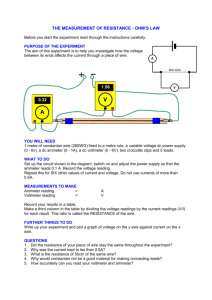
EXPERIMENT - Electric Jug Aim: To determine how much electrical energy is changed into heat energy with a simple electric jug circuit. Diagram: Power supply Thermome ter Wire Beaker Nichrome wire Ammeter Voltmeter Power supply Wire A Resistor (nichrome wire) Ammeter Voltmeter V EXPERIMENT - Electric Jug Method: 1. Set up the equipment as shown in the diagram 2. Pour 100mL of water into the beaker 3. Set the power pack to 6 volts (so that no more than 4 amps flows through the ammeter otherwise the wires will melt) 4. Turn the power pack on, measure the voltage and current and then turn the power pack off again. 5. Measure the temperature of the water to get a start value for the water. 6. Turn on the power pack and measure the temperature of the water every minute for 15 minutes. 7. Record your results in the table below Results: Variable Value Amount of water 100 mL Voltage across nichrome wire Current through wire Time (minutes) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Temperature (˚C) EXPERIMENT - Electric Jug 12 13 14 15 ● Graph the results from your table and put them in here. Discussion: 1. Do the calculations below to work out how much energy came from the power pack and how much energy got to the beaker of water. This is the energy delivered by the power pack This is the energy absorbed by the water in the beaker Energy = Voltage x Current x Time (in seconds) Energy = mass of water x specific heat of water x change in temperature Energy = Voltage x Current x 15 x 60 Energy = 100 x 4.18 x (temp at 15 mins temp at 0 mins) Energy = Energy = 2. The two amounts of energy above should be the same but they are not (the energy absorbed by the water in the beaker should be less than the energy delivered by the power pack). Why is there a difference in the energy delivered by the power pack and absorbed by the water? 3. What could be done to reduce the amount of energy lost in this experiment? 4. Using your graph, predict how long it would take for your jug of water to come to the boil. Conclusion: