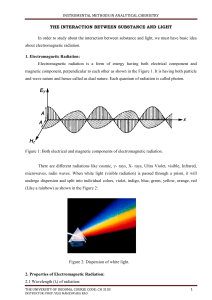
What is Heat? How can you warm up something in space? Heat can be defined as transfer of energy from one form to another form at different temperatures where the object or each body gets radiated, which results in the radiations of molecules. Mostly the amount of energy used in radiating the molecules is termed as Thermal Energy. Heat is a transformation of energy which is mostly related to atoms and molecules. Motion of molecules defines the intensity of heat, where motion of molecules is high intensity of heat is high. It is measured by the instrument calorimeter at constant temperature. Units: JOULES Example: when heat is generated substances/ objects changes its form from one phase to other Solids->Liquids->Gases ENERGY TRANSFER: It is done in Three ways a) Conduction - Energy may be conducted directly from one object to another as when a pan is in direct physical contact with a hot burner. Example: Piece of Metal placed in Fire b) Convection - The Sun bathes the Earth’s surface with radiant energy causing the air near the ground to increase in temperature. The less dense air rises, creating convectional currents in the atmosphere. Example: when water is heated, it becomes less dense, where heat carries out away c) Radiation- Electromagnetic energy in the form of electromagnetic waves may be transmitted through the vacuum of space from the Sun to the Earth Example: Best example for radiation is Infrared Radiation. Radiation occurs when an object gets heated up by the motion of photons at definite wavelength. Different wavelength regions are responsible for different radiations. In space, there is no proper way of communication medium or convective medium from space to earth to transfer. Radiative energy is the only least effective way to transfer the energy.