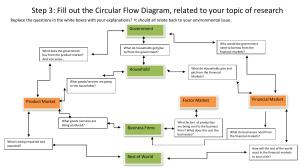
Chapter 2: The Market System and the Circular Flow Multiple-Choice Questions 1. Economic planning by central government agencies is primarily associated with (A) command economies (B) market economies (C) laissez faire economies (D) mixed economies (E) traditional economies (A) Government planning is the hallmark of a command economy. In other economies, individuals and firms play the central role in decision-making. Difficulty: Easy Style: Factual AP Economics Curricular Requirement Microeconomics: Economic Systems Book Section: Economic Systems 2. In market economies, the incentive that draws entrepreneurs into industry is (A) government bonuses for meeting production quotas (B) the opportunity to gain profit (C) government assumption of the risk of failure (D) government assistance with making output and pricing decisions (E) a guaranteed minimum income level (B) The profit motive draws new firms into industry in market economies, because private property rights allow firms to keep those profits. Difficulty: Easy Style: Conceptual AP Economics Curricular Requirement Microeconomics: Property Rights and the Role of Incentives Book Section: Characteristics of the Market System 3. In a mixed economy, the economic decisions of what to produce, how to produce, and who will receive products are made by (A) the government (B) consumers and firms (C) banks and stock markets (D) firms, consumers, and the government (E) banks and the government (D) Mixed economies provide for some government intervention, such as regulation and the provision of public goods, but primarily rely on the decision-making of firms and consumers in markets. Difficulty: Easy Style: Factual AP Economics Curricular Requirement Microeconomics: Economic Systems Book Section: Economic Systems 4. Fundamental economic questions that every society must answer include I. What will be produced? II. How will goods be produced? III. How will goods be distributed to consumers? (A) I only (B) III only (C) I and II only (D) II and III only (E) I, II, and III (E) Scarcity forces societies to answer these and other questions about economic growth and security. Difficulty: Easy Style: Factual AP Economics Curricular Requirement Microeconomics: Economic Systems Book Section: Five Fundamental Questions 5. What did economist Adam Smith identify as the "invisible hand" that directs the decisionmaking of firms and households in a market economy? (A) Government (B) Product demand (C) Self-interest (D) International trade (E) Entrepreneurial ability (C) In The Wealth of Nations, Adam Smith recognized that in market economies, market participants make decisions to benefit themselves, but at the same time their decisions will also indirectly benefit society. Difficulty: Easy Style: Factual AP Economics Curricular Requirement Microeconomics: Economic Systems Book Section: The “Invisible Hand” 6. In the product market of the circular flow model (A) firms buy finished products from households (B) consumers buy factors of production from firms (C) firms sell factors of production to the government (D) consumers buy finished products from firms (E) firms buy factors of production from consumers (D) In the product market, firms sell products to consumers. Difficulty: Easy Style: Factual AP Economics Curricular Requirement Macroeconomics: Circular Flow Book Section: Product Market 7. Which of the following activities would occur in the resource (factor) market? (A) A teacher buys a new truck from a car dealership. (B) The Department of Defense buys a tank from a weapons manufacturer. (C) A farmer buys farmland from a retiring farmer. (D) A retirement fund buys stock in a major corporation. (E) A welder buys a personal home computer from an electronics store. (C) In the resource (factor) market, firms buy factors of production (land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurial ability) from resource providers. Difficulty: Easy Style: Factual AP Economics Curricular Requirement Macroeconomics: Circular Flow Book Section: Resource Market 8. While resources and products flow in one direction of the circular flow model, what flows the other direction? (A) Money (B) Services (C) Public goods (D) Imported goods (E) Information (A) Money, in the form of paychecks, profit, and other payments, serves as an incentive for households to provide resources, and for firms to produce products in a market economy. Difficulty: Easy Style: Factual AP Economics Curricular Requirement Macroeconomics: Circular Flow Book Section: The Circular Flow Model 9. The use of money facilitates specialization because money I. facilitates trade II. forces a coincidence of wants III. establishes a medium of exchange (A) I only (B) III only (C) I and III only (D) I and II only (E) I, II, and III (C) Money, unlike barter, facilitates specialization because it does not require buyers and sellers to have exactly the same (coincidence of) wants. As a medium of exchange that is universally accepted, money allows buyers and sellers to engage in mutually beneficial trade. Difficulty: Easy Style: Factual AP Economics Curricular Requirement Macroeconomics: Definition of Financial Assets: Money, Stocks, Bonds Book Section: Use of Money 10. Unlike the command economic system, the merits of the market system are I. economic efficiency II. effective central planning III. individual freedom of choice IV. incentives generate innovation (A) I and IV only (B) I and III only (C) I, II, and IV only (D) I, III, and IV only (E) III and IV only (D) Unlike the command economic system that depends on government central planning, the free market system achieves economic efficiency through emphasis on competition, incentives, and the freedom of choice. Difficulty: Easy Style: Factual AP Economics Curricular Requirement Microeconomics: Economic Systems Book Section: Characteristics of the Market System 11. The major problems faced by a pure command economy include all of the following EXCEPT (A) limited consumer choice (B) lack of entrepreneurial incentives (C) a lack of central planning (D) inefficient use of resources (E) a lack of fluctuation in prices (C) The pure command economy functions through central planning by the government. Under the pure command system, the government rather than the market system determines what to produce, how to produce, where to produce, who will produce, how much to produce, and at what price to produce each good and service. Difficulty: Easy Style: Factual AP Economics Curricular Requirement Microeconomics: Economic Systems Book Section: The Demise of the Command Systems 12. The resource market determines all of the following EXCEPT (A) a worker’s wages (B) the incentives for entrepreneurs (C) the price of a worker’s clothing (D) the capital costs of a new factory (E) the per-acre price of farmland (C) The price of a worker’s clothing is determined in the product market, where the final goods and services produced by the economy are bought and sold. In this case, it is the interaction of supply and demand in the product market that determines the price and quantity of a worker’s clothing. Difficulty: Easy Style: Factual AP Economics Curricular Requirement Macroeconomics: Circular Flow Book Section: The Circular Flow Model 13. In the free market system, consumer sovereignty occurs for which of the following reasons? I. Consumers, through their dollar votes, determine how resources are distributed and what goods and services are produced to meet their wants. II. Consumers are free to determine how they earn their income and spend their wages. III. Consumers must buy goods and services that business decides to provide. (A) I only (B) II only (C) III only (D) I and II only (E) I, II, and III (A) Through their choices about what to buy (their dollar votes), consumers make decisions in the product market and determine the answers to the five fundamental questions that establish the basis for the free market system. Difficulty: Easy Style: Factual AP Economics Curricular Requirement Microeconomics: Economic Systems Book Section: Five Fundamental Questions 14. All of the following are key features of the market system EXCEPT (A) the interaction of supply and demand (B) change will be accommodated (C) economic growth and progress (D) the need for central economic planning (E) the trade-off between limited incomes and unlimited wants (D) Central economic planning is not a feature of a market system, but the central feature of a command economic system. Difficulty: Easy Style: Factual AP Economics Curricular Requirement Microeconomics: Economic Systems Book Section: Characteristics of the Market System 15. In a command economic system, the answers to the fundamental economic questions are determined by (A) government, businesses, and consumers (B) consumers through their dollar votes and government through its economic mandates (C) consumers, businesses, and government through their trade-offs (D) government alone (E) government and businesses (D) In a command economic system, the government through central planning determines all the answers to the key economic questions of what is to be produced, how to produce, what quantity to produce, what price will be charged, and for whom goods and services will produced. There is no consumer sovereignty. Difficulty: Easy Style: Factual AP Economics Curricular Requirement Microeconomics: Economic Systems Book Section: Economic Systems 16. In the circular flow model (A) households buy and businesses sell land, labor, and capital in the resource market (B) households sell and businesses buy land, labor, and capital in the product market (C) households sell and businesses buy land, labor, and capital in the resource market (D) households buy and businesses sell land, labor, and capital in the product market (E) both households and businesses buy land, labor, and capital in the resource market (C) In the resource market, households sell their resources or services to businesses and receive money income in return for their resources and services. Businesses buy the resources and services of households and pays for these with the revenues gained from the final sale of goods and services that those resources and services create. Difficulty: Easy Style: Factual AP Economics Curricular Requirement Macroeconomics: Circular Flow Book Section: The Circular Flow Model 17. In the circular flow model, the factor market determines all of the following EXCEPT (A) employee weekly wages (B) price of used student textbooks in the bookstore (C) price of printing presses for commercial use (D) office rents for lawyers and doctors (E) the price of fertilizer used in the production of cotton (B) Businesses provide used textbooks in the bookstore to be bought and sold by students in the product market. Difficulty: Easy Style: Factual AP Economics Curricular Requirement Macroeconomics: Circular Flow Book Section: The Circular Flow Model 18. Which of the following illustrate the use of economic incentives to create the potential for real, long-run economic growth? I. Government grants to students to pay for higher education II. Government tax credits to stimulate research into alternative energy production III. Tariffs and quotas to limit foreign imports (A) I only (B) II only (C) III only (D) I and II only (E) I, II, and III (D) Encouraging students to pursue higher education increases not only their skill as workers, but also their capacity to create new technology for the future output. Research into alternative energy production has the potential to provide the technology critical in the future. Neither tariffs nor quotas create incentives for increasing the potential for real, long-run economic growth. Difficulty: Medium Style: Conceptual AP Economics Curricular Requirement Microeconomics: Property Rights and the Role of Incentives Book Section: Characteristics of the Market System 19. Specialization of labor contributes to increased economic output by I. creating optimal use of human resources by taking advantage of the different skills of each individual in the workforce II. encouraging each individual to perform as many different tasks as possible III. taking advantage of skill development as each worker becomes more efficient in performing the same task (A) I only (B) II only (C) III only (D) I and III only (E) I, II, and III (D) Specialization takes advantage of human differences and builds on the efficiency created by skill development as workers focus on particular tasks. Because of potential for inefficiency, specialization does not encourage workers to perform as many tasks as possible. Difficulty: Medium Style: Conceptual AP Economics Curricular Requirement Microeconomics: Comparative Advantage, Absolute Advantage, Specialization, and Trade AP Economics Curricular Requirement Macroeconomics: Comparative Advantage, Specialization, and Exchange Book Section: Specialization 20. A country achieves an optimal point of production outside of its domestic production possibility curve by taking advantage of I. human and geographic specialization II. human and geographic specialization combined with tariffs and quotas III. international trade (A) I only (B) II only (C) III only (D) I and II only (E) I and III only (E) To achieve an optimal point outside of a country’s production possibilities curve, a nation must maximize the benefits and efficiencies of human and geographic specialization combined with efficiencies gained through unhindered international trade. Difficulty: Medium Style: Conceptual AP Economics Curricular Requirement Microeconomics: Comparative Advantage, Absolute Advantage, Specialization, and Trade AP Economics Curricular Requirement Macroeconomics: Comparative Advantage, Specialization, and Exchange Book Section: Specialization 21. In a laissez-faire economy, the primary role of government in the economy is to (A) establish price ceilings and floors (B) regulate industry to ensure worker safety (C) protect private property rights (D) promote international trade (E) stabilize the economy through fiscal and monetary policy (C) In a laissez-faire economy, the government is prevented from intervening in the economy, other than to protect property rights and create a legal environment for the enforcement of contracts. Difficulty: Easy Style: Factual AP Economics Curricular Requirement Microeconomics: Economic Systems Book Section: Laissez-Faire Capitalism 22. Private property rights are critically important for the development of I. entrepreneurship II. investment III. intellectual property (A) I only (B) III only (C) I and II only (D) II and III only (E) I, III, and III (E) Private property rights allow producers to keep the profits from their work, giving them the incentive to develop intellectual property, start businesses, and invest in future development. Difficulty: Easy Style: Factual AP Economics Curricular Requirement Microeconomics: Property Rights and the Role of Incentives Book Section: Private Property 23. Market systems promote economic growth and higher standards of living by (A) supporting the development of new technology (B) creating new firms to compete with private industry (C) increasing taxes on businesses that increase investment (D) imposing anti-pollution regulations on corporations (E) rationing capital to ensure all businesses have an opportunity to earn profit (A) Technological advance allows businesses to create more output with the same amount of resources or fewer resources. Production possibilities increase and standards of living increase. Difficulty: Easy Style: Factual AP Economics Curricular Requirement Microeconomics: Economic Systems Book Section: Five Fundamental Questions 24. In the resource market, income flows to households in each of the following forms EXCEPT (A) Wages (B) Rents (C) Interest (D) Taxes (E) Profits (D) In the resource market, income flows to households to pay for land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurial ability. Taxes are an income flow to the government, not to households. Difficulty: Easy Style: Factual AP Economics Curricular Requirement Macroeconomics: Circular Flow Book Section: Resource Market 25. Which type of economic system communicates changes in consumer tastes through price and profit signals? (A) A command economy (B) A market economy (C) A traditional economy (D) A communist economy (E) A directed economy (B) In a market economy, changes in demand cause changes in prices and profit, giving firms an incentive to respond to the change in demand. Difficulty: Easy Style: Factual AP Economics Curricular Requirement Microeconomics: Economic Systems Book Section: Five Fundamental Questions Free-Response Question Assume a closed economic system in which there is neither foreign trade nor government. Construct and correctly label a circular flow diagram that illustrates the money flow and exchange of goods and services between households and businesses. Free-Response Explanation 7 points: 1 point is earned for a correctly labeled circular flow diagram. 1 point is earned for correctly identifying that households buy products (goods and services) and sell resources. 1 point is earned for correctly identifying that businesses buy resources and sell products. 1 point is earned for correctly identifying the resource market, noting that households sell and businesses buy resources (land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurial ability). 1 point is earned for correctly identifying the product market, noting that households buy and businesses sell final goods and services. 1 point is earned for correctly identifying that resources (land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurial ability) and products (goods and services) flow in one direction. 1 point is earned for correctly identifying that money flows in the opposite direction. In the resource market, money is exchanged between households and businesses (rent for land, wages for labor, interest and profits for entrepreneurial ability). In the product market, money is exchanged between households and businesses for products (goods and services). Difficulty: Easy Style: Applied AP Economics Curricular Requirement Macroeconomics: Circular Flow Book Section: The Circular Flow Model