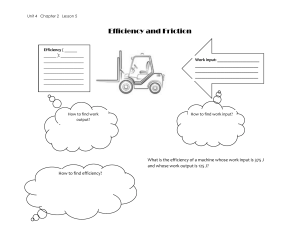
11.2 Types of Forces Question of the Day: If I push a beaker to slide it across the counter, why does it stop? Sort the following forces as Contact Force or Field Force Air Resistance Applied Electrical Frictional Gravitational Magnetic Normal Spring Tension Sort the list on a whiteboard as a team. Contact Force - Applied Force A force that is applied to an object by a person or another object. Contact Force - Normal Force The normal force is the support force exerted upon an object that is in contact with another stable object. What is providing a normal force for Spongebob? Friction The force exerted by a surface as an object moves across it or makes an effort to move across it. Friction results from the two surfaces being pressed together closely, causing intermolecular attractive forces between molecules of different surfaces. (Depends on what the materials are made from to determine how much friction there will be.) Though it is not always the case, the friction force often opposes the motion of an object. Friction Sometimes we ignore friction to make the math easier. Contact Force - Air Resistance The air resistance is a special type of frictional force that acts upon objects as they travel through the air. We can ignore air resistance for small objects moving at low speeds. Tension The tension force is the force that is transmitted through a string, rope, cable or wire when it is pulled tight by forces acting from opposite ends. Springs The spring force is the force exerted by a compressed or stretched spring upon any object that is attached to it. Types of Forces Examples Go to Google Classroom. Click on the link to the Jamboard. Provide one example of each type of contact force. What objects or scenarios would you see each type of force? Gravitational The force of gravity is the force with which the earth, moon, or other massively large object attracts another object towards itself. Fgrav = m * g where g = 9.8 N/kg (on Earth) and m = mass (in kg) What keeps the balloon stuck to the wall? Draw on the whiteboard what you think is happening. Electrical Attraction between opposite charges or repulsion between like charges. https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/html/balloons-and-static-electricity/latest/balloons-and-static-electricity_en.html Magnetic Attraction or repulsion that arises between electrically charged particles because of their motion or the alignment of atoms in a substance. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v= Vt8NOdINJ1s Free Body Diagrams A book is at rest on a tabletop. Diagram the forces acting on the book. Free Body Diagrams A car is coasting to the right and slowing down. Ignore air resistance. Diagram the forces acting upon the car. Net Force