combined effects of D1 and D2 are also shown above. The fact that the dc diode current is one-half the dc load current is best explained by examining its waveforms. This is also because, each diode supplies its own half-wave rectified waveform to the load, R1. 3. FULL-WAVE BRIDGE TYPE RECTIFIER CIRCUIT Diagram: The input sine signal is given to the bridge rectifier circuit and rectifier output signal is obtained. A bridge rectifier is an electronic circuit which converts AC voltage into a pulsating DC voltage using both half cycles of the applied AC. It consists of the transformer core semiconductor diodes and a load resistor R1, the AC voltage to be rectified is applied across one diagonal of the bridge through a power transformer. T1 is a step-down transformer, which provides the secondary voltage. When the top of the secondary is positive, diodes D2 and D3 are forward-biased. This produces current flow in the load, R1. For this polarity of secondary voltage, D1 and D4 are reverse-biased and do not conduct. When the top of the secondary is negative, D1 and D4 are forward-biased, producing current flow in the load R1. For this polarity of secondary voltage, D2 and D3 are reverse-biased and do not conduct. It is important to note that the direction of current through R1 is the same for both half-cycles of the secondary voltage. NAME: MA. THEREZA R. ZAMORA Design Activity 2 Using the Multisim, make a bridge-type power supply circuit according to the given block diagram. Measure the voltages in test points 1 to 4 using the voltmeter and place in the table below. Connect the virtual oscilloscope and draw the waveforms in each test points. 1 2 3 4 Transformer Vrms = 12V Freq = 60 Hz Rectifier 4 pcs- 1N4004 Filter 1 - 1000µF Regulator Vz = 12 volts zener diode For the bridge-type power supply circuit, the voltage across the capacitor is used and Vrms as the input voltage for the regulator circuit. A zener diode with Vz = 12 volts and a resistor, R1 is connected in series with each other and to the capacitor. Finally, a load resistor, R_L is placed in parallel connection to the series arrangement of the zener diode. This voltage regulator circuit is used to eliminate the ripple in the output of the filter capacitor and produces an output with almost no ripple. In designing the required voltage regulator that gives the filtered and regulated DC voltage of 12V from the given AC voltage of 12Vrms and a frequency of 60Hz, it passed through a power transformer to an obtained voltage output. The signal was then rectified using a full-wave bridge rectifier to obtain only a positive-side sine wave. Then passed it through the filter capacitor to obtain a particular voltage maximum boundary. Then voltage regulator is used to produce an even DC voltage that is of a constant output. Schematic Diagrams (Attach the diagram, including the connections of the test instruments.) Use separate diagrams for each test points. For a capacitor of 1µF: TEST POINT 1 2 3 4 VOLTAGE, VOLTS For a capacitor of 1000 µF: TEST POINT 1 2 3 4 VOLTAGE, VOLTS WAVEFORM Bridge-type Power Supply Circuit measured using Tektronix Oscilloscope: