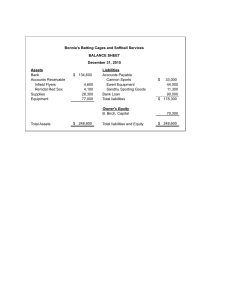
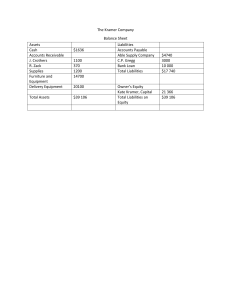
Senior High School QUARTER 1 – MODULE 1 Statement of Financial Position (SFP) Department of Education ● Republic of the Philippines Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business and Management 2 - Senior High School Alternative Delivery Mode First Edition, 2020 Republic Act 8293, section 176 states that: No copyright shall subsist in any work of the Government of the Philippines. However, prior approval of the government agency or office wherein the work is created shall be necessary for exploitation of such work for profit. Such agency or office may, among other things, impose as a condition the payment of royalty. Borrowed materials (I.e., songs, stories, poems, pictures, photos, brand names, trademarks, etc.) included in this book are owned by their respective copyright holders. Every effort has been exerted to locate and seek permission to use these materials from their respective copyright owners. The publisher and authors do not represent nor claim ownership over them. Writer : Glenn S. Manlupig Editor : Allen Joy A. Vedra Reviewer : Illustrator : Layout Artist : Development Team: Chairperson : Dr. Arturo B. Bayocot, CESO III Regional Director Jonathan S. Dela Peńa, PhD, CESO V Schools Division Superintendent Rowena H. Para-on, PhD Assistant Schools Division Superintendent Mala Epra B. Magnaong Chief, CLMD Printed in the Philippines by Department of Education - Alternative Delivery Mode (DepEd-ADM) Office Address: Masterson Avenue, Upper Balulang, Zone 1, Cagayan de Oro City Province of Misamis Oriental Telefax: E-mail Address: ii Introductory Message Dear Teachers and Learners! The writer welcomes you all to this module for the subject Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business and Management 2 in the ABM Strand of Senior High School. The discussion focussed on the preparation of financial statements and its analyses to determine the profitability, liquidity and solvency of the business. As your partner in learning, I hope that you will not miss out every detail that the writer would like you to learn in this material. Do enjoy as there are challenging and interesting activities inside this learning modules. Congratulations in advance for this will make you the master of your own learning. Ops! you wait for a while, for an easy use of this material take note of some few reminders 1. Take your time to read every detail that this module contains. 2. This material contains Module 1 and Module 2 and each of which is provided with activities/tests that will surely lead you to learn. 3. Here are the Icons used as your guide in every part of the lesson. Icons of this Module What I Need to Know What I know This part contains learning objectives that are set for you to learn as you go along the module. This is an assessment as to your level of knowledge to the subject matter at hand, meant specifically to gauge prior related knowledge. This part connects previous lesson with that of the current one. What’s In What’s New This is an introduction of the new lesson through various activities before it will be presented to you What is It This is a discussion of the activities as a way to deepen your discovery and understanding of the concept. What’s More What I Have Learned What I can do iii This is a follow-up activity that is intended for you to practice further in order to master the competencies. This activity is designed to process what you have learned from the lesson This is a task that is designed to showcase your skills and knowledge gained, and applied into real-life concerns and situations. 4. Please do follow the directions given per activity so your experience to the use of this material will be meaningful and fruitful. 5. Answer all the tests in this material. 6. As a courtesy to the future users, PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ANYTHING ON ANY PART OF THIS MODULE. Write your answer/s on a separate sheet of paper, notebook, workbook or whichever is specified by your facilitator Special Reminders for you learners; 1. Answer every activity intelligently and diligently. 2. Write your answer as directed by your facilitator. 3. Feel free to approach or communicate your teacher/facilitator whenever you need help. 4. Don’t forget to put a smiley face if you finish the activity within the allotted time. iv Table of Contents Page What This Module is About………………………………………………….. 1 Icons of this Module………………………………………………………….. 2 MODULE 1 Statement of Financial position…………………... 5 Introduction to Statement of Financial Position ……………………………….. 5 Activity 1.1.1 Prepare a Personal SFP…………………………….. 7 Lesson 1.1 Nature of Statement of Financial Position……… 7 Lesson 1.2 Elements of Statement of Financial Position And Steps in the Preparation…………………….. 9 Activity 1.1.2 1.1.3 1.1.4 1.1.5 11 12 13 14 LESSON 1 Classify Me…………………………………………… Fill Me Now…………………………………………… Can You Solve the Problem ……………………….. Choosing the Right One……………………………. v Module 1 Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business and Management 2 What I Need To Know Beloved Learner, Hello! I hope that you are okay. This module will guide you as you keep on asking many things on how financial statements are prepared and presented? How is net income measured? How are equity transactions presented? How are assets and liabilities classified? How are cash flows presented? How are financial ratios utilized? These are the enduring questions meant to be addressed by this self-learning module. This module is a response to the need for fresh and innovative instructional materials needed for the “New Normal” way of teaching for the Accountancy, Business and Management Track of Senior High School. This module deals with the preparation and analysis of financial statements of a service business and merchandising business using horizontal and vertical analyses and financial ratios. Knowledge and skills in the analysis of financial statements will aid the future entrepreneurs in making sound economic decisions. Basically, the module has five lessons: Lesson 1: Statement of Financial Position (SFP) Lesson 2: Statement of Comprehensive Income (SCI) Lesson 3: Statement of Changes in Equity (SCE) Lesson 4: Cash Flow Statement (CFS) Lesson 5: Analysis and Interpretation of Financial Statements Hence, at the end of this module, you are expected to: 1. Identify the elements of the SFP and describe each of them (ABM_FABM12Ia-b1); 2. Classify the elements of the SFP into current and noncurrent items (ABM_FABM12-Ia-b-2); 3. Prepare the SFP of a single proprietorship (ABM_FABM12-Ia-b-3); 4. Prepare an SFP using the report form and the account form with proper classification of items as current and noncurrent (ABM_FABM12-Ia-b-4); 5. Identify the elements of the SCI and describe each of these items for a service business and a merchandising business (ABM_FABM12-Ic-d-5); 1 6. Prepare an SCI for a service business using the single-step approach (ABM_FABM12-Ic-d-6); 7. Prepare an SCI for a merchandising business using the multistep approach (ABM_FABM12-Ic-d-7); 8. Discuss the different forms of business organization (ABM_FABM12-Ie-8); 9. Prepare an SCE for a single proprietorship (ABM_FABM12-Ie-9); 10. Discuss the components and structures of a CFS (ABM_FABM12-If-10); 11. Prepare a CFS (ABM_FABM12-If-11); 12. Define the measurement level namely, liquidity, solvency, stability, and profitability (ABM_FABM12-Ig-h12); 13. Perform vertical and horizontal analyses of financial statements of a single proprietorship (ABM_FABM12-Ig-h13) 14. Compute and interpret financial ratios such as current ratio, working capital, gross profit ratio, net profit ratio, receivable turnover, inventory turnover, debt-toequity ratio, and the like (ABM_FABM12-Ig-h14) Icons of this Module What I Need to Know This part contains learning objectives that are set for you to learn as you go along the module. What I know This is an assessment as to your level of knowledge to the subject matter at hand, meant specifically to gauge prior related knowledge What’s In This part connects previous lesson with that of the current one. What’s New An introduction of the new lesson through various activities, before it will be presented to you What is It These are discussions of the activities as a way to deepen your discovery and understanding of the concept. What’s More These are follow-up activities that are intended for you to practice further in order to master the competencies. 2 What I Have Learned What I can do Activities designed to process what you have learned from the lesson These are tasks that are designed to showcase your skills and knowledge gained, and applied into real-life concerns and situations. What I Know Directions. Read and analyze each item carefully. Write the letter that corresponds the best answer on your answer sheet. 1 point each. 1. A statement of financial position can be best described as a: A. Listing of money received and paid during the past year B. Summary of what happened last year C. Summary of all assets, expenses, liabilities, and revenues D. Summary of the position of an organization 2. An asset is an A. Expense that will recur in more than one year B. Obligation to transfer benefits as a result of past transactions C. Interest of the owner in the business D. Any financial resources that is used by the business in its operation 3. The Statement of Financial Position equation is: A. A – C = L B. L + C = A C. A – L = C D. all of the choices 4. XYZ Company have non-current assets of P 60,000, current assets of P 70,000, current liabilities of P 40,000, and a long-term loan of P 50,000; as such the owner’s equity will be: A. P 40,000 C. P 60,000 B. P 50,000 D. P 70,000 5. What is a financial statement that shows the financial position of an enterprise at a particular point in time? A. Balance Sheet C. Income Statement B. Cash Flow Statement D. Statement of Changes in Equity 3 6. A Statement of Financial Position A. Shows the changes of the owners interest B. Reports the assets and claims of an enterprise at a specified moment in time C. Presents revenue and expenses of an enterprise D. Reports the inflow and outflow of cash in an enterprise 7. Which of the following transactions would increase cash as well as non-current liabilities? A. Long-term bank loan B. Purchasing equipment on credit C. Payment to suppliers D. Payment from customers 8. Which of the following accounts is a current asset? A. Bond Payable B. Property, Plant and Equipment C. Notes payables D. Accounts receivables 9. Which of the following accounts is a non-current asset? A. Accounts Payable B. Capital C. Cash D. Trademarks 10. Which of the following accounts is a current liability? A. Trade receivables B. Retained Earnings C. Trade Payables D. Machineries 4 lesso n 1 STATEMENT OF FINANCIAL POSITION (SFP) What’s In Accounting can be defined as the “process of identifying, recording, and communicating economic information about an organization or another entity, in order to permit informed judgments by users of the information.” (Meyer 2009) Based on the definition, accounting consists of inputs, several processes, and an output. The inputs needed by an accountant are the economic transactions entered into by the business, evidenced by supporting documents. These include capital contribution by owners, rendering of services to customers, and payment of expenses to suppliers. The end product or output of accounting is useful financial information. This useful financial information is the “story” that accounting tells to the interested users. Useful financial information helps the owners to answer the question. “Should I invest more cash in the business?” Creditors are also guided by this information in answering the question. “Should we lend more money to the business?” These transactions will undergo the process of identification, measurement, and recording. The end product or output of accounting is useful financial information. Identification answers “what transactions/accounts are concerned?” Measurement, on the other hand, answers the question “how much money is involved?” Recording then captures the transaction in the business book of accounts. Financial information is contained and communicated through the financial statements. Financial statements are like chapters of a novel, telling different stories of an interrelated subject. Specifically, financial statements are organized depictions of the events that happened in a business. A complete set of financial statements are composed of the following 1. Statement of Financial Position or Balance Sheet 2. Statement of Comprehensive Income or Income Statement 3. Statement of Changes in Equity 4. Statement of Cash Flow 5 What’s New To achieve the objectives of this module, you must remember to do the following: Read the lessons carefully. Follow all directions and given instructions. Answer all given tests and activities. Learn to familiarize the following terms: TERM DEFINITION Statement of Financial Position Also known as the Balance Sheet. This statement includes the amounts of the company’s total assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity which in totality provides the condition of the company on a specific date. (Haddock, Price, & Farina, 2012) Permanent Accounts As the name suggests, these accounts are permanent in a sense that their balances remain intact from one accounting period to another. (Haddock, Price, & Farina, 2012) Examples of permanent account include Cash, Accounts Receivable, Accounts Payable, Loans Payable and Capital among others. Basically, assets, liabilities and equity accounts are permanent accounts. They are called permanent accounts because the accounts are retained permanently in the SFP until their balances become zero. This is in contrast with temporary accounts which are found in the Statement of Comprehensive Income (SCI). Temporary accounts unlike permanent accounts will have zero balances at the end of the accounting period. Contra-Assets Contra assets are those accounts that are presented under the assets portion of the SFP but are reductions to the company’s assets. These include Allowance for Doubtful Accounts and Accumulated Depreciation. Allowance for Doubtful Accounts is a contra asset to Accounts Receivable. This represents the estimated amount that the company may not be able to collect from delinquent customers. Accumulated Depreciation is a contra asset to the company’s Property, Plant and Equipment. This account represents the total amount of depreciation booked against the fixed assets of the company. 6 Activity 1.1.1 Prepare a Personal SFP: A. Get a piece of paper. B. Write your current savings and everything that you own (clothes, money, gadgets, jewelry etc.) C. Write the amount that you owe to your friends, family members, parents (tuition) D. Deduct the amount you owe from the amount you own E. Associate amounts owned with assets and amount owed with liabilities with the net amount as equity. Processing Questions: 1. How much is your equity? 2. Do you have greater assets than your liabilities? Or vice versa? 3. There might be some cases your computation is zero or even negative. This means that your liabilities to your friends, relatives and/or parents are higher than your assets. 4. In business, having more assets does not mean that the business is earning but usually companies have assets that are bigger than their liabilities. 5. Reflect on the importance of having a personal statement of financial position. What Is It Lesson 1.1 Nature of Statement of Financial Position One can compare a Statement of Financial Position to a static picture or portrait. This statement literally presents a company’s “position” when it comes to the resources it owns (assets), obligations claimed against it (liabilities), and the owner’s residual interest (equity). There are three major elements of the Statement of Financial Position: (1) assets, (2) liabilities (3) owner’s equity. Always remember that the total amount of assets is equivalent to the total amount of liabilities and owner’s equity combined. (Accounting Equation) There are two forms of Statement of Financial Position namely; 1. Report Form – A form of the SFP that shows asset accounts first and then liabilities and owner’s equity accounts after. (Haddock, Price, & Farina, 2012) 2. Account Form – A form of the SFP that shows assets on the left side and liabilities and owner’s equity on the right side just like the debit and credit balances of an account. (Haddock, Price, & Farina, 2012) 7 Sample Statement of Financial Position ABM COMPANY Heading Statement of Financial Position As of December 31, 2020 ASSETS Current Assets Cash and Cash Equivalents Accounts Receivables Less: Allowance for Bad Debts P 1,119,250.00 240,000.00 20,000.00 220,000.00 Notes Receivables 22,000.00 Inventories Current Assets 220,000.00 Total Current Assets P 1,581,250.00 Noncurrent Assets Property, Plant and Equipment P Long-term Investment 407,000.00 1,100,000.00 Intangible Assets 198,000.00 Total Noncurrent Assets Noncurrent Assets 1,705,000.00 TOTAL ASSETS P 3,286,250.00 ============ LIABILITIES & EQUITY Current Liabilities Accounts Payable P 220,000.00 Accrued Expenses 55,000.00 Unearned Income 99,000.00 Notes Payable Current Liabilities 110,000.00 Total Current Liabilities P 484,000.00 Noncurrent Liabilities Mortgage Payable P 395,000.00 Loans Payable 100,000.00 Total Noncurrent Liabilities P 495,00.00 TOTAL LIABILITIES P 979,000.00 Noncurrent Liabilities OWNER’S EQUITY Owner’s, Capital P 2,307,250.00 TOTAL LIABILITIES & OWNER’S EQUITY P 3,286,250.00 ============= Fig. 1.1 Sample of Statement of Financial Position in Report Form 8 Owner’s Equity Lesson 1.2. Elements of Statement of Financial Position and Steps in Preparation Note: The repot form of Statement of Financial Position is used in this discussion. Refer to the sample given in Figure 1.1 1. Prepare the Statement Heading The statement heading includes the name of the company, name of the statement, and the date covered. The date of the statement of financial position is “as at” or “as of” the end of the period (e.g. As of December 31, 2020). The use of “as of” in the SFP means that the amounts are cumulative from the beginning of the life of the company since these amounts are permanent. 2. Prepare the Asset Section Assets are categorized as current or non-current. Current assets and noncurrent assets are arranged by liquidity. Liquidity, for this purpose, means the ease of converting such assets into cash. Current Assets – Assets that can be realized (collected, sold, used up) one year after year-end date. Examples include Cash, Accounts Receivable, Merchandise Inventory, Prepaid Expense, etc. Noncurrent Assets – Assets that cannot be realized (collected, sold, used up) one year after yearend date. Examples include Property, Plant and Equipment (equipment, furniture, building, land), long term investments, Intangible Assets etc. 3. Prepare the Liabilities Section Liabilities are categorized as current or non-current. Finally, current and noncurrent liabilities are arranged by liquidity. Liquidity, for this purpose, means the ease of converting such liabilities into cash. Current Liabilities – Liabilities that fall due (paid, recognized as revenue) within one year after yearend date. Examples include Notes Payable, Accounts Payable, Accrued Expenses (example: Utilities Payable), Unearned Income, etc. Noncurrent Liabilities – Liabilities that do not fall due (paid, recognized as revenue) within one year after year-end date. Examples include Loans Payable, Mortgage Payable, etc. Note: Noncurrent assets and noncurrent liabilities are also called long term assets and long term liabilities respectively. 4. Prepare the Owner’s Equity Section This section is basically lifted from the ending balances of accounts in the statement of changes in equity. 5. Ensure that the Accounting Equation is Balanced Total assets will have to equate to total liabilities and equities. Furthermore, the statement is footed and tested for mathematical accuracy. 9 Sample Statement of Financial Position in Account Form ASSETS Current Assets: Cash and Cash Equivalents Accounts Receivables Less: Allowance for Bad Debts Notes Receivables Inventories Total Current Assets Noncurrent Assets: Property, Plant & Equipment Long-term Investment Intangible Assets Total Noncurrent Assets TOTAL ASSETS ABM COMPANY Statement of Financial Position As of December 31, 2020 LIABILITIES & EQUITY Current Liabilities: 1,119,250.00 Accounts Payable 240,000.00 Accrued Expenses 20,000.00 220,000.00 Unearned Income 22,000.00 220,000.00 1,581,250.00 407,000.00 1,100,000.00 198,000.00 1,705,000.00 3,286,250.00 ========== Notes Payable Total Current Liabilities Noncurrent Liabilities: Mortgage Payable Loans payable Total Noncurrent Liabilities 220,000.00 55,000.00 99,000.00 110,000.00 484,000.00 395,000.00 100,000.00 495,000.00 979,000.00 TOTAL LIABILITIES OWNER’S EQUITY Owner’s, Capital 2,307,250.00 TOTAL LIABILITIES & EQUITY 3,286,250.00 ========== Figure 1.2 Sample of Statement of Financial Position in Account Form Remember that the two are only formats and will yield the same amount of total assets, liabilities and equity. The assets should always be equal to liabilities and equity. “There are many ways to skin a cat”. This is an expression that means there are different ways of doing the same thing. And that also applies with the Statement of Financial Position because there are different ways or forms to do it but still it’s the same thing – the same content but different presentation or arrangement. Total assets are double ruled and total liabilities and equity is double ruled because they represent the end of a part of the financial statement. 10 What’s More Activity 1.1.2. Classify Me .For you to advance your learning and understanding of the Statement of Financial Position, you have to gradually learn each of its elements and components. Classify the following accounts whether they are assets, liability, or equity accounts. For asset and liability accounts, classify whether they are current or non-current. ACCOUNTS Ex. Accounts Payable Accounts Receivable Cash Interest Payable Acain, Capital Notes Payable Notes Receivable Prepaid Rent Property and Equipment Raw Materials Salaries Payable Supplies Utilities Payable Cash in Bank Finished Goods Accrued Interest Bonds Payable Prepaid Insurance Unearned Income Land Goods in Process Acain, Personal Furniture and Fixtures Accrued Salaries Income Tax Payable Intangible Assets Delivery Truck Interest Receivable ELEMENT Liability 11 CLASSIFICATION Current What Have I Learned When the company has a lot of assets (example: cash, accounts receivable, prepaid expenses), owners may sometimes think that the company is doing well. There are instances that owners forget that they might also have a lot of liabilities which may result to their equities having a very small balance. With the preparation of the SFP, the owner can easily see the assets, liabilities and equity balances of his/her company which will show exactly the financial position of the company as of a given point in time. Without the SFP, the company cannot know if it truly owns anything because in case of bankruptcy, liabilities are paid first. - Small businesses don’t usually account for their assets and liabilities as long as the owners see that cash is coming in. They sometimes forget that when liabilities become due, if they don’t have enough current assets to be able to pay those liabilities, then they can get in trouble with their debts. Activity 1.1.3. Fill Me Now Instruction: Fill in the blanks the correct answer to the question. 1. Learning is Fun Company had current assets amounting to Php 100,000. Noncurrent assets for the year totaled Php 76,000. How much is the company’s total assets? Answer: _______________ 2. Happy Selling Company’s total liabilities amounted Php 10,000. Total equity had an ending balance of Php 20,000. How much is total assets? Answer: _______________ 3. Happy Selling’s had the following accounts at year end: Cash-250,000, Accounts Payable-70,000, and Prepaid Expense-15,000. Compute for the company’s current assets. Answer: ______________ 4. Happy Selling’s Accounts Receivable amounted to Php 500,000. Prepaid Expense and Unearned Income totaled Php 30,000 and Php 10,000 respectively. Cash balance amounted to Php 100,000 while Accounts Payable and Inventory totaled to Php 20,000 and Php 10,000 respectively. How much is the company’s current assets? Current liabilities? Answer: ___________ and ________________ 5. Company’s Total Liabilities and Equity amounted to Php 285,000. Total noncurrent assets ended at Php 85,000. Cash totalled Php50,000. Inventory amounted to Php100,000. Assuming the company had no other assets, how much is Accounts Receivable? Answer: _______________ 6. Total assets amounted to Php575,000. Total equity amounted to Php 250,000. Accounts Payable amounted to Php 50,000 while Unearned Income totalled Php 85,000. Assuming there are no other current liabilities, compute for the company’s noncurrent liabilities. Answer: ______________ 12 What I Can Do Report form vs Account form – these are just formats. Usually depends on the reader for preference. Report form is the normal format for those not familiar with accounting. Account form easily shows that the SFP is balanced and separates assets from liabilities and equities. Separation of the current and noncurrent – current liabilities are upcoming liabilities and the company should be prepared to pay them. Companies should prepare as early as today for payment of noncurrent liabilities as these usually have large balances. Current assets shows the company’s ability to sustain its current operations while noncurrent assets shows the company’s ability to sustain long-term operations. Activity 1.1.4. Can You Solve the Problem? Construct the Report Form and Account Form of the Statement of Financial Position using the Post-Closing Trial Balance of Dela Cruz Law Office. DELA CRUZ LAW OFFICE POST-CLOSING TRIAL BALANCE JANUARY 1, 2020 ACCOUNTS DEBIT Cash 588,500.00 Accounts Receivable 75,000.00 Office Supplies 2,000.00 Prepaid Rent 110,000.00 Office Furniture 36,000.00 Accumulated Depreciation-Office Furniture Accounts Payable Notes Payable Unearned Revenue Accrued Interest Mortgage Payable-Long Term Juan Dela Cruz, Capital 811,500.00 13 CREDIT 1,000.00 25,000.00 50,000.00 35,000.00 500.00 50,000.00 650,000.00 811,500.00 Activity 1.1.5. Choosing the Right One Read and carefully examine the statements and choose the best answer. .1. A statement of financial position can be best described as a: A. Listing of money received and paid during the past year B. Summary of what happened last year C. Summary of all assets, expenses, liabilities, and revenues D. Summary of the position of an organization 2. An asset is an A. Expense that will recur in more than one year B. Obligation to transfer benefits as a result of past transactions C. Interest of the owner in the business D. Any financial resources that is used by the business in its operation 3. The Statement of Financial Position equation is: A. A – C = L B. L + C = A C. A – L = C D. all of the choices 4. XYZ Company have non-current assets of P 60,000, current assets of P 70,000, current liabilities of P 40,000, and a long-term loan of P 50,000; as such the owner’s equity will be: A. P 40,000 C. P 60,000 B. P 50,000 D. P 70,000 5. What is a financial statement that shows the financial position of an enterprise at a particular point in time? A. Balance Sheet C. Income Statement B. Cash Flow Statement D. Statement of Changes in Equity 6. A Statement of Financial Position A. Shows the changes of the owners interest B. Reports the assets and claims of an enterprise at a specified moment in time C. Presents revenue and expenses of an enterprise D. Reports the inflow and outflow of cash in an enterprise 7. Which of the following transactions would increase cash as well as non-current liabilities? A. Long-term bank loan B. Purchasing equipment on credit C. Payment to suppliers D. Payment from customers 8. Which of the following accounts is a current asset? A. Bond Payable B. Property, Plant and Equipment C. Notes payables D. Accounts receivables 14 9. Which of the following accounts is a non-current asset? A. Accounts Payable B. Capital C. Cash D. Trademarks 10. Which of the following accounts is a current liability? A. Trade receivables B. Retained Earnings C. Trade Payables D. Machineries Congratulations! You have just finished Lesson 1 of this module. Let’s recap! The Statement of Financial Position (SFP) lists the business’s assets, liabilities, and equity. It reflects the financial standing of a business in a given period. An asset is defined as a resource controlled by the enterprise as a result of past events and from which future economic benefits are expected to flow to the enterprise. Simply, assets are possessions of a business that will bring business benefits in the future. It adds value to your business! Assets are classified as current and non-current assets. For an asset to be classified as current it needs to meet some of the following criteria: 1. expected to be realized, sold, or consumed in the entity’s normal operating cycle; 2. Held primarily for trading; 3. Expected to be realized 12 months after the reporting period; and 4. an asset is a cash or cash equivalent unless restricted for at least 12 months after the reporting period. Liability is officially defined as a present obligation arising from past events; the settlement of which is expected to result in an outflow from the entity of resources embodying economic benefits. Liabilities can be also classified as current and non-current liabilities. Liabilities are classified as current if the entity has no unconditional right to defer settlement for at least 12 months, otherwise it is noncurrent. The last element of the Statement of Financial Position is the owner’s equity. Owner’s equity is the residual interest of the owner in the business. Keep in mind that the total amount of the assets must equate to the total amount of the liabilities and owner’s equity combined. To wit: Asset = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity. 15 Answer Key What I Know / Pre-test & Post Test 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. C D D A A 6. B 7. A 8. D 9. D 10. C Activity 1.1.1 – Prepare a Personal SFP Answers may vary What’s More / Activity 1.1.2 – Classify Me ACCOUNTS Accounts Receivable Cash Interest Payable Acain, Capital Notes Payable Notes Receivable Prepaid Rent Property and Equipment Raw Materials Salaries Payable Supplies Utilities Payable Cash in Bank Finished Goods Accrued Interest Bonds Payable Prepaid Insurance Unearned Income Land Goods in Process Acain, Personal Furniture and Fixtures Accrued Salaries Income Tax Payable Intangible Assets Delivery Truck Interest Receivable ELEMENT Asset Asset Liability Capital Liability Asset Asset Asset Asset Liability Asset Liability Asset Asset Liability Liability Asset Liability Asset Asset Capital Asset Liability Liability Asset Asset Asset 16 CLASSIFICATION Current Current Current Current Current Current Noncurrent Current Current Current Current Current Current Current Noncurrent Current Current Noncurrent Current Noncurrent Current Current Noncurrent Noncurrent Current What Have I Learned / Activity 1.1.3 – Fill Me Now 1. P 176,000.00 2. P 30,000.00 3. P 265,000.00 4. Current Assets=P 640,000.00; Current Liabilities= P 30,000.00 5. P 190,000.00 Activity 1.1.4. Can You Solve the Problem? 1. Report Form of Statement of Financial Position DELA CRUZ LAW OFFICE Statement of Financial Position As of January 31, 2020 ASSETS Current Assets: Cash 588,500.00 Accounts Receivable 75,000.00 Office Supplies 2,000.00 Prepaid Rent 110,000.00 Total Current Assets 775,500.00 Noncurrent Assets: Office Furniture 36,000.00 Less: Accumulated Depreciation-Furniture ( 1,000.00) Total Noncurrent Assets 35,000.00 TOTAL ASSETS 810,500.00 ======== LIABILITIES Current Liabilities: Accounts Payable 25,000.00 Notes Payable 50,000.00 Unearned Revenue 35,000.00 Accrued Interest 500.00 Total Current Liabilities 110,500.00 Noncurrent Liabilities: Mortgage Payable- Long-term 50,000.00 Total Noncurrent Liabilities 50,000.00 Total Liabilities 160,500.00 OWNER’S EQUITY Dela Cruz, Capital 650,000.00 Total Liabilities & Owner’s Equity 810,500.00 ======== 17 2. Account Form of Statement of Financial Position DELA CRUZ LAW OFFICE Statement of Financial Position As of January 31, 2020 ASSETS LIABILITIES & EQUITY Current Assets: Current Liabilities: Cash 588,500.00 Accounts Payable Accounts Receivables 75,000.00 Notes Payable Office Supplies 2,000.00 Unearned Revenue Prepaid Rent 110,000.00 Accrued Interest Total Current Assets 775,500.00 Total Current Liabilities Noncurrent Assets: Noncurrent Liabilities: Office Furniture 36,000.00 Mortgage Payable Total Noncurrent Liabilities Accumulated Depreciation-Furniture (1,000.00) Total Noncurrent Assets 35,000.00 TOTAL LIABILITIES TOTAL ASSETS 810,500.00 OWNER’S EQUITY ========== Dela Cruz, Capital Total Liabilities & Owner’s Equity 18 25,000.00 50,000.00 35,000.00 500.00 110,500.00 50,000.00 50,000.00 160,500.00 650,000.00 810,500.00 ========== References Arganda, A. M. (2016). Fundamentals of Accounting Bookkeeping 1. Anvil Publishing, Inc. Josefina L. Beticon, J. C. (2017). Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business and Management 2 - Teacher's Manual. Vibal Group. Inc. Reyes, V. D. (2017). Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business and Management 2. GIC Enterprises & Co., Inc. Salazar, D. R. (2017). Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business and Management 2. Rex Bookstore. Additional References: Teacher’s Guide in Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business and Management 2 https://edge.pse.com.ph/openDiscViewer.do?edge_no=5b3feb584ad68ec41db82e3 77ee70f3b) 19