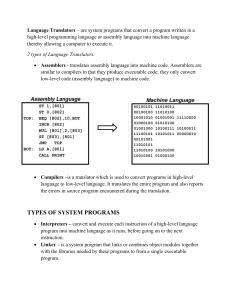
High- and Low-Level Languages Key definitions Computer program A list of instructions that enable a computer to perform a specific task. Translator Translators convert a program into binary instructions that computers can understand. Computer programs A computer program is a list of instructions that enable a computer to perform a specific task. Computer programs can be written in high-level languages and low-level languages depending on the task to be performed and the computer to be used. Most programmers write programs in high-level languages. High-level languages High-level languages enable a programmer to focus on the problem to be solved and require no knowledge of the hardware and instruction set of the computer that will use the program. High-level programming languages are portable and can be used on different types of computer. Low-level languages Low-level languages relate to the specific architecture and hardware of a particular type of computer. Low-level languages can refer to machine code, the binary instructions that a computer understands, or assembly language that needs to be translated into machine code. Assembly languages Assembly language is a low-level programming language that needs to be translated into machine code by an assembler. Machine code Machine code is the binary instructions that a computer understands. No translation is required. Common errors • Students often say that machine code needs translation. • Students often reverse the definitions of high- and low-level languages. Sample question a) a Give one advantage of writing a program in a high-level language. b) b Give one advantage of writing a program in assembly language. c) c Give one advantage of writing a program in machine code. Examiner's tip Read the question carefully; does it ask for advantages or benefits or disadvantages or limitations? Answer the question as set; both advantages and disadvantages require a comparison. No comparison is required for benefits and limitations. Student answer a) Programs are easy to understand. b) To make use of hardware. c) Programs do not need to be translated. Translators In order to be used by a computer, programs need to be translated into the binary instructions, machine code, that the computer understands. Compilers A compiler is a computer program that translates a program written in a high-level language (HLL) into machine code so that it can be directly used by a computer to perform a required task. Interpreters An interpreter is a computer program that reads a statement from a program written in a high-level language performs the action specified and then does the same with the next statement and so on. Assemblers An assembler is a computer program that translates a program written in an assembly language into machine code so that it can be directly used by a computer to perform a required task. Summary Complier Interpreter Assembler Translates a high-level language program into machine code Executes a high-level language program one statement at a time. Translates a low-level language program into machine code. An executable file of machine code is produced. No executable file of machine code is produced. An executable file of machine code is produced. One high-level language statement can be translated into several machine code instructions. One high-level language program statement may require several machine code instructions to be executed. One low-level language statement is usually translated into one machine code instruction. Compiled programs are used without the compiler. Interpreted programs cannot be used without the interpreter. Assembled programs can be used without the assembler, A compiled program is usually distributed for general use. An interpreter is often used An assembled program is when a program is being usually distributed for developed. general use. Sample question a) Describe two differences between a compiler and an interpreter. b) State, with a reason, a situation where you would use each one. Each situation must be different. Student answer a) A compiler translates a whole program at one go, an interpreter translates a line at a time. A compiler produces a translated program, an interpreter does not. b) Compiler: for distributing a program for general use, because the program will not require the compiler to run. Interpreter: for developing a program as errors are shown on a line by line basis. Examiner's comments In part a, the student has given two differences by explaining what happens in the same situation in each case. For the first difference, it would have been more accurate to state that the interpreter executes the program a line at a time. In part b, the student has identified two different situations correctly. both reasons given identify what is happening but not why it is useful. For the compiler, the users do not have to download or purchase the compiler. For the interpreter, the developer can resume the development of the program immediately one error has been corrected without having to correct every error in the program. Exam-style questions 1. Which translators are being described here? a. 'translates a high-level language into machine codex b. 'translates a low-level language into machine codex c. 'executes a high-Level language program line by line' [3 marks] 2. Identify the type of language that the following programs have been written in. a) LDA NoOne ADD NoTwo STO' Answer b) Answer := NoOne + NoTwo c) 1 4 0 d) 0001 0100 0000 12 13 1A 00010010 00010011 00011000 3. Name three different types of language translator and explain what each one is used for. 4. a) Give two disadvantages of writing a program in a high-level language. b) Give two disadvantages of writing a program in a low-level language.