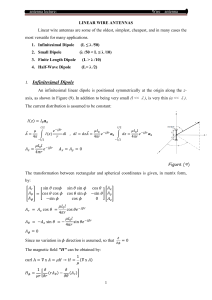
BICONICAL ANTENNA 1 INTRODUCTION A biconical antenna consists of an arrangement of two conical conductors, which is driven by potential, charge, or an alternating magnetic field (and the associated alternating electric current) at the vertex. The conductors have a common axis and vertex. The two cones face in opposite directions WHY BICONICAL ANTENNA AND CYLINDRICAL DIPOLE ? Used to produce wide bandwidths, i.e when coverage over a broad range of frequencies is required BICONICAL GEOMETRY BICONICAL ANTENNA IS FORMED BY PLACING TWO CONES OF INFINITE EXTENT TOGETHER WHICH IS USED TO ACHIEVE BROADBAND CHARACTERISTICS 4 MAIN FEATURES From 75 MHz to 400 MHz Excellent azimuth pattern symmetry Low loss, high efficiency USES: Biconical (or "Bicon") antennas are often used in electromagnetic interference (EMI) testing either for immunity testing, or emissions testing from 25-200 MHz (Commercial specifications) or 30200 MHz (Military applications). DRAWBACK: While the Bicon is very broadband, it exhibits poor efficiency at low frequencies, resulting in low field strengths when compared to the input power UNIPOLE Whenever one of the cones is mounted on an infinite plane conductor (i.e the lower cone is replaced by the ground plane) , it forms a unipole and its input impedance is one half of the two-cone structure CYLINDRICAL DIPOLE ANTENNA 9 CYLINDRICAL DIPOLE Cylindrical dipole antennas are those antenna whose radiation characteristics are dependent upon frequency(i.e. a wire of finite diameter and length) and it’s diagram is shown below :- 10 CHARACTERSTICS OF CYLINDRICAL DIPOLE Another simple and inexpensive antenna whose radiation characteristics are frequency dependent. It is a special form of biconical antenna when α=0 -A very thin linear dipole has very narrowband input impedance characteristics. -if we decrease l/d ratio the operational bandwidth will be enlarged. -This can be done by holding the length the same and increasing the diameter of the wire. INPUT IMPEDANCE For a given length wire its impedance variations become less sensitive as a function of frequency as the l/d ratio decreases- more broadband characteristics can be obtained by increasing the diameter of a given wire. PROPERTIES OF RADIATION PATTERN OF CYLINDRICAL ANTENNA -It is noted that the patterns are essentially unaffected by the thickness of the wire in regions of intense radiation. -As the radius of wire increases, the minor lobe diminish in intensity and the nulls are filled by low –level radiation. CHARACTERSTICS OF COATED LINEAR DIPOLE The optimum bandwidth of the antenna can be achieved by choosing a lossy dielectric material with maximum imaginary parts of P and Q and minimum real parts.-This decreases the radiation efficiency. APPLICATIONS Wideband antennas are needed in television reception of all channels. Radio