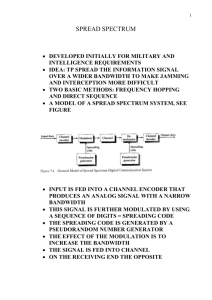
Basics of Communication Nithin Kumar N.R HOD Dept of EEE Sanjay Memorial Polytechnic Curriculum References Importance of Electronic Communication • Long distance communication is not possible without electronic media. • More and more people are looking for electronic means to transmit information. • Well-known forms of electronic communications, such as the telephone, radio and television, have increased our ability to share information. Today they are major part of the our lives. • An unexpected development in the role that computers play in communication E-mail and Internet allows: • Most economical way to get informations and communication. • Very high speed. • High security because of individual log-in and passwords. • On-line shopping, booking. Communication systems system carrier signal carried as hilltop beacons light on-off (fire or no fire) telegraph electric current on-off (Morse code) cable TV infrared in optical fibres ultra-fast (on-off) pulses mob phone microwave ultra-fast (on-off) pulses AM radio radio wave changing amplitude (AM) FM radio radio wave changing frequency (FM) Comms technologies change Communications: key terms transmitter ……………........… receiver encoding …………………….. decoding modulation…………….... demodulation All communication systems must contend with noise – unwanted interference. Engineers consider signal-to-noise ratio. Other parameters: data transmission rate, range, signal encoding. Source–journey–detector A useful model when describing communication systems based on: – visible light – infrared – microwaves – radio waves Fibre optic systems use light A simple transmitter: button cell & LED A simple detector: phototransistor + multimeter Infrared light is used more commonly than visible light - less attenuation and dispersion. Definitions 1.Analog signal Analog signal is the signal, in which voltage or current varies continuously with time. 2.Digital signal Digital signal is the discontinuous signal, which has only two levels, high and low or one and zero. 3.Baseband signal The electrical equivalent of original information (For example, sound) is known as Baseband signal. Elements of Basic Electronic Communication System Noise in Communication System and Types Noise is an unwanted electrical signal which gets added to the transmitting signal while travelling. Due to noise the quality of transmitted information will be degrade. Types of Electronic Communication Classification based on Direction of Communication Depending on direction used for communication, the communication system is classified as: Comparison of communication system The Electromagnetic Spectrum The frequency of EM signal ranges from few Hertz to several GHz. This entire range of frequencies of EM waves is called Electro-magnetic spectrum. Segments of EM spectrum EM Spectrum and Applications Concept of Transmission Bandwidth Transmission bandwidth is that portion of the electromagnetic spectrum occupied by a signal. Transmission bandwidth is also the frequency range over which an information signal is transmitted or over which an a receiver or other electronic circuit operates. B/W Continued…. ANY QUESTIONS?