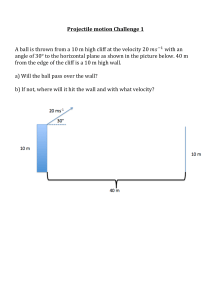
NYS Regents Physics Physics in 2D Chapter Problems Slides 2020-03-30 www.njctl.org 1 For the triangle pictured (not drawn to scale): a. find the length of the third side. b. determine the angle θ. 2 For the triangle pictured (not drawn to scale): a. find the length of the third side. b. determine the angle θ. 3 For the triangle pictured (not drawn to scale): a. find the length of the third side. b. determine the angle θ. 4 For the triangle pictured (not drawn to scale): a. find the length of the third side. b. determine the angle θ. 5 For the triangle pictured (not drawn to scale): a. find the length of the third side. b. determine the angle θ. 6 For the triangle pictured (not drawn to scale): a. find the length of the third side. b. determine the angle θ. 7 Two forces pull an object. The first is 300 N along the x-axis, the second is 400 N along the y-axis. a. Draw a diagram showing the forces acting on the object. b. Draw a sketch showing the vector sum of two forces. c. Calculate the magnitude of the resultant force. d. Calculate the direction of the resultant force. 8 A girl swims with a velocity v1 = 1 m/s across a river (perpendicular to the riverbank as pictured). If there were no current, she could swim from point A to point B, but the river has a current with velocity v2 = 2 m/s. a. If the river is 50 m wide, how much time would it take the girl to cross the river? 8b. During this time, how far would the current push her downstream? 8c. Calculate the distance she travels (from A to C). 8d. Calculate the magnitude of her resultant velocity. 8e. Calculate the direction of her resultant velocity (relative to the line AB). 9 Two forces pull on an object. The first is 45 N along the x-axis, the second is 65 N along the y-axis. a. Draw a diagram showing the forces acting on the object. b. Draw a sketch showing the vector sum of the two forces. c. Find the magnitude of the resultant force. d. Find the direction of the resultant force. 10 An airplane flies with a velocity v1 = 120 m/s to the north, but there is a cross wind of v2 = 20 m/s to the east. a. What is the magnitude of the plane's resultant velocity? b. What is the plane's resultant direction (from north)? 11 Two forces pull an object. The first is 50 N along the x-axis the second is 80 N along the y-axis. a. Draw a diagram showing the forces acting on the object. b. Draw a sketch showing the vector sum of two forces. c. Calculate the magnitude of the resultant force. d. Calculate the direction of the resultant force. 12 A boat crosses a river with a velocity v1 = 12 m/s (perpendicular to the riverbank as pictured). If there were no current, the boat would cross from point A to point B, but the river has a current with velocity v2 = 5 m/s. a. If the river is 168 meters wide, how much time would it take the boat to cross the river? 12b. During this time, how far would the current push the boat downstream? 12c. Calculate the distance the boat travels (from A to C). 12d. Calculate the magnitude of the boat's resultant velocity. 12e. Calculate the direction of the boat's resultant velocity (relative to the line AB). 13 Two forces pull on an object. The first is 150 N along the x-axis, the second is 120 N along the y-axis. a. Draw a diagram showing the forces acting on the object. b. Draw a sketch showing the vector sum of two forces. c. Find the magnitude of the resultant force. d. Find the direction of the resultant force. 14 An airplane flies with a velocity v1 = 90 m/s to the west, but there is a crosswind of v2 = 40 m/s to the south. a. What is the magnitude of the plane's resultant velocity? b. What is the plane's resultant direction (from west)? 15 What are the x- and y-components of the force vectors shown below? 16 What are the x- and y-components of the force vectors shown below? 17 What are the x- and y-components of the force vectors shown below? 18 What are the x- and y-components of the force vectors shown below? 19 A ball is thrown horizontally from the roof of a building 75 m tall with a speed of 4.6 m/s. a. How much later does the ball hit the ground? b. How far from the building will it land? 19c. What is the magnitude of the velocity of the ball just before it hits the ground? 19d. What is the angle (relative to the ground) of the velocity of the ball just before it hits the ground? 20 A ball is thrown horizontally from the roof of a building 55 m tall with a speed of 3.8 m/s. a. How much later does it hit the ground? b. How far from the building will it land? c. What is the magnitude of the velocity of the ball just before it hits the ground? 21 A cannon is fired horizontally from a cliff 112 m high with a speed of 25 m/s. a. How much later does the cannon ball hit the ground? b. How far from the cliff will it land? 21c. What is the magnitude of the velocity of the cannon ball just before it hits the ground? 21d. What is the angle (relative to the ground) of the velocity of the cannon ball just before it hits the ground? 22 A ball is thrown horizontally from the roof of a building 12 m tall with a speed of 3.1 m/s. a. How much later does the ball hit the ground? b. How far from the building will it land? 22c. What is the magnitude of the velocity of the ball just before it hits the ground? 22d. What is the angle (relative to the ground) of the velocity of the ball just before it hits the ground? 23 A gazelle leaps from a cliff 2.5 m high with a speed of 5.6 m/s. a. How much later does the gazelle hit the ground? b. How far from the cliff will it land? 23c. What is the magnitude of the velocity of the gazelle just before it hits the ground? 23d. What is the angle (relative to the ground) of the velocity of the gazelle just before it hits the ground? 24 A ball rolls off a 1.5 m tall table horizontal table and lands on the floor 0.70 m away. a. How much time is the ball in the air? b. How does that time compare with the time it takes for a dropped ball to fall that same height? 24c. What is the ball's velocity while it is on the table top? 24d. What is the horizontal component of its velocity just prior to impact? 24e. What is the vertical component of its velocity just prior to impact? 24f. What is the magnitude of its velocity just prior to impact? 24g. What is the direction of its velocity just prior to impact? 25 A projectile is fired with an initial speed of 150 m/s at an angle of 47o above the horizontal. a. Determine the total time in the air. b. Determine the maximum height reached by the projectile. 25c. Determine the maximum horizontal distance covered by the projectile. 25d. Determine the velocity of the projectile 5 s after firing. 26 A projectile is fired from the edge of a cliff 95 m high with an initial speed of 50 m/s at an angle of 37o above the horizontal. a. Determine the total time in the air. b. Determine the maximum height reached by the projectile. 26c. Determine the maximum horizontal distance covered by the projectile. 26d. Determine the velocity of the projectile just before it hits the bottom of the cliff. 27 A projectile is fired with an initial speed of 110 m/s at an angle of 36o above the horizontal. a. Determine the total time in the air. b. Determine the maximum height reached by the projectile. 27c. Determine the maximum horizontal distance covered by the projectile. 27d. Determine the velocity of the projectile 4 s after firing. 28 A projectile is fired with an initial speed of 40 m/s at an angle of 23o above the horizontal. a. Determine the total time in the air. b. Determine the maximum height reached by the projectile. 28c. Determine the maximum horizontal distance covered by the projectile. 28d. Determine the velocity of the projectile 2 s after firing. 29 A hose held near the ground shoots water at a speed of 3.5 m/s at and angle of 72o above the horizontal. a. Determine the total time of the water in the air. b. Determine the maximum height reached by the water. c. Determine the maximum horizontal distance covered by the water. 30 An archer fires an arrow with a velocity of 42 m/s at an angle of 35o above the horizontal. a. What is the horizontal component of its initial velocity? b. What is the vertical component of its initial velocity? c. What is the maximum height attained by the arrow? d. How long does it take the arrow to reach that height? 30e. What is the total amount of time that it's in the air? 30f. How far away does it strike the ground? 30g. What is the horizontal component of its velocity just prior to impact? 30h. What is the vertical component of its velocity just prior to impact? 30i. What is the magnitude of its velocity just prior to impact? 30j. What is the direction of its velocity just prior to impact? 31 A box of mass 26 kg is sliding down a frictionless incline that makes an angle of 27o with the horizontal. a. Draw the free body diagram showing all forces. b. Resolve the gravitational force into its x- and ycomponents along the rotated coordinate system. 31c. Find the value of the normal force. 31d. What is the acceleration of the box? 32 A box of mass 26 kg is sliding down a frictionless incline that makes an angle of 27o with the horizontal. a. Draw the free body diagram showing all forces. b. Resolve the gravitational force into its x- and ycomponents along the rotated coordinate system. 32c. Find the value of the normal force. 32d. What is the acceleration of the box? 33 A box of mass 26 kg is sliding down a frictionless incline that makes an angle of 27o with the horizontal. a. Draw the free body diagram showing all forces. b. Resolve the gravitational force into its x- and ycomponents along the rotated coordinate system. 33c. Find the value of the normal force. 33d. What is the acceleration of the box? 34 A box of mass 26 kg is sliding down a frictionless incline that makes an angle of 27o with the horizontal. a. Draw the free body diagram showing all forces. b. Resolve the gravitational force into its x- and ycomponents along the rotated coordinate system. 34c. Find the value of the normal force. 34d. What is the acceleration of the box? 35 Light enters water (n = 1.33) from air (n = 1). The angle of incidence is 45o. What is the angle of refraction? 36 Light passing through water (n = 1.33) is incident on a slab of glass (n = 1.7). The angle of refraction is 30o. What is the angle of incidence? 37 Light enters diamond (n = 2.42) from air (n = 1). The angle of incidence is 45o. What is the angle of refraction? 38 Light passes from lucite (n = 1.5) into an unknown material. The angle of incidence is 20o. The angle of refraction is 27o. What is the index of refraction (n) of the unknown material? 39 Light enters lucite (n = 1.5) from air (n = 1). The angle of incidence is 65o. What is the angle of refraction? 40 Light passing through corn oil (n = 1.47) is incident on a slab of glass (n = 1.52). The angle of refraction is 57o. What is the angle of incidence? 41 Light enters diamond (n = 2.42) from water (n = 1.33). The angle of incidence is 38o. What is the angle of refraction? 42 Light passes from air (n = 1) into an unknown material. The angle of incidence is 30o. The angle of refraction is 22o. What is the index of refraction (n) of the unknown material?