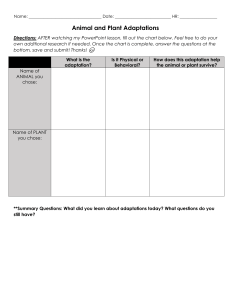
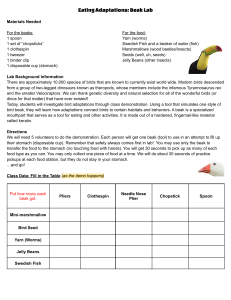
7.1 Adaptations and Variations -STUDENT Organisms are in a constant struggle to survive in the natural world. The interaction between organisms and their environment helps explain the diversity of species we see in the world. Activity- Different Beaks for Different Foods Video: Camel Adaptation Song (w/ lyrics) What are some environmental challenges? ______________________________________________________________________________ How do organisms cope with these challenges? _____________________________ -If a species does not adapt, it can go _____________. Species that go extinct no longer exist anywhere in the world. Adaptation: a structure, behavior, or physiological process that helps an organism survive and reproduce in a particular environment. “Changes in the body to suit its’ location!!!” 1.) Behavioral adaptations ______________________________________________________. EG. -hunting, running away, mating calls (bird video) 2.) Physiological adaptations ____________________________________________________. EG. Hibernation, venom 3.) Structural adaptations _____________________________________________________. -colour, shape Mimicry: A special type of structural adaptation. One species copies, or mimics, the appearance of another more harmful species. -viceroy vs. the monarch butterfly. Camouflage: appears to blend into environmental surroundings to hide/not be seen How do adaptations occur? Variation: _____________________________________________________________________. -Due to differences in genetic material (genotypes allele variation, or random mutations) -Adaptations exist because of the variations between individuals within a species. -heritable mutations provide new alleles in a species and are the starting point for genetic variation in species. -Mutations and the resulting phenotypic variations can have a positive, neutral or negative effect on a organism. If the effect is positive, the variation can accumulate in the population. -Environmental conditions determine whether a variation in an individual has a positive, negative, or no effect on the individual’s ability to survive or reproduce. The Case of the English Peppered Moth: Pre-industrial England vs. Industrial England How does genetic variation happen? 1.) Inheritance of different combination of alleles from parents 2.) Mutation: a permanent change in the genetic material of an organism; only source of new genetic material What causes mutations? ________________________________________________________ -Some mutations can be harmful, have no effect, or can be beneficial. -mutations can only be passed onto offspring if they occur in gamete cells -Beneficial mutations can cause a _________________________________. -Selective advantage ____________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ RAPID REPRODUCTION – rapid rate of reproduction allows the beneficial mutation to spread throughout the population as the population grows -When rapidly reproducing organisms develop a beneficial mutation, the affected organism may outlive other individuals and pass on their mutation to their offspring. The Case of Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria: pg 302 – Video: antibiotic resistant bacteria Homework: pg 299 pause and check, pg 304 # 1,2,3,7,8 Ticket in the Door: research a cool animal or plant that has an adaptation on youtube and determine whether it is a behavioral, structural or physiological adaptation – submit a written paragraph with the link of your findings on Edsby or hard copy. “BEAK” Adaptations Organisms living in the wild often face many challenges when it comes to finding and securing food to survive. Species often must adapt to their environment in order to successfully hunt or forage for their food. Some bird species for example, have different beaks in order to successfully secure different types of food. You will simulate the feeding method of three different types of bird : “beaks” using a spoon, forceps , and cotton ball to eat the three different types of “food”. Procedure: 1) Split up into groups of three. Have one group member collect the kit that contains the different beaks and food types. 2) Remove each food type from the kit and put them in an evenly distributed pile on the desk. 3) Starting with the spoon “beak” and small beads, try to “eat” as many food items within 10 second by picking them up and placing them in the provided paper cup. 4) Record the number of food items placed in the paper cup within the given 10 seconds. 5) Repeat for each “beak” type. “Food” Types “Beak” Types Spoon Forceps Cotton Ball Small Beads Large Beads Elastic Bands 1) In general, which beak is the most successful at gathering food? 2) Which beak is least successful at gathering food? What would happen to this species of bird if it does not manage to secure food in the long term? 3) How can the least successful species “adapt” in order to acquire more food? 4) With this adaptation in mind, redo the experiment once more using the newly adapted beak only. Is this newly adapted beak better at securing a type of food? 5) If the elastic band food type were to disappear, which species would be most affected? What might happen to that species?