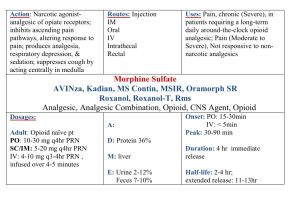
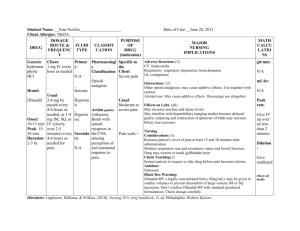
ANALGESICS DEFINITION 1. Analgesics are drugs that relieve pain. 2. An agent that relieves pain without causing loss of consciousness CLASSIFICATION OF ANALGESICS Non-Opioid analgesics Used in mild to moderate pain • • Non-Steroidal Anti-inflammatory drugs Paracetamole Opioid analgesics Used in moderate to severe pain - Morphine - Pethidine NON-STEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS AND PARACETAMOL • NSAIDs are a group of agents that share in common the capacity to induce Anti-inflammatory, Analgesic and Antipyretic effects. • Paracetamol is an Analgesic-Antipyretic with No Anti-inflammatory action. MECHANISM OF ACTION OF NSAIDs AND PARACETAMOL • NSAIDs act by inhibiting cyclo-oxygenase enzyme which is responsible for conversion of arachdonic acid. This results in inhibition of production of prostaglandins and leucotrines which are pain mediators and inflamatory agents. • Acetyl Salicylic acid (Aspirin), the prototype NSAID induces irreversible inhibition of both COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes. • Other NSAIDs cause competitive reversible inhibition of COX enzymes. • Paracetamol inhibits PG synthesis in CNS resulting in Analgesic and Antipyretic effects but is a weak inhibitor of PG in periphery. Thus, Paracetamol has NO Anti-inflammatory effect. Classification of NSAIDs NSAIDs are classified according to their Cox specificity as follows; i) Cox 2 selective: celecoxib, rofecoxib, melocoxib ii) Non-Cox-2 selective: All other NSAIDs ACETYL SALICYLIC ACID (ASPIRIN) Therapeutic uses of Aspirin 1) Anti-inflammatory: • Uses: Rheumatic fever, Rheumatoid arthritis 2) Analgesic effect: • Uses: Mild to moderate pain especially secondary to inflammation; Arthritis, Dental pain, Headache (decreases cerebral vasodilator effect of PGs), Dysmenorrheal and Postpartum pain. Cont`d 3) Antipyretic effect: • Uses: Antipyretic (Lowers body temperature) in fever. 4) Anti-platelet effect: • Uses: Prophylaxis against transient ischemic attacks, Myocardial infarction and Unstable Angina. ASPIRIN Dosages: • Antiplatelets: 150 (75 – 325) mg/day. • Analgesic and Antipyretic: 0.3 gram, 1-2 tablets when necessary. • Anti-inflammatory: 4-8 grams/ day. Contra-indications 1) History of peptic ulcer 2) Hemophilia or other bleeding disorders 3) Liver disease 4) Patient receiving anticoagulant therapy ASPIRIN Adverse drug effects • GI. side effects: - Dyspepsia, nausea, vomiting, gastritis, ulceration with risk of hemorrhage (due to direct irritant effect on the mucosa and decreased protective PGs). • Renal damage (Analgesic nephropathy): due to decreased renal vasodilator PGs. Adverse effects cont`d • Hypersensitivity reactions: Skin rash, Rhinitis, Asthma. Since blockade of the synthesis of PG, leukotriene and other lipoxygenase metabolites from arachidonic acid are increased. They are endogenous bronchial smooth muscle constrictors and may result in bronchospasm and asthma. • Hyper-uricemia in patients with Gout (in low doses): Competes with uric acid for excretion by organic acid secretory mechanism in renal tubules. ASPIRIN Adverse drug effects • Reye’s syndrome: encephalopathy, liver injury in adolescents and children recovering from febrile viral infections. • Attention: hepatic coma! • Paracetamol is preferred for such febrile illnesses in children under 12 years. Adverse Effects • Chronic toxicity (Salicylism): Large doses (>5g/d) used for long periods lead to dizziness, tinnitus, deafness and gastric upset • Acute toxicity: Respiratory alkalosis (hyperpnoea and washing out of CO2) followed by respiratory acidosis due to respiratory depression and metabolic acidosis (due to accumulation of acidic metabolites). Adverse effects • Coagulation disorders: Aspirin prolongs bleeding time. Contraindication in patients with bleeding diseases. Aspirin should be avoid in patients receiving anticoagulants such as coumarin and heparin Inhibiting platelet Prostaglandin syntheses and TXA2 production. Drug interactions • Alcohol- Likely to cause gastritis • Anticoagulants- Increases bleeding • Antacids- Excretion of aspirin increased in alkaline urine • Anti-epileptics- Phenytoin, valproate effect enhanced. • Corticosteroids- Increased risk of bleeding and peptic ulceration. OTHER NSAIDs 1) Ibuprofen (Brufen); • Anti-pyretic, anti-inflammatory , anti-rheumatic • Effect less than aspirin • Effective and better tolerated (decreased incidence of side effects than other NSAIDs). First choice in inflammatory joint disease. 2) Naproxen; • It is related to Ibuprofen, more potent with moderate risk of side effects. It is longer acting (given twice daily). 3) Piroxicam; • Potent and long acting, given once daily. • No accumulation in the elderly or in patients with renal impairment. 20% of patients develop side effects e.g. GIT bleeding. • Used in long-term treatment of chronic inflammatory musculoskeletal disorders e.g.: Rheumatoid arthritis, Osteoarthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis, Renal colic and Post-operative pain. An ophthalmic solution is used for post-operative inflammation. 4) Diclofenac; • It is very potent • Used in long-term treatment of chronic inflammatory musculoskeletal disorders e.g.: Rheumatoid arthritis, Osteoarthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis, Renal colic and Post-operative pain. An ophthalmic solution is used for postoperative inflammation. 5) Indomethacin • It has stronger anti-pyretic, anti-inflammation, antirheumatic effect and more side effects than aspirin • Due to its serious adverse effects, its use is limited to: Acute Gouty arthritis, Rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing Spondylitis, Post-operative pain, Patent ductus arteriosus (inhibits PG synthesis closing the ductus). • It can be used to prevent premature labour. Because it can prolong gestation and labour time. (but it causes transient constriction of ductus arteriosus in some fetuses). Adverse effects of Indomethacin • GIT: Nausea, vomiting, ulcer, bleeding. • CNS: Dizziness, confusion, ataxia, severe headache (cerebral vasodilatation). • Salt and water retention (antagonize antihypertensives) and hyperkalemia. It aggravates pre-existing renal failure. • Aplastic anemia. Selective COX-2 inhibitors Colecoxib and Rofecoxib • Colecoxib and Rofecoxib are selective COX-2 inhibitors that spare COX-1, thus they do not inhibit synthesis of protective PGs in the GIT. Hence they have less GIT side effects. PARACETAMOL CHARACTERISTICS: • The intensity of anti-Antipyretic and analgesic effect is equal to aspirin, but slow and lasting. • It inhibits PG synthesis in the brain but hardly at all in the periphery. • I t has no Gastrointestinal tract reaction • Anti-inflammation effect is weak, it has no practical use. PARACETAMOL • Mainly used to treat patients who can’t sustain the therapy of aspirin such as: a) Patients allergic to Aspirin. b) Peptic ulcer (No GIT disturbances). c) Gout (Aspirin may cause hyper-uricemia). d) Viral infection in children (to avoid Reye’s syndrome with Aspirin). e) Bleeding disorders (does not affect platelet function). PARACETAMOL • Paracetamol is ineffective in high fever because excess free radicals generated by leucocytes antagonize antipyretic effect of Paracetamol. • Dose: It is usually given orally (500mg to 1g, 3-4 times daily) Paracetamole Side effects It causes liver damage in case of overdose. Toxic doses (15 grams or more) cause nausea and vomiting, followed in 24-48hrs by potentially fatal liver damage. Interactions 1) Anticoagulants-enhances the effect of warfarin after regular use. 2) Metoclopramide & Domperidone- absorption of paracetamole is enhanced. OPIOID ANALGESICS are also called narcotic analgesics Opioid are natural or synthetic compounds that produce morphine-like effect. Opiate is the generic term for drugs obtained from opium Sources of Opioid analgesics: • Plant: - Morphine, Codeine (natural products of Opium poppy) • Synthetic: - Fentanyl, Methadone, Pethidine, Heroin. • Endogenous: - Endorphins, Encephalins and Dynorphins (Opiopeptides) released in the body, acting on Opioid receptors and producing Morphine-like effects. Opium:A dried exudate of fruit capsule of the poppy(Papaver Somniferum) Mechanism of action • The brain contains chemical substances called encephalins and endophins which act on opioid receptors in the brain, and spinal cord. When these receptors are stimulated, transmission of nerve impulses related to pain and the appreciation of pain are inhibited • Opioid analgesics also react with these receptors and thus relieve pain • Opioid receptor include Mu, Kappa and delta. Classification of Opioid analgesics Pure agonists: examples include: • Morphine. • Fentanyl. • Methadone. • Pethidine. • Heroin. • Codeine Partial Agonists: examples include: • Buprenorphine • Tramadol • nalbuphine. Antagonists • Naloxone • Naltrexone Pharmacological actions of Opioids: Main effects: • Analgesia: - Decreases pain perception and emotional response to pain. • Sedation. • Euphoria (sometimes dysphoria). Pharmacological actions of Opioids: Inhibitory effects: • Vasomotor centre: causing venular and arterial dilatation. • Respiratory depression. • Inhibition of the cough centre. • Inhibition of uterine muscle. Pharmacological actions of Opioids: Stimulatory effects: • Stimulation of the oculomotor nucleus producing miosis. • Stimulation of CTZ producing nausea and vomiting. • Increases smooth muscle tone but inhibit peristalsis leading to constipation. • Stimulation of the release of anti diuretic hormone. • Histamine release producing hypotension, itching and bronchospasm. • Tolerance develops to all effects except constipation and miosis. THERAPEUTIC USES OF OPIOIDS • Analgesics in: – Acute pain (trauma). – Chronic dull pain (visceral). – Post-operative pain and Cancer pain. • Anesthesia (Morphine or Fentanyl). • Myocardial infarction and acute pulmonary edema (Morphine): Decreases pain and anxiety, arteriolar and venodilator (decreases venous congestion and pulmonary edema). • Antitussive (Codeine and Dextromethorphan). Adverse effects of Opioids • • • • • • • • Sedation and narcosis. Drug dependence. Respiratory depression. Nausea and vomiting. Miosis. Constipation and urine retention. Hypotension, itching and bronchospasm (due to Histamine release). Delay labor and Asphyxia neonatorum (Respiratory depression in the newborn). • Mask the diagnosis of acute abdomen (mask pain). • Biliary spasm Contraindications of Opioids • Acute undiagnosed abdomen (mask pain). • Head injury (Opioids cause respiratory depression leading to increased CO2 resulting in cerebral vasodilatation with increased intracranial tension). • Bronchial asthma (Opioids cause Histamine release). • Biliary colic (Opioids increase intra-biliary pressure and aggravate the colic). • Patients with enlarged prostate (Opioids decrease motility of the bladder wall and cause urine retention). • Extremes of age, Hypothyroidism and liver dysfunction (decreased Opioid metabolism). Drug interactions of Opioids: • Addictive CNS depression with other CNS depressants e.g. Sedative-hypnotics, Alcohol, Antidepressants, Antipsychotics. • Pethidine + MAOIs results in Hyper-pyrexic coma, Respiratory depression and Convulsions. Morphine • Pharmacokinetics -often given parenterally (sc, im, iv) - t1/2 : 2-3 hr; duration:3-6 hr. -can pass though blood-placenta barrier -can secrete in milk of breast-feeding mothers. Pharmacological Effects - CNS - Cardiovascular system -Smooth muscle 1. CNS a. Analgesia • - relieve moderate to severe pain • - relieve continuous, dull pain > • intermittent sharp pain • -produce sedation and Euphoria • at the same time b. Respiratory depression • - decrease respiratory rate, respiratory failure, death • - direct inhibition of respiratory • center • - decreased sensitivity of • respiratory center to carbon dioxide. c. Emesis(vomiting) and nausea - caused by direct stimulate the chemoreceptor trigger zone(CTZ). - also a direct vestibular component. d. Depression of cough reflex - inhibition of the cough center e. Miosis : “pinpoint pupils” • - characteristic symptom of opioids poisoning 2. Cardiovascular system Hypotension peripheral vasodilation - inhibition of the vasomotor center -increase histamine release increased intracranial pressure Cerebral vasodilation -the result of the increased Pco2 caused by respiratory depression 3. Smooth muscle Constipation: Urinary retention Increased biliary pressure Constipation: - increased tone, decreased motility in many parts of the gastrointstinal tract. Urinary retention -increase urethral sphincter tone Increased biliary pressure - constrict biliary smooth muscle and the sphincter of oddi -may result in biliary colic Clinical uses • - Analgesia • - Cardiogenic asthma • - Diarrhea 1. Analgesia - severe pain only when other analgesics are useless • Trauma, burn, acute myocardial infarction, postoperative pain • renal or biliary colic, use morphine+ atropine • cancer (long term use) 2. Cardiogenic asthma • dyspnea from acute pulmonary edema caused by left ventricular failure. • sedation ( relieves anxiety) • vasodilation (reduction cardiac preload and afterload ) • respiratory depression breathing more slowly , deeply and effectively 3. Diarrhea - usually use tincture camphor compound. Adverse Effect • 1. Side Effects -Dizziness, nausea, vomiting , constipation • • - respiratory depression -increased biliary tract pressure,urinary retension 2. Tolerance and dependence Tolerance Dependence - psychic dependence - physical dependence -withdrawal syndrome: lacrimation, yawning, sweating, restlessness, dilated pupils, anorexia, irritability, tremor, diarrhea, flushing, cramps, muscle spasms. 3. Toxicity symptoms -Coma -respiratory depression -pinpoint pupil Treatment - Support respiration - Opioid antagonist: Naloxone I.V. - Gastric lavage. 4. Contraindications • -delivery, breast-feeding women • -bronchial asthma, pulmonary • heart disease • - high intracranial pressure • - impaired hepatic function • patients. Codeine • Antitussive (cough suppression) equal to 1/4 morphine • Analgesia:equal to 1/12 morphine. • adverse effects:lower than morphine - tolerance and addition - respiratory depression - ... Pethidine • Artificial synthetic analgesic • Routes: I.M S.C., and Oral. potency: equal to 1/8 morphine • -less adverse effects • constipation, respiratory depression, tolerance ,dependence • - Clinical Uses • analgesia, cardiogenic asthma, premedication Pethidine differs from Morphine in the following ways: • Less potent. • Less spasmogenic: Less biliary spasm, less constipation, less urine retention (due to short duration of action). • Less respiratory depression in neonates • Shorter duration of analgesia • Little hypnotic effect • It does not delay labour therefore preferred during labour with less risk of Asphyxia neonatorum. • Does not usefully suppress cough • Atropine-like action: - Dry mouth, Blurring of vision, tachycardia. Natasha mukwai! Life is precious Be good and be careful