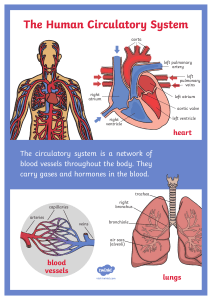
THE HEART Cardiovascular system THE HEART It is a conical hollow muscular pump inside the pericardium occupying a major part in the chest. It is formed of four chambers two atria (right and left) and two ventricles (right and left). THE HEART The heart has an apex, base and two surfaces. The surfaces are the sternocostal and diaphragmatic. The borders are right, left, upper and lower borders. THE HEART Apex It is formed only by the left ventricle. It is directed downwards, forwards and to the left. It lies below nipple of the left breast, in the left 5th intercostal space. THE HEART Apex It lies below nipple of the left breast, in the left 5th intercostal space. THE HEART Base It is formed mainly by the left atrium and the back of the right atrium. It is directed backwards and to the right. THE HEART Sternocostal surface It is directed forwards, upwards and to the left. It is divided by the coronary groove into arterial portion and ventricular portion. THE HEART Sternocostal surface Arterial portion: mainly the right auricle and a small part of the left atrium form it. Ventricular portion: One third of this surface is formed by left ventricle, and two thirds by the right ventricle. THE HEART Diaphragmatic surface It is directed downwards and slightly backwards. It is formed by the two ventricles. Two thirds by the left ventricle and one third by the right ventricle. THE HEART Borders Upper border is formed by the two atria, mainly the left. Right border is formed only by the right atrium. Lower border is formed by the right ventricle and the apical part of left ventricle. Left border is formed mainly by the left ventricle and partly by the left atrium. Chambers of the heart There are 4 chambers of the heart Right atrium Left atrium Right ventricle Left ventricle THE HEART Right atrium It is separated from the left atrium by the inter-atrial septum. The right atrium is composed of two main parts, a smooth posterior portion and a rough walled anterior portion. The rough portion contains the pectinate muscles. THE HEART Left atrium The left atrium forms the greater part of the base of the heart. The left auricle lies to the left and in front of the pulmonary trunk. THE HEART Left atrium Its interior presents a smooth surface excepts for view rough part. The left atrium shows the following orifices: 1. Four Pulmonary veins convey blood from lungs to the heart. 2. Mitral valve: It connects the left atrium with the left ventricle. Two cusps guard it. THE HEART Right ventricle Separated from left ventricle by interventricular septum. Its wall is muscular &is more thicker than the atrial. Pulmonary trunk arises from it and divides into two pulmonary arteries one to each lung. THE HEART Right ventricle There are three papillary muscles attached to the wall of the ventricle. Form the apices of the papillary muscles, fibrous cords (chorda tendinae) pass to the cusps of the tricuspid valve. THE HEART Right ventricle There are three papillary muscles attached to the wall of the ventricle. Form the apices of the papillary muscles, fibrous cords (chorda tendinae) pass to the cusps of the tricuspid valve. THE HEART Left ventricle It forms the apex of the heart. Its wall is nearly three times thicker than right. The ascending aorta arises from it. THE HEART Left ventricle Its cavity presents two papillary muscles, which are attached to the two cusps of the mitral valve by chorda tendinae. Valves of the heart Tricuspid valve – It is valve between right atrium and right ventricle Bicuspid valve ( Mitral valve ) – It is valve between left atrium and left ventricle Pulmonary valve – It is the valve between pulmonary trunk and right ventricle Aortic valve – It is the valve between aorta and left ventricle Valves of heart THE HEART Pericardium The pericardium is the serous sac, which invests the heart. It consists of an outer fibrous sac lined with an inner serous sac. The heart lies inside the fibrous sac and invaginates the serous sac from behind. So the serous pericardium has a visceral layer covering the heart and a parietal layer lining the fibrous pericardium. The fibrous pericardium limits movements of the heart. THE HEART Arterial supply Two coronary arteries arise from the aortic sinuses in the initial portion of the ascending aorta and supply the muscle and other tissues of the heart. They circle the heart in the coronary sulcus, with marginal and interventricular branches, in the interventricular sulci, converging toward the apex of the heart. They are end and tortuous arteries. THE HEART Venous drainage The returning venous blood passes through cardiac veins, most of which empty into the coronary sinus. This large venous structure is located in the coronary sulcus on the posterior surface of the heart between the left atrium and left ventricle. The coronary sinus empties into the right atrium between the opening of the inferior vena cava and the right atrioventricular orifice. THE HEART Arterial supply