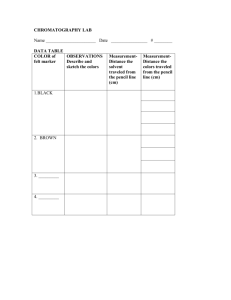
Whodunit Lab Investigation: The Murder Scene: Room B101 Alfred P. Newman was a fun-loving student at Lamar High School. Sometimes he would cut up in class, act disrespectfully towards his teachers, and not do his work. Alfred’s body was found in Ms. Boardman’s class yesterday. Police have given the task of investigating the note left on his body to Mrs. Boardman’s chemistry students, who know her as a fair, but cool teacher. Alfred had a note attached to his body that read, “Yo, respect!”. The note was written with a black marker. Your job is to complete the lab to determine which marker was the marker that wrote the note, and determine through Crime Scene Investigation, who the murderer is. The suspects in this case are: 1. Ms. Pineda: whom students saw arguing with Alfred the day before about him insisting it was OK for him to wear his hat, but it wasn’t hat day. He skirt; Ms. Pineda uses a Papermate pen. 2. Ms. Thomas: Alfred told Ms. Thomas to stop text messaging in the hallway; Alfred called Ms. T an obscene name; Ms. Thomas uses a Crayola pen 3. Ms. Troutman: Alfred was in Ms. Troutman’s Biology class last year. Alfred had been disrespectful towards her and complained to Dr. McGrew. Ms. T. uses a Write Stuff pen. 4. Ms. Boardman: Alfred was mad at Ms. Boardman for taking up his cell phone. Alfred vandalized the classroom, but Ms. Boardman couldn’t prove it. Ms. Boardman uses Sharpie pen. 5. Mr. Cervantes: Mr. Cervantes met with Alfred and his mom, but they both threatened to kill Mr. Cervantes’ cat. He found his cat dead the next day. He uses a Bic pen. 6. Dr. Milstead: He heard about Dr. Cervantes’cat, but couldn’t prove it was Alfred or his mom. The principal is very protective of his staff. Dr. Milstead uses a Vis a Vis pen. Which of the suspects killed Alfred? Was Ms. Boardman framed? The colored sharpie will give the killer away….. Fundamental understanding: · Different molecules exert different forces of attraction on each other resulting in different solubilities within given solvents. Essential Questions: How is chromatography a separation of mixture technique? What kind of substance is contained in marker ink? Chromatography Background Paper chromatography is a specialized form of chromatography that is relatively fast and inexpensive yet powerful enough to separate a range of different chemicals. This type of chromatography uses a piece of paper and a solvent to separate the components of a mixture. Paper chromatography is used in this experiment to separate and identify different colors of inks in an aqueous solution. Purpose: to separate components of inks or dyes by their different solubilities. Safety Precautions: Be careful not to stain clothing or hands. Materials and Equipment: each group needs 1. Filter paper 2. pencil 3. Tape 4. Beaker (250 ml) 5. Ink pen to be tested waterproof and water based inks (your teacher will give you a pen to test 6. Water/ Acetone 50/50 Solution or Isopropyl Alcohol Solution USE ISOPROPYL ALCOHOL (IPA) IF YOUR PEN BRAND IS: SHARPIE BIC HEB WRITE STUFF USE ACETONE IF YOUR PEN BRAND IS: PAPERMATE CRAYOLA VIS A VIS Procedure: 1. Cut appropriate size chromatography paper so that the width of the paper fits in the beaker without touching the sides, handle by the edges. 2. Mark a pencil (do not use ink) line (~1.0 cm) from the bottom; make 3 pencil dots spaced 2 cm apart on the line 3. Obtain the marker from your teacher. With the marker, make 3 very small dots on each of the pencil dots. The smaller the dot, the better the chromatography. 4. Tape the paper to the pencil so that the paper does not touch the sides and the paper is just slightly above the bottom of the beaker. See front desk for example of apparatus. Remove the pencil and chromatograph while you add solution. 5. Carefully add a very small amount of solution to the beaker, then place pencil with taped, marked paper in beaker. The solution should barely touch the bottom of the paper, but not the marker dots. 6. Observe the chromatograph until the dyes have separated. Pull out and place on a piece of paper to dry. 7. Mark where the water ends with a pencil and ruler 8. Measure the distance the solvent moved and the distance each dye moved. Measure from the bottom of the color to where it stops. How many colors did the dye separate into? Measure each color separately! Results: Observations: Tape your chromatogram into the lab book Data table: Determine the Rf values for each component in each ink. Calculate Rf values for each dye (color that was separated) using the formula Rf = distance traveled by the compound ÷ distance traveled by the solvent (Acetone or Isopropyl Alcohol. ) Lab Report: Names of all investigators: Title: Hypothesis: Variables: Independent Dependent Control Graph: y-axis x-axis Materials and Equipment: Brand of pen tested: Data: Include chromatogram and name the brand of marker you were given. Include a data table with all the colors that were separated in the chromatogram and the distance each traveled. How far did the solvent travel? Record these in your data table in centimeters. Analysis and Conclusions: Calculate the Rf factors for each dye in your chromatogram. Add a column to your data table with this information. 1. What color dyes were present in your marker? 2. What marker did you have? Write the brand name here. How does it compare to the teacher’s chromatogram? 3. What kind of mixture is the ink in a marker? What marker brand was the marker that the note was written from? 4. Who killed Alfred? 5. If your marker was the marker that wrote the note, who would be the murder suspect? 6. Is Rf factor an intensive or extensive property? How can an Rf factor identify a specific dye? Explain. 7. Is chromatography a physical or chemical process? Look in your textbook if needed. Explain. 8. How is chromatography a separation process? Explain. 9. Is the ink in the marker Homogeneous or heterogeneous? Explain. 10. How would you change or improve this activity? Lab Report: Names of all investigators: Title: Hypothesis: If the process of chromatography separates the marker ink into separate dyes, then the chromatograms of each different pen can be compared to the chromatogram from the note to determine the murder suspect. Materials and Equipment: . 1. Filter paper 2. pencil 3. Tape 4. Beaker (250 ml) 5. Ink pen to be tested waterproof and water based inks (your teacher will give you a pen to test 6. Water/ Acetone 50/50 Solution or Isopropyl Alcohol Solution Brand of pen tested: Data: Dye color Distance dye traveled Distance solvent traveled Analysis and Conclusions: 1. What color dyes were in your marker? Depends on marker: a. Bic: 2 colors b. Crayola: yellow, purple, blue c. Papermate: purple, yellow, blue, violet d. Vis A vis: yellow, pink, turquoise e. Heb Write Stuff: look at student’s results f. Sharpie: look at student’s results Rf factor 11. What marker did you have? Write the brand name here. How does it compare to the teacher’s chromatogram? 1st period: 4th period: 6th period: 7th period: 8th period: 2. crayola: Ms. Thomas papermate: Ms. Pineda Vis a vis: Mr. Milstead papermate: Ms. Pineda crayola: Ms. Thomas What kind of mixture is the ink in a marker? What marker brand was the marker that the note was written from? The ink is a homogeneous solution Look above for the results per period 3. Who killed Alfred? 1st period: 4th period: 6th period: 7th period: 8th period: 4. crayola: Ms. Thomas papermate: Ms. Pineda Vis a vis: Mr. Milstead papermate: Ms. Pineda crayola: Ms. Thomas What was the purpose of this lab? To learn about the process of chromatography as used in crime scene investigations 5. Is Rf factor an intensive or extensive property? How can an Rf factor identify a specific dye? Explain. The Rf factor can identify a specific dye because it is an intensive property. The ratio of distance dye traveled to distance of the solvent is a constant specific to any given dye. It doesn’t vary, and can be repeated 6. Is chromatography a physical or chemical process? Explain. Chromatography is a physical means of separating ink dyes based on solubility. Solubility is a physical property. 7. How is chromatography a separation process? Explain. The chromatography solution separated the ink into its component dyes based on solubility. The more soluble the dye is, the less the dye traveled in the solvent. 8. Is the ink in the marker Homogeneous or heterogeneous? Explain. It is homogeneous because the ink in the marker is uniform throughout. 9. How would you change or improve this activity? Answers vary, but they better put something constructive.