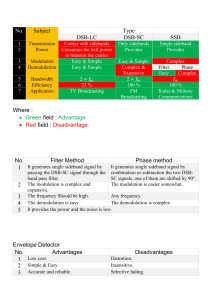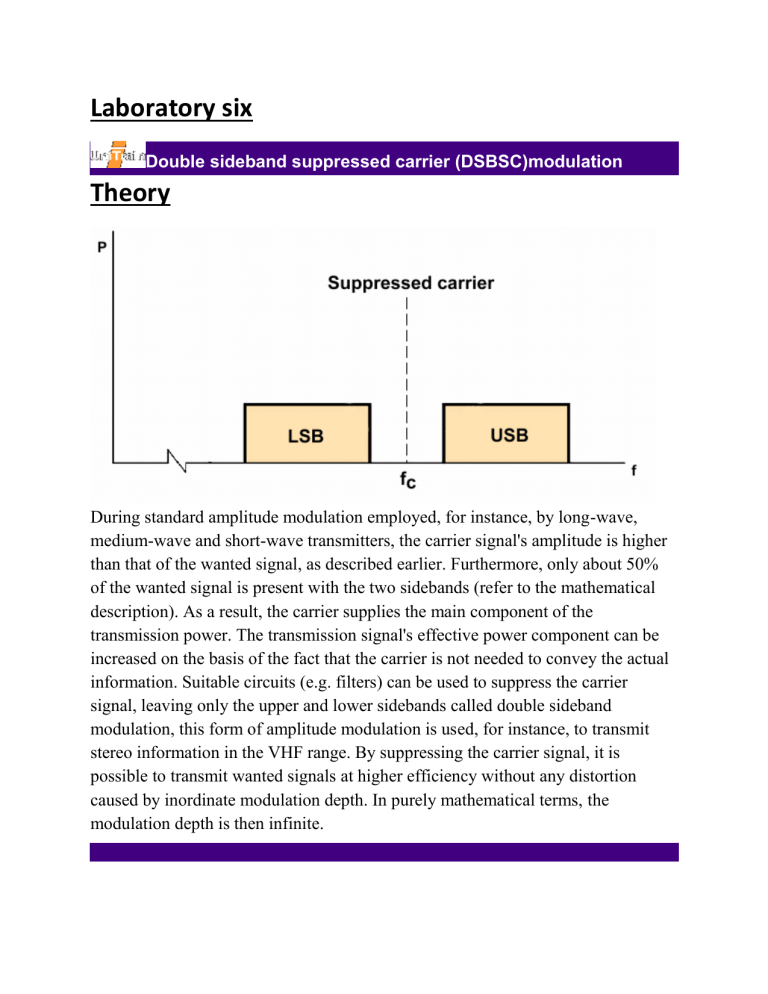
Laboratory six Double sideband suppressed carrier (DSBSC)modulation Theory During standard amplitude modulation employed, for instance, by long-wave, medium-wave and short-wave transmitters, the carrier signal's amplitude is higher than that of the wanted signal, as described earlier. Furthermore, only about 50% of the wanted signal is present with the two sidebands (refer to the mathematical description). As a result, the carrier supplies the main component of the transmission power. The transmission signal's effective power component can be increased on the basis of the fact that the carrier is not needed to convey the actual information. Suitable circuits (e.g. filters) can be used to suppress the carrier signal, leaving only the upper and lower sidebands called double sideband modulation, this form of amplitude modulation is used, for instance, to transmit stereo information in the VHF range. By suppressing the carrier signal, it is possible to transmit wanted signals at higher efficiency without any distortion caused by inordinate modulation depth. In purely mathematical terms, the modulation depth is then infinite. objective To understand the advantage of double side band suppressed carrier modulation and to determine the modulation index. Required material 1: Interface board 2 :BNC connector 3 :AM modulator 4:USB cabels 5 :Computer 5.1 osciloscope 5.2 spectrum analyiser 5.3 function Generator 5.4 Digital Multimeter Experiment Setup (Procdure) This experiment is meant to elucidate the principle of double sideband modulation. Oscilloscope measurements will demonstrate how the carrier signal's amplitude is suppressed almost fully during DSB, so that just the two sidebands are transmitted. 1.The experiment set up as shown below. • the bridging plug was fit on the AM modulator's "DSB/AM" contacts. • On the Colpitts oscillator, the carrier signal's amplitude increased to 200 mVpp. 2.On oscilloscope channel A, the signal supplied by oscillator output 1:1 was measured . After that the signal at the "AMout" output (without the modulation signal),was measured. .Observation A B C The modulator's output supplies the carrier signal with a very small amplitude, termed residual carrier. The modulator's output supplies no measurable signal. Answer: A The amplitude of the carrier signal at the modulator's output is larger than in the case of AM. 3. the value (residual carrier) at the "AMout" measurement point was minimized with the help of the "Carrier Null" potentiometer (near centre setting) , the function generator was opened via the menu path Instruments | Voltage sources | Function generator or by clicking on the icon below, and the settings shown in the adjacent table was performed. . Function generator settings Mode: SINE Amplitude: 1:10, 50% (approx. 1 Vpp) Frequency: 10 kHz 4. The oscilloscope was opened by clicking on the right on the toolbar. Instrument: symbol at the top Oscilloscope Time base: 10 µs / div Channel A: 200 mV / div, DC Channel B: 500 mV / div, AC Trigger: Channel A 5. The low-frequency signal on oscilloscope channel A , and the modulated output signal on channel B were measured. Channel B's input was set to AC coupling and the low-frequency signal was used as a basis for the trigger. X/T X = 10 µs/DIV (A) Channel 200mV/DIVDC A= Channel 500mV/DIVAC B= The signal measured at the modulator's output given a minimal residual carrier and low-frequency input signal was described as follows. The measured signal is shaped like an AM signal A with a modulation depth of 0.5. The measured signal is shaped like an AM signal Answer: C B with a modulation depth of 1. The measured signal is shaped like an AM signal C with over-modulation m>1). The obtained measurement result was viewed using the oscilloscope's X / Y display mode and copied the oscillogram on the placeholder provided below. X = 10 µs/DIVX/Y Channel 200mV/DIVDC A= Channel 500mV/DIVAC B= The appearance of the measured signal in the oscilloscope's X / Y display mode was described. The signal appears in the form of two adjacent A trapezoids. The signal appears in the form of two adjacent, B .Answer: C vertical lines. The signal appears in the form of two adjacent C triangles. The oscilloscope was switched back to the X / t display mode and set so that the modulated signal's characteristic at a zero crossing can be specifically observed . the trigger point was shifted to the middle of the oscilloscope screen and a time base of 2 µs was selected. X= X/T (A, 2 µs/DIV PT 50%) Channel 200mV/DIVDC A= Channel 500mV/DIVAC B= Describe the modulator's output signal at the envelope's zero crossing. A phase jump occurs at the zero A crossing. No phase jump occurs at the zero ANSWER:A B crossing. The amplitude is irregular at the zero C crossing. When a phase jump occurs, what is its magnitude? The phase jump amounts to °. Describe the measurement result. The observed phenomenon is caused by When both signals cross 180 the X-axis simultaneously but at a phase displacement of 180°, Answer: The addition of upper and lower side band’s values the direction of addition is reversed phase jump is produced. Conclusion -The double Side Band Suppressed Carrier (DSBSC) Modulation is used to transmit the wanted signals at higher efficiency without any distortion caused by inordinate modulation depth. - When upper and lower side band values are added, the direction of addition is reversed and phase jump is produced in DSBSCM - The double Side Band Suppressed Carrier (DSBSC) Modulation is used for power efficient modulation. REVIEW QUESTIONS 1.Describe the advantage of DSBSC modulation over AM modulation. Ans. - In DSBSC since carrier is suppressed ,hence power consumption is reduced and nominal. - The power in the modulator signal is contained in all four sidebands - The Bandwidth of the DSBSC signal is double that of the message signal that is BWDSB-SC=2B(Hz). 2. Describe the disadvantage of DSBSC modulation over AM modulation. Ans. - carrier signal is not available in receiver. - envelop detection is not possible. 3. Describe the application of DSBSC modulation. Ans. - Analogue Tv system: to transmit color information -CB Radio -Air traffic control Radio -Two way Radio communications -Tv broadcasting -For transmitting stereo information in FM sound broadcasting at VHF 4. Design and simulate DSBSC modulator circuit. Ans. It is shown in the following page. 1 1.11113ddble sideband suppressed carrier (DSBSC)modulation