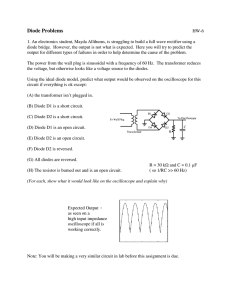
Republic of the Philippines BATANGAS STATE UNIVERSITY Pablo Borbon Campus II Batangas City COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, ARCHITECTURE AND FINE ARTS Department of Electronics Engineering EXPERIMENT NO. 1 Diode Application (Rectifier, Clipper and Clamper Circuits) Submitted by: TEAM 1 Velasquez, Christine Joyce P. Javier, John Raphael Martinez, Vince Harvey Z Perez, Rhon Paolo M. GROUP 1 ICE - 2201 Submitted to: Engr. Iris R. Tejada April 10, 2022 Abstract: The experiment aims to demonstrate application of the junction diodes and investigate the use of diode in its application such as rectifier, clipper, and clamper circuits. In line with this is to show the uses of diodes among the three specifically how they differ with each other. In order to obtain accurate data, using of Simulation Software such as Multisim is a must to compare the measured values to the calculated values through given and derived formulas for Rectifiers such as Half-Wave and FullWave Rectifier. Even though the gathered data had minimal difference, it did not affect the result as it will lead to similar whole values and differ only in terms of decimal point which shows the accuracy of getting similar values as shown in the percent difference – may it be with the use of a programmed application or the actual computation. However, Clipper and Clamper Circuit forms Triangular and Rectangular Waveforms that shows the input and output of a designed circuit. Also, its diode has two types which is the Forward Biased and Reverse Biased Circuit. Doing this experiment do not limits what simulation software should be use as long as it will give the unknown values and the needed diagrams for the success of this experiment. I. INTRODUCTION Diodes are one of the simplest, but most useful of all semiconductor devices. Many types of diode are used for a wide range of applications. Rectifier diodes are a vital component in power supplies where they are used to convert AC mains line voltage to DC. Diodes are made from semiconductor materials, mainly silicon, with various compounds (combinations of more than one element) and metals added depending on the function of the diode. Early types of semiconductor diodes were made from Selenium and Germanium, but these diode types have been almost totally replaced by more modern silicon designs. The application areas of diodes include communication systems as limiters, clippers, gates; computer systems as logic gates, clampers; power supply systems as rectifiers and inverters; television systems as phase detectors, limiters, clampers; radar circuits as gain control circuits, parameter amplifiers, etc. In this experiment, we will investigate the use of diode in its application such as rectifiers, clipper and clamper circuits. This experiment will give us insights on how diode works in a circuit and why it is important. II. OBJECTIVES 1. To demonstrate application of the junction diodes. 2. To investigate the use of diode in its application such as rectifier, clipper and clapper circuits. III. IV. MATERIALS AND EQUIPMENTS • Adjustable DC Power Supply • Function generator • Resistors • 1N4001 Silicon Diode • Breadboard • Connecting wires (size #22) • Multimeter • Oscilloscope • Simulation Software (Multisim or online software) PROCEDURES A. HALF WAVE RECTIFIER CIRCUIT 1. Construct the circuit in Figure 1.1 using 1N4001 diode or any equivalent. Figure 1.1 Half-wave Rectifier Circuit 2. Apply 5Vp with frequency of 1 KHz sinusoidal input to circuit using function generator. 3. Obtain the output waveform using oscilloscope. 4. Measure the 𝑉𝑝,𝑣𝑒, and the 𝑃𝐼𝑉 using multimeter. 5. Calculate 𝑉𝑝, 𝑉𝑎𝑣𝑒, and𝑃𝐼𝑉 using eq. 1.1, 1.2, and 1.3. 𝑉𝑝= 𝑉𝑖𝑛−𝑉𝑡�𝒆𝒒. 𝟏.𝟏 𝑤�𝑒𝑟𝑒: 𝑉𝑖𝑛= 𝑖𝑛𝑝𝑢𝑡𝑣𝑜𝑙𝑡𝑎𝑔𝑒 6. Compare values in a.5 and a.6. A. HALF WAVE RECTIFIER CIRCUIT Table 1 Values for Half Wave Rectifier Circuit Vp Vave PIV Simulation 4.38V 1.32V 5V Computation 4.3V 1.36V 5V % Difference 1.04% 3.03% 0% , Analysis: B. FULL WAVE RECTIFIER 1. Construct the circuit in Figure 1.2 using 1N4001 diode or any equivalent. Figure 1.2 Full-wave Rectifier Circuit 2. Apply 7Vp with frequency of 1 KHz sinusoidal input to circuit using function generator. 3. Obtain the output waveform using oscilloscope. 4. Measure the 𝑉𝑝,𝑣𝑒, and the 𝑃𝐼𝑉 using multimeter. 5. Calculate 𝑉𝑝, 𝑉𝑎𝑣𝑒, and 𝑃𝐼𝑉 using eq. 1.4, 1.5, and 1.6. 𝑉𝑝= 𝑉𝑖𝑛− 2𝑉𝑡�𝒆𝒒.𝟏. 𝟒 2𝑉𝑝 𝟓 6. Compare values in b.5 and b.6. B.FULL WAVE RECTIFIER CIRCUIT Table 2 Values for Full Wave Rectifier Circuit Vp Vave PIV Simulation 5.82V -3.42V 7V Computation 5.6V 3.56V 6.3V % Difference 3.78% 2.04% 10% Analysis: C. CLIPPER 1. Construct the circuit in Figure 1.3 using 1N4001 diode or any equivalent. 2. Apply 15 𝑉𝑝𝑝with frequency of 1 KHz sinusoidal input to circuit using function generator. 3. Obtain and compare the input and output waveform using the oscilloscope. Figure 1.3 Clipper Circuit 4. Repeat the process by applying 15 𝑉𝑝𝑝 with frequency of 1 KHz triangular and rectangular wave input. 5. Repeat the process c.1 to c.4 in figure 1.4. Figure 1.4 Biased Clipper Circuit 6. Compare the output waveforms from figure 1.3 and 1.4. D. CLAMPER 1. Construct the circuit in Figure 1.3 using 1N4001 diode or any equivalent. Figure 1.3 Positive Clamper Circuit 2. Apply 10 𝑉𝑝𝑝 with frequency of 1 KHz sinusoidal input to circuit using function generator. 3. Obtain and compare the input and output waveform using the oscilloscope. 4. Repeat the process by applying 10 𝑉𝑝𝑝 with frequency of 1 KHz triangular and rectangular wave input. 5. Reverse the diode by flipping it horizontally. Repeat the process d.1 to d.4 in 6. Compare the output waveforms. V. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION 1. Attach the screenshot of the following: A. schematic diagram created at the multism. B. With connecting function generator and oscilloscope C. Waveform (per stage) 2. Your observation 3. Calculation 4. Comparison with theoretical value and measured value. VI. CONCLUSION VII. DOCUMENTATION