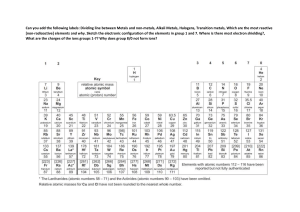
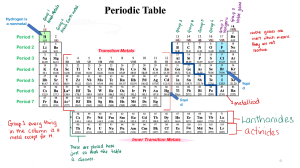
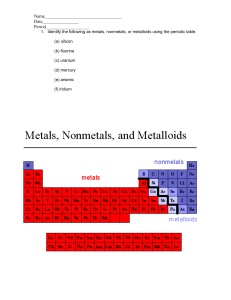
Elements & their Properties Ch. 17 Metals Metals are elements that are shiny, malleable, ductile, and good conductors of heat and electricity. -Everything left of zigzag. Group 1: Alkali Metals Characteristics ● Alkali metals are soft metals due to weak metallic bonding. They can be easily cut by knife. The hardness of the alkali metals decreases down the group. ● They have low melting and boiling points. ● They are highly reactive metals. ● Readily lose their two outermost electrons to form cations with a 1+ charge. Group 2: Alkaline Earth Metals Characteristics ● shiny. ● silvery-white. ● somewhat reactive metals at standard temperature and pressure. ● readily lose their two outermost electrons to form cations with a 2+ charge. ● low densities, low melting points, low boiling points Groups 3-12: Transition Elements Characteristics ● they are good conductors of heat and electricity. ● they can be hammered or bent into shape easily. ● they have high melting points (but mercury is a liquid at room temperature) ● they are usually hard and tough. ● they have high densities. ● Show variable oxidation states (different amounts of electrons gained or lost) nonMetals Hydrogen Characteristics ● ● ● ● ● Colorless Odorless Tasteless non poisonous gas under normal conditions on Earth. It typically exists as a diatomic molecule, pure hydrogen is commonly expressed as “H2“ Group 7A or 17: Halogens Characteristics ● They all form acids when combined with hydrogen. ● are all fairly toxic ● readily combine with metals to form salts ● have seven valence electrons in their outer shell ● are highly reactive and electronegative ● all exist as diatomic molecules (two atoms) when in their pure form Group 8A or 18: Noble Gas Characteristics ● ● ● ● ● Fairly nonreactive Complete outer electron or valence shell Very low electronegativities Low boiling points No color, odor, or flavor under ordinary conditions (but may form colored liquids and solids) ● Nonflammable ● At low pressure, they will conduct electricity and fluoresce Metalloids Metalloid Characteristics Metalloids are elements that have some properties of metals and some properties of nonmetals. ● Form ionic bonds and covalent bonds ● Can conduct electricity better than nonmetals but not as well as many metals ● Located along the stair step line. Group 3A or 13: Boron Group ● Boron is used in borax and boric acid in laundry products and heat-resistant glass (lab equipment) ● Aluminum is the most abundant metal in earth’s crust ● Gallium is used in electronic components ● Indium and Thallium = very rare metals Carbon and its Allotropes ● ● Carbon, nonmetal, occurs in coal and foods and is essential for life. Allotrope: different molecular structures of same element. Silicon and Semiconductors ● ● Silicon, metalloid, is second only to oxygen in abundance in Earth’s crust. Found in sand and almost all rocks and soil. Semiconductors are elements that conduct an electric current under certain conditions. Group 4A or 14: Carbon Group Characteristics ● Have 4 valence electrons, ● Includes nonmetals, metalloids, and metals ● Tin, metal, is used to coat other metals to prevent corrosion. ● Lead is used in car batteries. Group 5A or 15: Nitrogen, nonmetal, used to make ammonia and nitrates. Nitrogen is the 4th most abundant element in your body. Phosphorus is a nonmetal that has 3 allotropes. Used for water softeners to fertilizers, and match heads. Arsenic and antimony are metalloids, toxic Bismuth, metal, used in fire sprinkler heads because of low melting point. Group 6A or 16: Oxygen Group ● Oxygen, nonmetal, exists in air as diatomic ● Is essential for life ● Sulfur, nonmetal, combines with metals to be used in pigments in paints. ● Selenium is a trace element in diet, toxic in excess ● Tellurium and polonium, metalloids