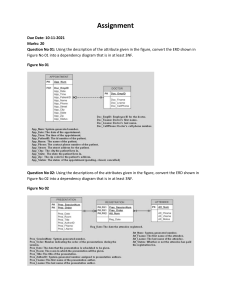
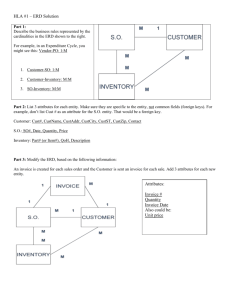
INFOST 410-202 Midterm Exam 1. From the following business rules draw the Crow’s Foot ERD. (5 points) The business rules may be written as follows: A lecturer can lecture many classes. Each class is lectured by one lecturer. A lecture can advise many scholars. Each scholar is advised by one lecture. Answer: 2. With a diagram explain the difference between mandatory and optional participation in an entity relationship. 2 points) Answer: Mandatory Participation In the mandatory participation, for every instance of entity A, there must exist an instance of entity B and vice versa. Optional participation In optional participation, it is not necessary for all the instances of the entity to participate in a relationship. It may be that the number of instances participating for a particular entity may even be zero. 3. What is a strong relationship? Provide an example. (2 points) Answer: A strong or identifying relationship is when the primary key of the related entity contains the primary key of the “parent”. Example: A ROOM can only exist in a BUILDING. On the other hand, a TIRE might be considered as a strong entity because it also can exist without being attached to a CAR. 4. Describe the use of the INTERSECT operator. (1 points) Answer: The SQL INTERSECT clause/operator is used to combine two SELECT statements, but returns rows only from the first SELECT statement that are identical to a row in the second SELECT statement. This means INTERSECT returns only common rows returned by the two SELECT statements. 5. What is a foreign key and how is it important in a relational model? Give example (3 points) Answer: A foreign key is an attribute that completes a relationship by identifying the parent entity. Foreign keys provide a method for maintaining integrity in the data (called referential integrity) and for navigating between different instances of an entity. Importance: he FOREIGN KEY constraint is crucial to relational database design. It lets us link the data according to our needs. As it creates some dependencies between the columns of primary and foreign tables, it also lets us decide what to do ON UPDATE and ON DELETE actions performed on the rows of the primary table. Example: An example of a foreign key could be in a school database, STU_ID could be a primary key that enables the school to link students with classes in another table, where STU_ID would be present as foreign key and allows them to link the class table back with the original student table. 6. Define entity integrity. What are the two requirements to ensure entity integrity? (3 points) Answer: Entity integrity is one of the primary rules of effective database construction. It refers to the process of enforcing a primary key for each table in a database, where the key must be either a row or a combination of rows that are unique non-null values. The two requirements to ensure entity integrity are: 1. The primary key for each row is a unique value 2. The primary key is not null 7. State and briefly describe the four basic characteristics of Big Data databases. (8 points) Answer: The four basic characteristics of Big Data databases are: Volume: These databases are capable of housing huge amounts of data as well as having powerful processing capabilities. Variety: These databases collect data from more than one source, and this data can come in different forms such as structured, semi-structured and unstructured. Velocity: These databases have large amounts of data from different sources, the velocity of the data means that more data is available at once. Veracity: Since these databases collect and store so much data, veracity describes the quality and accuracy of the data that is collected. 8. What do business rules require to be effective? (2 points) Answer: A business rule is a statement that imposes some form of constraint on a specific aspect of the database. Business rules allow the creator to develop relationship participation rules and constraints and to create a correct data model. They also allow the creators to understand business processes, and the nature, role and scope of the data. 9. List 5 sources of business rules, and what is the database designer’s role regarding business rules? (6 points) Answer: The five sources of business rules are 1. Company Managers, 2. Policy Makers, 3. Department Managers, 4. Written Documentation 5. Interviews With End Users. Regarding business rules, the database designer’s role is to ensure that the business rules are appropriate and accurate. 10. List and briefly describe 5 problems associated with file systems? (While describing focus on “how they challenge the types of information that can be created from the data as well as the accuracy of the information”) (5 points) Answer: 1. Even the simplest data-retrieval tasks require extensive programming. 2. The need to write programs makes ad hoc queries impossible. 3. System administration becomes more difficult as the number of the files in the system 4. expands. 5. Lack of security and limited data sharing 6. Making changes to an existing file structure forces changes in all of the programs that 7. use the data in that file and changes often result in bugs 11. List and briefly explain any three functions performed by the DBMS that guarantee the integrity and consistency of the data in the database. (3 points) Answer: The first function performed by the DBMS that helps to guarantee the integrity and consistency of its data would be the authorization and security management. A database needs security against unauthorized access, ensuring that only those who are supposed to have access to the database do. A second function that helps to guarantee the integrity and consistency of data is the management of data manipulation. This is the mechanism that allows users to retrieve, update and delete existing data within the database. A third and final function that helps to guarantee the integrity and consistency of data is the backup and recovery management. If something were to go wrong with the database and the data within it was lost or corrupted, backups of the system help to protect against this from happening. This prevents the loss of any data. 12. List and describe the different types of databases regarding/considering site location and data structure. (5 points) Answer: A single-user database is a database that supports one user at a time, A desktop database is a type of single-user database that runs on a personal computer. A multiuser database is a database that supports multiple users at a time, A workgroup database is a type of multi user database used for a specific department in an organization. An enterprise database is a database that supports an entire company overall. A centralized database is a database that has a single site location, whereas a distributed database is a database that has two or more physically independent sites. A Cloud database is a database that is created and maintained by using cloud services. 13. Create a Crow’s Foot ERD for each of the following descriptions. (Note: The word many merely means “more than one” in the database modeling environment.) a. Each of the OmwandoCo. Corporation’s division(s) is composed of many departments. Each of those departments has many workers assigned to it, but each worker works for only one department. Each department is managed by one worker, and each of those managers can manage only one department at a time. (2 points) b. During some period of time, a student can take many classes. Each of the class can be taken by many students during that period of time. (Hint: Only 2 entities) (2 points) 14. Create the ERD from the relationship diagram between DIRECTOR and PLAY shown in figure 14. For each entity identify all the keys, and business rules (5 points) Figure 14 The Relational Diagram Answer: Each director can direct many plays, but each play is directed by only one director. The primary keys are DIR_NUM and PLAY_CODE. The probable foreign key is DIR_NUM. 15. Identify and describe the components of the table shown in Figure 15, using correct terminology. Use your knowledge of naming conventions to identify the table’s probable foreign key(s). (5 points) FIGURE 15. The Ch03_NoComp Database EMPLOYEE Table Answer: There are ten records shown by the employee names. One entity set, being the table labeled EMPLOYEE. Six attributes: EMP_NUM, EMP_LNAME, EMP_INITIAL, EMP_FNAME, DEPT_CODE, and JOB_CODE. There are two probable foreign keys within this table, the attribute DEPT_CODE and JOB_CODE. Both of these probably reference separate tables with information regarding the specific job and department. 16 Based on the following business rules, draw the crow’s foot ERM with only 1:M relationship. (5 Points) Hint: During some time interval, a DRIVER can drive many CARs and any CAR can be driven by many DRIVERs Business rules: A driver may receive many (driving) assignments. Each (driving) assignment is made for a single driver. A car may be driven in many (driving) assignments. Each (driving) assignment is made for a single car. Answer: 17. From the Crow’s Foot ERD for the Benji Company write six business rules. (3 points) Answer: 1. Each sales rep writes many invoices. 2. Each invoice is written by one sales rep. 3. Each sales rep is assigned to one department. 4. Each department has many sales reps. 5. Each customer can generate many invoices. 6. Each invoice is generated by one customer. Use the database shown in Figure Ch03_StoreCo to answer Problems 18-22. FIGURE Ch03_StoreCo Database Tables 18. For each table, identify the primary key and the foreign key(s). If a table does not have a foreign key, write None in the space provided. (3 points) Answer: TABLE PRIMARY KEY FOREIGN KEY(S) EMPLOYEE EMP_CODE STORE_CODE STORE STORE_CODE REGION_CODE, EMP_CODE REGION REGION_CODE - 19. Do the tables exhibit entity integrity? Answer yes or no and then explain your answer. Particularly explain in terms of unique values and "null" values. Is it unique? Can it be Null? (3 points) Answer: TABLE EMPLOYEE ENTITY INTEGRITY YES EXPLATION Each value (EMP_CODE) in the table is unique and there are no null values. STORE YES Each value (STORE_CODE) in the table is unique and there are no null values. REGION YES Each value (REGION_CODE) in the table is unique and there are no null values. 20. Do the tables exhibit referential integrity? Answer yes or no and then explain your answer. Write NA (Not Applicable) if the table does not have a foreign key. (3 points) TABLE REFERENTIAL INTEGRITY EXPLATION Each EMPLOYEE YES value (STORE_CODE) in the EMPLOYEE tables links to an existing (STORE_CODE) value in the STORE table. Each value (REGION_CODE) in the STORE STORE YES table links to an existing (REGION_CODE) value in the REGION table. Each value (EMP_CODE) in the STORE table links to an existing value (EMP_CODE) in the EMPLOYEE table. REGION NO Table does not have a foreign key. 21. Describe the type(s) of relationship(s) between STORE and REGION. And, create the ERD to show the relationships. (5 points) Answer: 1. STORE and REGION have a 1:M relationship. 2. Each REGION can contain many STOREs, but each STORE is located in only one REGION. ERD: 22. Describe the type(s) of relationship(s) between EMPLOYEE and STORE. And draw the ERD to show the relationships among EMPLOYEE, STORE, and REGION. (Hint: Each store employs many employees, one of whom manages the store.) (6 points) Answer: 1. EMPLOYEE and STORE have a 1:M and a 1:1 relationship. 2. Each STORE has many EMPLOYEEs, but each STORE can only have one EMPLOYEE to manage the one STORE. 23. Using the descriptions of the attributes given in the figure, convert the ERD shown in Figure 23 into a dependency diagram that is in at least 3NF or BNCF. (2 points) An initial dependency diagram depicting only the primary key dependencies is shown in Figure 23 below. Figure 23 Initial dependency diagram for Problem. In your answer you can show functional dependencies with arrows: i.e Doc_EmpID --> (Doc_FName, Doc_LName, Doc_CellPhone) or draw using MS word tools for shapes 24. Use the dependency diagram shown in Figure 24 to work the following problems. Figure 24 Initial Dependency Diagram for Problem 24 A B C D E F G a. Break up the dependency diagram in Figure 24 to create two new dependency diagrams, one in 3NF and one in 2NF. (2 points) 3NF Dependency Diagram: 2NF Dependency Diagram: b. Modify the dependency diagrams you created in Problem 24a to produce a collection of dependency diagrams that are all in 3NF. (Hint: You will have more than two diagrams). (3 points) Answer: c. Modify the dependency diagrams you created in Problem 24b to produce a collection of dependency diagrams that are all in BCNF. (4 points) 25. a. What are the applications of ERD and normalization? Give an example. (2 points) Answer: ERD or the entity relationship diagram is used to develop and design databases and normalization is used in optimizing those databases. An example of the application of these would be anything that required data to be stored into a database like a retail inventory system, a school’s student database and much more. b. Briefly describe the conditions that must be met for a table(s) to be in 1NF, 2NF, 3NF, BCNF and 4NF. (5 points) Answer: 1NF (First Normal Form) Rules Each table cell should contain a single value. Each record needs to be unique. 2NF (Second Normal Form) Rules Rule 1- Be in 1NF Rule 2- Single Column Primary Key that does not functionally dependant on any subset of candidate key relation 3NF (Third Normal Form) Rules Rule 1- Be in 2NF Rule 2- Has no transitive functional dependencies BCNF (Boyce-Codd Normal Form) It is stricter than 3NF. A table is in BCNF if every functional dependency X → Y, X is the super key of the table. For BCNF, the table should be in 3NF, and for every FD, LHS is super key. 4NF (Fourth Normal Form) Rules If no database table instance contains two or more, independent and multivalued data describing the relevant entity, then it is in 4th Normal Form.