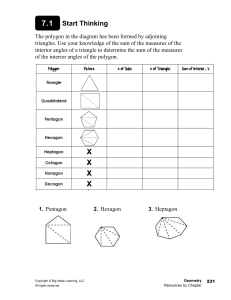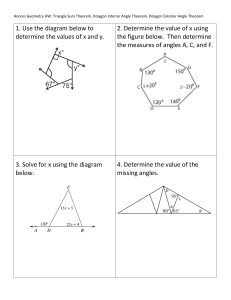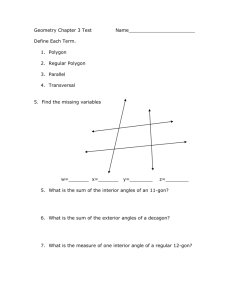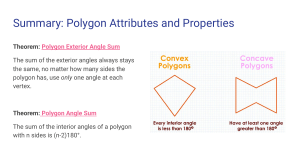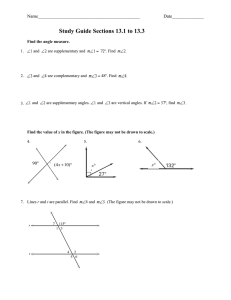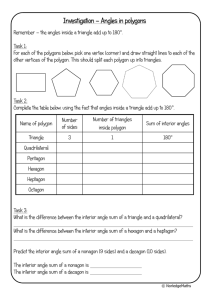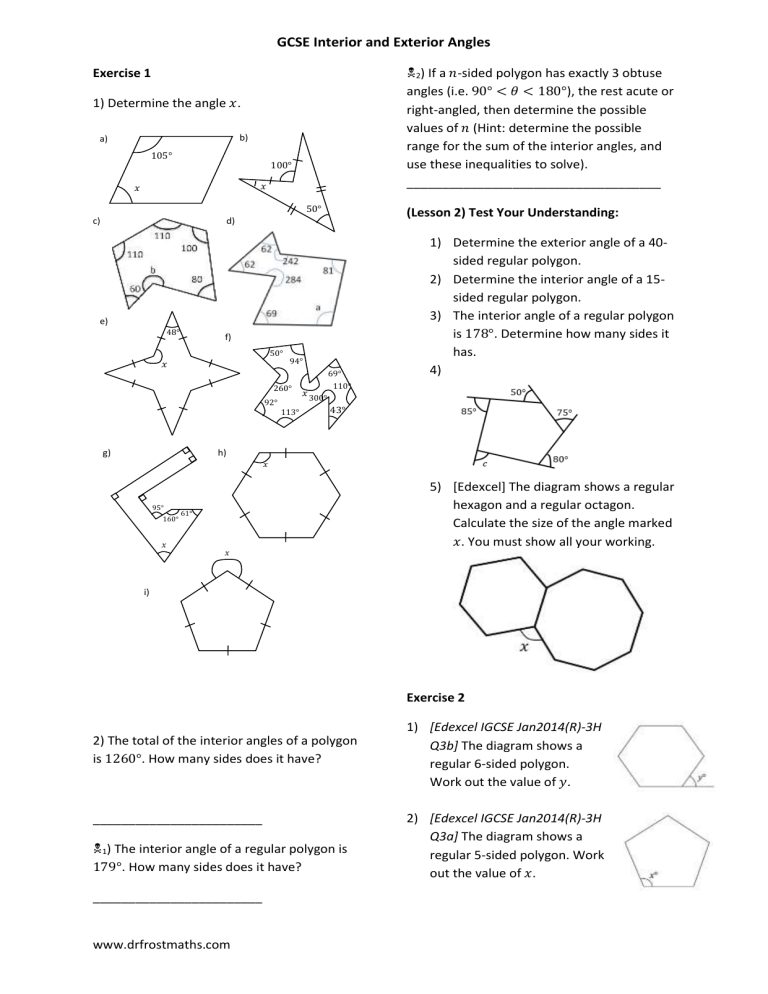
GCSE Interior and Exterior Angles 2) If a 𝑛-sided polygon has exactly 3 obtuse angles (i.e. 90° < 𝜃 < 180°), the rest acute or right-angled, then determine the possible values of 𝑛 (Hint: determine the possible range for the sum of the interior angles, and use these inequalities to solve). ____________________________________ Exercise 1 1) Determine the angle 𝑥. b) a) 105° 100° 𝑥 𝑥 50° c) (Lesson 2) Test Your Understanding: d) e) 48° f) 50° 𝑥 94° 69° 260° 92° 113° g) 𝑥 1) Determine the exterior angle of a 40sided regular polygon. 2) Determine the interior angle of a 15sided regular polygon. 3) The interior angle of a regular polygon is 178°. Determine how many sides it has. 4) 110° 300° 43° h) 𝑥 95° 160° 𝑥 5) [Edexcel] The diagram shows a regular hexagon and a regular octagon. Calculate the size of the angle marked 𝑥. You must show all your working. 61° 𝑥 i) Exercise 2 2) The total of the interior angles of a polygon is 1260°. How many sides does it have? ________________________ 1) The interior angle of a regular polygon is 179°. How many sides does it have? ________________________ www.drfrostmaths.com 1) [Edexcel IGCSE Jan2014(R)-3H Q3b] The diagram shows a regular 6-sided polygon. Work out the value of 𝑦. 2) [Edexcel IGCSE Jan2014(R)-3H Q3a] The diagram shows a regular 5-sided polygon. Work out the value of 𝑥. 3) Determine the value of 𝑎. 4) Determine how many sides a regular polygon with the following exterior angle would have: a. 30° ______________ b. 45° ______________ c. 12° ______________ d. 9° ______________ 5) Determine how many sides a regular polygon with the following interior angle would have: a. 156° ______________ b. 162° ______________ c. 144° ______________ d. 175° ______________ 6) [Edexcel GCSE Mar13-1H Q13] The diagram shows a square and 4 regular pentagons. Work out the size of the angle marked 𝑥. 7) [Edexcel IGCSE May2015(R)-3H Q2b] The diagram shows 3 identical regular pentagons. Work out the value of 𝑦. 8) [Edexcel IGCSE May2015(R)-3H Q2b] The diagram shows 3 identical regular pentagons. Work out the value of 𝑦. www.drfrostmaths.com 9) [JMO 2007 A6] The sizes in degrees of the interior angles of a pentagon are consecutive whole numbers. What is the size of the largest of these angles? 10) [IMC 2015 Q9] What is the value of 𝑝 + 𝑞+𝑟+𝑠+𝑡+𝑢+ 𝑣 + 𝑤 + 𝑥 + 𝑦 in the diagram? ____________________________________ Lesson 3: Test Your Understanding 1 The diagram shows 4 congruent regular pentagons that form the sides of an 𝑛-sided regular polygon. Determine the value of 𝑛. Test Your Understanding 2 [IMC 2006 Q19] The diagram shows a regular pentagon and a regular hexagon which overlap. What is the value of 𝑥? Test Your Understanding 3 [IMC 2009 Q12] The diagram shows a square inside a regular hexagon. What is the size of the marked angle at 𝑋? Exercise 3 1) [KS3 SATs 2004 L6-L8 Paper 2 Q19 Edited] A pupil has three tiles. One is a regular octagon, one is a regular hexagon, and one is a square. The side length of each tile is the same. The pupil says the hexagon will fit exactly like this. Is the pupil correct? 2) [Edexcel IGCSE Nov2009-3H Q3a] The diagram shows a regular octagon, with centre O. Work out the value of 𝑥. 7) [IMC 2003 Q22] The diagram shows a regular dodecagon (a polygon with twelve equal sides and equal angles). What is the size of the marked angle? 3) [Edexcel IGCSE Nov-2010-4H Q13] The size of each interior angle of a regular polygon is 11 times the size of each exterior angle. Work out the number of sides the polygon has. 8) [JMO 2014 B1] The figure shows an equilateral triangle ABC, a square BCDE, and a regular pentagon BEFGH. What is the difference between the sizes of ∠ADE and ∠AHE? 4) [Edexcel GCSE Nov2014-1H Q17] ABCDEFGH is a regular octagon. BCKFGJ is a hexagon. JK is a line of symmetry of the hexagon. Angle 𝐵𝐽𝐺 = angle 𝐶𝐾𝐹 = 140°. Work out the size of angle KFE. 5) A regular polygon 𝐴 is surrounded by squares and equilateral triangles in an alternating pattern, as shown. Show that 𝐴 is a hexagon. 6) A regular polygon 𝐵 with 𝑛 sides is surrounded by squares and regular pentagons in an alternating pattern, as shown. Determine the value of 𝑛. www.drfrostmaths.com 9) [IMC 2005 Q14] Ten stones, of identical shape and size, are used to make an arch, as shown in the diagram. Each stone has a cross-section in the shape of a trapezium with three equal sides. What is the size of the smallest angles of the trapezium? 10) [IMC 2018 Q18] The diagram shows a regular pentagon and an equilateral triangle placed inside a square. What is the value of 𝑥? 11) Find all regular polygons which tessellate (when restricted only to one type of polygon). 1. By thinking about interior angles, prove that the regular polygons you identified above are the only regular polygons which tessellate.