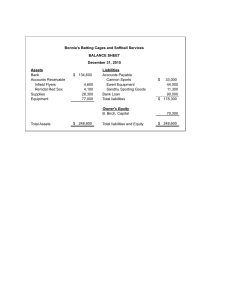
IASB’S FRAMEWORK IASB stands for International Accounting Standard Board; it is an independent, privately funded accounting standard setter organization. IASB develops Accounting Standards that harmonize the accounting practices globally. Objective: Main objective of the framework is to provide a rational and sensible guide for preparing accounting standards and applying them accordingly. This framework is used preparation and preparation of financial statements. Purpose of IASB’s Framework: It provides assistance in: • Development of new IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards) • Review of existing IAS (International Accounting Standards) • Promoting Harmonization • Developing National Standards Components of Financial Statements and their objectives The framework is concerned with “general purpose financial statements”. Components of financial statements include: Balance Sheet Balance sheet is prepared to know the financial position Income Statement Income statement shows financial performance/profitability Statement of Changes in Equity This statement is prepared to show the movement in different heads of owners’ equity Cash Flow Statement It is prepared to know the cash inflows and outflows during the year divided into operating, investing and financing activities Notes Notes are prepared to disclose significant accounting policies selected and applied in preparing the financial statement. It also contains some imperative disclosures to make financial statements understandable. Users of the financial statements Communication of the financial information flows towards the users of the financial statements. • • • • • • • Shareholders (assess the ability of enterprise to pay the dividend) Lenders (determine the ability of enterprise to pay their loan and interest) Employees (concerned about their pay, retirement benefits etc.) Govt. agencies (determine tax, regulate the activities ) Public (enterprises make substantial contribution to the local economy) Suppliers (evaluate whether the entity will be fine as a customer and pay its dues) Customers (decide whether the company will be able to continue producing and supplying goods with the same quality) Underlying Assumptions 1) Accrual Basis Accrual concept is used to measure the incomes and expenses of the entity. According to the accrual concept incomes and expenses are not measured at the amount of cash received or paid during the year but for incomes the measurement basis are earnings and for expenses measurement basis are incurrence. They are recorded in the accounting records and reported in the financial statement for the period to which they relate. 2) Going Concern Going concern means that the entity will continue its operations for the foreseeable future and there is no intention to liquidate it or to significantly curtail its operations. Qualitative Characteristics of Financial Statements Qualitative characteristics are the attributes that make the information provided in financial statements useful to the users. Qualitative characteristics that make the financial information useful Materiality It is threshold quality which must be checked before studying the further qualitative characteristics. Information is material if its omission/misstatement could influence the economic decisions of users taken on the basis of financial statements. 1) Relevance Information must be relevant to the decision making needs of users. It helps users to evaluate past, present or future events. It also helps users to confirm or correct past evaluations. What makes financial information relevant? Predictive role Current level/structure of asset holding issued to predict the ability of the entity to take advantages of opportunities and its ability to react to adverse situation. Confirmative role Some information plays confirmatory role as outcome of the planned operations. Information about financial position and past financial performance is used as predicting future financial position and performance. 2) Reliability Information may be relevant but so unreliable in nature that its recognition may be potentially misleading. What makes financial information reliable? Faithful representation Information must represent faithfully the transactions it purport to represent in order to be reliable. Substance over form It is the principle that transactions and other events are accounted for and presented in accordance with their economic substance (economic reality) and not merely their legal form. Neutrality Information must be free from bias and should not be focused on predetermined results. Prudence Financial information presented in the financial statements relating to the assets and incomes should not be overstated and relating to the liabilities and expenses should not be understated. Completeness Financial information must be complete in terms of cost measurement and documentation. Omission may cause information to be misleading. Qualitative characteristics that make the presentation useful 1) Comparability Users should be able to compare an entity’s performance over time and to compare one entity’s performance with other. Consistency To make the financial statements comparable accounting policies and classification should be consistent over the years. Requirements of the applicable accounting standards should also be applied consistently. Disclosure of accounting policies Significant accounting policies should be disclosed in the notes this makes the financial statements comparable with financial statements of other entities. 2) Understandability Financial statements should be presented in such a way that these are understood by a user having average knowledge of commerce and business. Readily understandable by users Users are assumed to have basic knowledge of accounting to understand the published financial statements. Aggregation and classification Presentation of financial information in the financial statements should be aggregated if these are not material. Information relating to the same class should be classified in one group. Constraints to relevancy and reliability of financial information Quality of relevancy and reliability depends upon three constrains: 1) Balance between qualitative characteristics Relevance and reliability are often in conflict. For example; market values of fixed tangible assets more relevant than historical cost, but these are less reliable. 2) Timeliness If there is unjustified delay in the reporting of information it may lose its relevancy. Information may be reported on a timely basis when all aspects of the transaction are not known, thus compromising reliability. 3) Balance between cost and benefit When information is provided, its benefits must exceed the costs of obtaining and presenting it. ELEMENTS OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS Financial information of an entity are classified into five main heads, these main heads are elements of financial statements. Assets: These are the resources in control of the entity as a result of past events and from which future economic benefits are expected to flow to the entity. Points to remember: 1. Resources in control 2. Past event 3. Future inflow Liabilities: These are the present obligations of the entity arising from past events, the settlement of which is expected to result in an outflow from the entity of resources embodying economic benefits. Points to remember: 1. Present obligation 2. Past event 3. Future outflow Equity: It is the residual interest in the assets after deducting all its liabilities. In other words, equity is what is left when all liabilities have been settled. Points to remember: 1. Equity contributed 2. Reserves created Incomes: Incomes establish increases in economic benefits during the accounting period in the form of inflows or enhancements of assets or decreases of liabilities that result in increases in equity other than those relating to contributions from equity participants. Incomes include: 1. Revenue a. Sales of goods b. Sales of services c. Returns on investments 2. Gains a. Disposal of assets at a value higher than its carrying amount b. Discharge of liabilities at a value lesser than its carrying amount Expenses: Expense is decrease in economic benefits during the accounting period in the form of outflows or decrease in assets or incurrence of liabilities that result in decreases in equity, other than those relating to distributions to equity participants. Expenses include: 1. Revenue Expenses a. Expenses that arise in the course of ordinary activities of an entity. 2. Losses a. Disposal of assets at a value lesser than its carrying amount b. Discharge of liabilities at a value higher than its carrying amount Measurement of the Elements of Financial Statements A number of different measurement bases are employed to different degrees and combinations in financial statements. These include: 1. Historical Cost Assets are recorded at the amount of cash paid to acquire them. Sometimes the terms cash equivalents or fair value at acquisition will be used instead. Liabilities are recorded at the proceeds received in exchange for the obligation on the date of transaction. 2. Current Cost Assets are carried at their current purchase price. Liabilities are carried at the undiscounted amount currently required to settle them. 3. Realizable Value Assets are carried at the amount, which could currently be obtained by an orderly disposal. Liabilities are carried at their settlement values, the amount to be paid to satisfy them in the normal course of business. 4. Present Value Assets are carried at the present discounted value of the future net cash inflows that the item is expected to generate in the normal course of business. The most common measurement basis adopted by the entity in preparing financial statements is historical cost. This is usually combined with other bases.