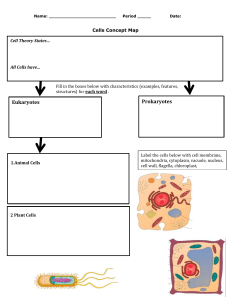
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION 2 Organelles • Very small (Microscopic) • Perform various functions for a cell • Found in the cytoplasm • May or may not be membrane- bound 3 ANIMAL CELL ORGANELLES Nucleolus Nucleus Nuclear envelope Rough endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus Ribosome (attached) Ribosome (free) Cell Membrane Mitochondrion Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Centrioles 4 Plant Cell Organelles Cell Structure and Function Chart Organelle • • • • • • • • Cell wall Cytoplasm Nucleus Nuclear membrane Nucleolus Cytoskeleton Centrioles Mitochondria Structure • • • • • • • • • Function Rough endoplasmic reticulum Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Ribosome Golgi bodies Lysosome Cilia Flagella Vacuole Chloroplast 6 Cytoplasm of a Cell cytoplasm • Jelly-like substance enclosed by cell membrane • Provides a medium for chemical reactions to take place 7 The Control Organelle - Nucleus • Controls the normal activities of the cell • Contains the DNA in chromosomes • Surrounded by a nuclear membrane with pores • Usually the largest organelle Nuclear Membrane • Double membrane surrounding nucleus • Also called nuclear envelope • Contains nuclear pores for materials to enter & leave nucleus • Connected to the rough ER Nuclear pores 8 9 Inside the Nucleus The genetic material (DNA) is found 10 Nucleolus • Inside nucleus • Makes ribosomes that make proteins Cytoskeleton • Helps cell maintain cell shape • Also help move organelles around • Made of proteins 11 12 Cytoskeleton MICROTUBULES MICROFILAMENTS 13 Mitochondrion (plural = mitochondria) • “Powerhouse” of the cell • Generate cellular energy (ATP) • Both plants & animal cells have mitochondria • Site of CELLULAR RESPIRATION (burning glucose) 14 MITOCHONDRIA Surrounded by a DOUBLE membrane Has its own DNA Folded inner membrane called CRISTAE (increases surface area for more chemical Reactions) Interior called MATRIX 15 Interesting Fact --• Mitochondria comes from cytoplasm in the EGG cell during fertilization Therefore … • You inherit your mitochondria from your mother! Endoplasmic Reticulum - ER 16 • Network of membranes • Connects to nuclear envelope & cell membrane • Functions in Synthesis of cell products & Transport Two kinds of ER ---ROUGH & SMOOTH 17 Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough ER) • Has ribosomes on its surface • Makes membrane proteins and proteins for EXPORT out of cell 18 Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum • Smooth ER lacks ribosomes on its surface • Is attached to the ends of rough ER • Makes cell products that are USED INSIDE the cell (ex: lipids) and helps destroy toxic substances 19 Endomembrane System Includes nuclear membrane connected to ER connected to cell membrane (transport) 20 Ribosomes • Made of PROTEINS and rRNA • “Protein factories” for cell • Join amino acids to make proteins • Process called protein synthesis 21 Ribosomes Can be attached to Rough ER OR Be free (unattached) in the cytoplasm 22 Golgi Bodies • Stacks of flattened sacs • Receive proteins made by ER • Package proteins and ship them to other parts of the cell OR outside the cell CIS TRANS Transport vesicle 23 Lysosomes • Contain digestive enzymes • Break down food, bacteria, and worn out cell parts for cells 24 Cilia & Flagella • Both function in movement • Cilia are shorter and more numerous on cells • Flagella are longer and fewer (usually 1-3) on cells 25 Vacuoles • Fluid filled sacks for storage • Small or absent in animal cells • Plant cells have a large Central Vacuole 26 Centrioles • Found only in animal cells • Paired structures near nucleus • Appear during cell division • Help to pull chromosome pairs apart to opposite ends of the cell 27 Chloroplasts • Found only in plant cells • Use energy from sunlight to make own food (glucose) • Energy from sun stored in the Chemical Bonds of Sugars 28 Chloroplasts • Surrounded by DOUBLE membrane • Outer membrane smooth • Inner membrane modified into sacs called Thylakoids • Thylakoids in stacks called Grana & interconnected • Stroma – gel like material surrounding thylakoids 29 Cell Wall • Nonliving layer • Found in plant cells • Supports and protects cell • Outside of cell membrane Cell wall Plant vs. Animal Cell Cell wall Chloroplast Large, central vacuole Sometimes lysosomes Plant Cytoplasm Nucleus Nuclear membrane Nucleolus Mitochondria ER Ribosome Golgi Cilia Flagella Vacuole Centrioles Many smaller vacuoles All have lysosomes Cytoskeleton Animal Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells • Prokaryotes • Bacterial cells • Smaller • More primitive structures • No nucleus or membrane-bound organelles • Usually unicellular organisms • Eukaryotes • Plant and animal cells • Have a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles Characteristic Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Size of cell Typically 0.2-2.0 m m in diameter Typically 10-100 m m in diameter Nucleus No nuclear membrane or nucleoli True nucleus, consisting of nuclear membrane & nucleoli Membrane-enclosed organelles Absent Present; examples include lysosomes, Golgi complex, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria & chloroplasts Flagella Consist of two protein building blocks Complex; consist of multiple microtubules Cell wall Usually present Present in plant cells Plasma membrane Simple cell membrane Present Cytoplasm Present Present Ribosomes Smaller size Larger size Chromosome (DNA) arrangement Single circular chromosome Multiple linear chromosomes