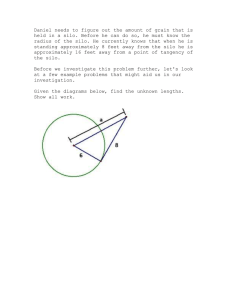
The Functional Organizational Structure 1 Learning Objectives 01 02 03 Understand the evolution of organizational structure Describe the functional organizational structure Identify the core functional areas of an organization Growth of a Company Entrepreneur starts a company Business is good! – needs to hire someone to help Business continues to grow – hire more people and assign them to functions: Sales, Operations, Accounting, etc Functional Areas hire more people – Hierarchical structure emerges This is the most common organizational structure This Results in a Functional Hierarchical Organizational Structure Functions of the organization are hierarchically managed Functional areas perform tasks and make decisions related to their function Processes cut across functions and these task and decision will impact other functional areas 4 Functional Hierarchical Organizational Structure Sales & Mkt Acct & Fin Operations R&D Functional Areas of an Organization • Functions are distinct (e.g. marketing, operations, accounting) but – Are interdependent – Data flows from and to other functional areas • Integrate of data across functional areas impacts organizational effectiveness – Increases communication across functions – Increases efficient processes – Leads to • More timely information • More accurate information • Better decision making Core Functional Areas • • • • Purchasing Production and/or Operations Sales & Marketing Finance & Accounting Additional Potential Functional Areas • • • • • Warehousing Research and Development Human Resources Information Systems Varies some by Industry and Business • But core are similar Procurement • • • • • • • All activities related to carefully sourcing and obtaining goods and services needed to support business operations Sourcing – What goods and services does firm need? – Who should the goods and services be purchased from Negotiating and Contracting – Negotiate pricing and terms with suppliers Monitoring and managing supplier performance – Quality control Receiving – Inspection Also helps manage the supply chain And more Production • The function of a business that produces products or delivers services to customer • Controls Identifying inputs – Parts – Labor • Schedules production • Minimizes production costs • Maintains machines and equipment • And more Marketing and Sales • • • • • • Help develop products Determining pricing Promoting products to customers Taking customers’ orders Helping create a sales forecast And more 1 2 Accounting and Finance • • • • • • • Accounts payable (AP) and accounts receivable (AR) Payroll Budgeting Reporting and financial statements Legal and Compliance Controlling And more This structure can Lead to “Functional Silos” The Silo Effect • This is NOT what you get when you drive across I80 in Iowa • It is what you get when you focus on the functional areas of a business • The silo effect can have negative consequences • Optimization of functional goals vs. organizational goals • Focus on functional process and not cross functional goals • However, to deliver goods and services, an organization needs to communicate and coordinate across all business functions Functional Optimization Warehouse Silo Sales Silo Production Silo Accounting Silo Customer Focus on Organizational Goals Sales Warehouse Customer Production Accounting Functional Information Needs • Employees working in one functional area need data from employees in other functional areas – Functional area information systems should be integrated, so shared data are accurate and timely • Managers think in terms of business processes that integrate the functional areas – Need to share information between functions and functional areas – ERP software provides this capability by means of a single common database 17 The Functional Structure 18 Michael Porter’s Value Chain Functional Areas and Business Processes • To understand ERP, you must understand how a business functionals – Functional areas of operation – Business processes 21 Sharing data effectively and efficiently between and within functional areas leads to more efficient business processes Business Processes Integrated information systems: Systems in which functional areas share data 22 Summary Basic functional areas: Marketing and Sales, Supply Chain Management, Accounting and Finance, and Human Resources Marketing and Sales: Sets product prices, promotes products through advertising and marketing, takes customer orders, supports customers, and creates sales forecasts Supply Chain Management: Develops production plans, orders raw materials from suppliers, receives raw material, manufactures products, maintains facilities, and ships products to customers 23 QUESTIONS The End BUSINES PROCESSES Summary • Basic functional areas: Marketing and Sales, Operations/Production/Supply Chain Management,Purchasing Accounting and Finance, and Others (Human Resources, Project Management, etc.) • Marketing and Sales: Sets product prices, promotes products through advertising and marketing, takes customer orders, supports customers, and creates sales forecasts • Supply Chain Management: Develops production plans, orders raw materials from suppliers, receives raw material, manufactures products, maintains facilities, and ships products to customers 25 Summary (cont’d.) • Accounting and Finance: Financial accounting to provide summaries of operational data in managerial reports, controlling accounts, planning and budgeting, and cash-flow management • Human Resources: Recruits, hires, trains, and compensates employees, ensures compliance with government regulations, and oversees the evaluation of employees • Information systems capture, process, and store data to provide information needed for decision making 26 Summary (cont’d.) • Accounting and Finance: Financial accounting to provide summaries of operational data in managerial reports, controlling accounts, planning and budgeting, and cash-flow management • Human Resources: Recruits, hires, trains, and compensates employees, ensures compliance with government regulations, and oversees the evaluation of employees • Information systems capture, process, and store data to provide information needed for decision making 27 Summary (cont’d.) • Employees working in one functional area need data from employees in other functional areas – Functional area information systems should be integrated, so shared data are accurate and timely • Managers think in terms of business processes that integrate the functional areas – Need to share information between functions and functional areas – ERP software provides this capability by means of a single common database 28