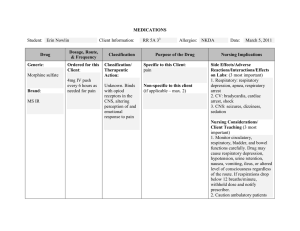
N480: Advanced Medical Surgical Nursing Course Pre-Work Name: _____________________________________________ Date: ______________ CRITICAL CARE Critical Care - Airway Management and Mechanical Ventilation 1. Differentiate the various certification opportunities for critical care nurses. 2. Select appropriate nursing interventions to manage common problems and needs of critically ill patients. 3. Develop strategies to manage issues related to caregivers of critically ill patients. 4. Differentiate the indications for and modes of mechanical ventilation. 5. Select appropriate nursing interventions related to the care of an intubated patient. 6. Relate the principles of mechanical ventilation to the nursing and interprofessional management of patients receiving this intervention. LOWER RESPIRATORY PROBLEMS Lower Respiratory Problems 1. Compare and contrast the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and nursing and interprofessional management of pneumothorax, fractured ribs, and flail chest. 2. Describe the purpose, function, and nursing responsibilities related to chest tubes and various drainage systems. 3. Explain the types of chest surgery and appropriate preoperative and postoperative care. 4. Describe the etiology, clinical manifestations, and nursing and interprofessional management of patients with restrictive lung disorders such as pleural effusion, pleurisy, and atelectasis. 5. Describe the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and nursing and interprofessional management of pulmonary embolism ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE AND ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME Acute Respiratory Failure and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome 1. Compare the pathophysiologic mechanisms and clinical manifestations that result in hypoxemic and hypercapnic respiratory failure. 2. Differentiate between the nursing and interprofessional management of the patient with hypoxemic or hypercapnic respiratory failure. 3. Relate the pathophysiologic mechanisms and the clinical manifestations associated with acute respiratory failure and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). 4. Select appropriate nursing and interprofessional interventions for the patient with ARDS. 5. Prioritize measures to prevent or reverse complications that may result from acute respiratory failure or ARDS.