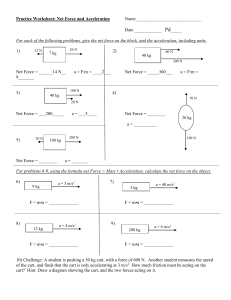
Newton’s second laws Experiment: Using the electric vibration device 1. State and analyze the new concept to be taught - What is the quantitative relationship between the acceleration of an object, force causing that acceleration and the mass of the object? 2. How to elicit problem Situation: - Use a shopping cart when at supermarket. - When there is no item in the cart, we push it with a light force, we see the cart move slowly. But when we push it with a stronger force, we see the cart move much faster, which means the acceleration of the cart has been increased. - Similarly, now we put some item in the cart, and then push it. Then, keep applying the same force but we add to the cart more items so that its mass is twice the initial one. We will see that, when there is more items in the cart, the car will move much slower, which means the acceleration has been decreased. Problem: - What is the quantitative relationship between the acceleration of an object, force causing that acceleration and the mass of the object? 3. How to deduce theoretically - Suppose I have a cart with 2 weights, which runs on a flat bench with rail, one end of the bench is connected to a pulley of negligible weight. A string is attached with the pulley, connected to the cart and hung another weight as shown. - In this system what force changes the movement of the cart? - When the mass of the object is constant, we change the force exerted on the object by taking the weights down from the cart. At this point, gravitational force is increased. We see the cart moves faster then before, which mean the acceleration of the object has been increased. - Keep the gravitational force constant, arrange the same objects as above, but the cart has no weights yet, let the cart move. And then place 2 weights on the cart and. We will see that when increasing the mass of the object, the cart moves much slower, which means the acceleration of the object has been decreased. - We may predict: acceleration of an object in motion is directly proportional to the force on it when the mass is constant and acceleration of objects with different masses under the same force is inversely proportional to the mass. 4. How to design experiments Using the electric vibration device - To carry out the experiment, we need a cart, 3 weights, an aluminum track at the end with 1 fixed pulley, 1 electric vibration device operating at voltage 220V, frequency of 50 Hz. The structure of the electric vibration device includes an electromagnet inside with a vibration device at the end with a pen nib. - Under the nib is a roller to support the paper tape. When the car is in motion, the paper tape will roll over the top of the roller and the nib will mark the paper tape with small dots; the string is connected to the cart, pulley and masses; an inkpot and a ruler. - Firstly case: m is constant Keep the mass of the system unchanged, increase force acting on the cart by moving a mass from the cart to the hanging end-point of the string. - Secondly case: F is constant Because the force acting on the cart is the mass, so we keep the force acting on the cart unchanged and put some more masses on the cart in order that the weigth of the system increases 2 or 1.5 times. Image of paper we may have... And use ruler to measure the distance between two nearest spots.