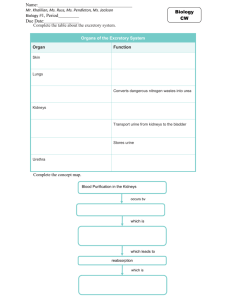
Excretion Lesson Objectives: ● Describe what excretion is ● Explain the process of excretion in animal and plants ● Define the differences in the processes that ultimately lead to excretion in animals and plants. Warm Up: Which factors can affect the rate of gas exchange? Excretion Excretion is the removal of the following substances: ● toxic materials ● waste products of metabolism ● excess substances from organisms Excretion is not the same as egestion - which is the passing out of undigested food through the anus as faeces. Excretion Plants need to excrete excess carbon dioxide and oxygen. Carbon dioxide is a waste product of aerobic respiration in plant cells. Oxygen is a waste product of photosynthesis. Unlike animals, plants do not have specialised excretory organs. Excess carbon dioxide and oxygen are excreted from the plant through the stomata in the leaves. Excretion The organs of excretion in humans include the skin, lungs and kidneys. Skin Sweat glands in the skin produce sweat. The water in sweat helps to keep the body cool in hot conditions, and it contains salts and urea. Lungs Excess carbon dioxide and some water vapour are removed through the lungs when humans breathe out. Kidneys The kidneys are organs of the urinary system - which removes excess water, salts and urea. Urinary System Blood is brought to the kidney in the renal artery. The kidneys filter the blood and then reabsorb useful materials such as glucose. After it has been purified, the blood returns to the circulation through the renal vein. Urine is taken from the kidneys to the bladder by the ureters. The bladder stores the urine until it is convenient to expel it from the body. Note that ‘ureter’ differs from the word ‘urethra’. The ureters are tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder, whereas the urethra is the tube that carries urine out of the body. Urine contains water, urea and salts. Urea is produced in the liver when excess amino acids are broken down. It is the main waste product removed in the urine. Kidneys The inner part of the kidney is called the medulla and the outer part is the cortex. A renal artery carries blood to the kidney and a renal vein carries it away. The ureter carries urine from the kidney to the bladder. Blood is filtered at high pressure to remove glucose, water, salts and urea. All the glucose, and some water and salts, are reabsorbed back into the blood. Note that urea is not reabsorbed. Nephron Urine is produced in microscopic structures in the kidney called nephrons. Each kidney contains around a million nephrons. The Bowman’s capsule (renal capsule): ● ● ● surrounds a ball of capillaries called the glomerulus the blood is put under high pressure ultrafiltration of the blood happens, in which water, ions,glucose and other small molecules pass into the tubule (but not proteins or cells) Nephron The first convoluted tubule (proximal convoluted tubule) is responsible for: ● the selective reabsorption of glucose The collecting duct is responsible for: ● ● the selective reabsorption of water sending urine to the ureter ADH The water content of the blood is controlled by a hormone called ADH (anti-diuretic hormone). Different amounts of ADH are released into the bloodstream according to the concentration of the blood plasma. The diagrams show what happens when there is either too little or too much water in the blood. Nephron Summary