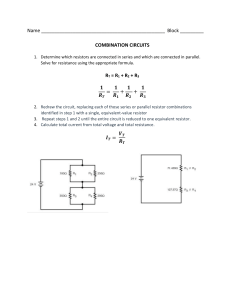
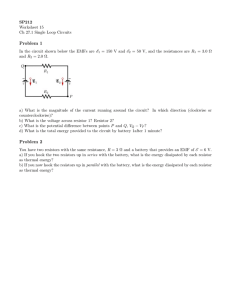
AP PHYSICS 2 Scoring Guide Unit 4 Progress Check: MCQ Part A A battery, a switch , and four identical lightbulbs 1. 2. How does the current in lightbulb , , , and are arranged in a circuit as shown above. change, if at all, when the switch is closed, and why? (A) It does not change because the closed path through the battery and lightbulbs changed. (B) It increases because the equivalent resistance of parallel lightbulbs lightbulb . (C) It decreases because the current now passes through both lightbulbs around the circuit. (D) The currents cannot be compared without knowing the values of the resistances and the battery’s potential difference. Which of the following correctly ranks the current and and in each lightbulb after switch , , and has not is less than the resistance of as it travels clockwise is closed? (A) (B) (C) (D) 3. The resistance of each lightbulb is What is the of the battery? . When the switch is closed, the current through lightbulb is . (A) (B) (C) (D) 4. Cylindrical rods of various lengths and cross-sectional areas are made of different materials. Each rod is connected individually to the same battery, whose potential difference is known, and the current in the circuit is measured. Can the resistivities of the rods be compared? AP Physics 2 Page 1 of 15 Scoring Guide Unit 4 Progress Check: MCQ Part A (A) Yes, because the lengths and cross-sectional areas of the rods can be measured. (B) Yes, because the rods will be connected to the same battery and will have the same currents. (C) No, because the resistivity of a material depends on its atomic structure, which is unknown. (D) No, because the rods have different lengths. 5. A student has a collection of resistors of unknown resistance made of various materials and wants to experimentally determine the effect of resistivity on resistance. The student connects each different resistor in the circuit shown above, without changing the other components, and measures the current in the circuit and the potential difference across each of the different resistors. Will measurement of just these two quantities provide sufficient information? Why or why not? (A) Yes, because the of the battery is held constant, so the current in the resistors will vary. (B) Yes, because the resistance of the resistors can be determined from the measurements. (C) No, because even though the resistances can be determined, resistance also depends on the dimensions of the resistor. (D) No, because the 6. of the battery must be changed to get a range of measurements. Four cylindrical wires of different sizes are made of the same material. Which of the following combinations of length and cross-sectional area of one of the wires will result in the smallest resistance? Page 2 of 15 AP Physics 2 Scoring Guide Unit 4 Progress Check: MCQ Part A Length Area Length Area Length Area Length Area (A) (B) (C) (D) 7. Resistance ( ) 5 10 15 20 Length ( 2 4 8 16 ) A student has four pieces of wire of different lengths but with the same cross-sectional area. The wires look the same, but the student wants to be sure they are made of the same material and records the data shown in the table above. Which of the following is a correct analysis of the data? (A) The wires are made of the same material because the resistance doubles as the length doubles. (B) The wires are made of the same material because the resistance increases by doubles. each time the length (C) The wires are not made of the same material because the resistance doubles as the length doubles. (D) The wires are not made of the same material because the resistance increases by length doubles. each time the AP Physics 2 Page 3 of 15 Scoring Guide Unit 4 Progress Check: MCQ Part A 8. A student has a set of identical capacitors that have the same dielectric material between the plates. The student wants to determine the dielectric constant of the material. The student connects one capacitor to a battery and resistor in the circuit shown above and measures the current through the resistor after the circuit reaches steady state. The student then adds a second capacitor to the circuit, in parallel with the first, and measures the new current through the resistor at steady state. The student continues to add capacitors to the circuit in parallel and take measurements, then plots the current as a function of the total number of capacitors in the circuit. Will this allow the student to determine the dielectric constant of the material, and why or why not? (A) Yes, because the potential differences across the resistor and the capacitor are the same. (B) Yes, because the currents in the resistor and the capacitor are the same. (C) No, because the capacitor is fully charged when the circuit reaches steady state. (D) No, because the information does not allow comparison of different capacitances. 9. Each of the two circuits shown above has reached steady state. Measuring which of the following would give the of one of the batteries? Page 4 of 15 AP Physics 2 Scoring Guide Unit 4 Progress Check: MCQ Part A (A) The potential difference across either resistor in circuit 1 (B) The potential difference across the capacitor in circuit 1 (C) The potential difference across either resistor in circuit 2 (D) The potential difference across the capacitor in circuit 2 10. A resistor of unknown resistance is connected to a power source with variable potential difference. The figure above shows a graph of the power dissipated by the resistor as a function of the square of the current through the resistor and a best-fit line for the data. The slope of the best-fit line is equal to the (A) average potential difference of the power supply (B) resistance of the resistor (C) total amount of energy dissipated by the circuit (D) internal resistance of the power supply AP Physics 2 Page 5 of 15 Scoring Guide Unit 4 Progress Check: MCQ Part A 11. A student wants to determine how increasing the total resistance in a circuit affects the current through the battery in the circuit. The student connects the circuit shown above and is going to replace one resistor with others of different resistance to increase the total resistance of the circuit. Which of the following will accomplish this? Select two answers. (A) Replacing resistor with resistors of greater resistance (B) Replacing resistor with resistors of greater resistance (C) Replacing resistor with resistors of smaller resistance (D) Replacing both resistors Page 6 of 15 AP Physics 2 and with resistors of smaller resistance Scoring Guide Unit 4 Progress Check: MCQ Part A 12. A student connects the circuit shown above and measures the potential difference across and current in the resistor. The student then adds one resistor at a time in series, recording the potential difference and current for the original resistor each time. Finally, the student calculates the power for each set of measurements and creates several graphs of the data. Which of the following graphs of power as a function of current gives the best prediction for what the student's data will show? AP Physics 2 Page 7 of 15 Scoring Guide Unit 4 Progress Check: MCQ Part A (A) (B) Page 8 of 15 AP Physics 2 Scoring Guide Unit 4 Progress Check: MCQ Part A (C) (D) AP Physics 2 Page 9 of 15 Scoring Guide Unit 4 Progress Check: MCQ Part A 13. The circuits shown above have the same physical arrangement, but one resistor and the capacitor have different values. The circuits have reached steady state. Which of the following correctly compares potential difference or current and gives a correct justification? Select two answers. (A) The potential difference across each capacitor is battery. (B) The potential difference across the resistor in circuit and the corresponding circuit are different because the resistances are different. (C) The current through the battery in circuit resistance of circuit is greater. is less than that of circuit (D) The current in the capacitor branch in circuit 14. because they are each connected across the resistor in because the equivalent is greater because the capacitance is less. A student is conducting an experiment to compare the resistivity of two unknown materials by using two wires, each made of one of the materials and each connected in a circuit. The student measures the potential difference across and current in the wires. Which of the following must be the same to be able to compare the resistivities using just the potential difference and current measurements? Select two answers. (A) The length of each wire (B) The cross-sectional area of each wire (C) The potential difference across each wire (D) The current in each wire Page 10 of 15 AP Physics 2 Scoring Guide Unit 4 Progress Check: MCQ Part A 15. Three identical resistors are connected to a battery, as shown above. Which of the following is a correct method for determining the potential difference across the resistor with resistance ? (A) Find the equivalent resistance of the circuit, . The current through the battery is . Finally, the potential difference across the resistor with resistance is . then Find the equivalent resistance of the parallel resistors, . The equivalent resistance of (B) the circuit is then . The current through the battery is then is . potential difference across the resistor with resistance 16. (C) Find the equivalent resistance of the circuit, resistor with resistance is then . (D) The potential difference across the resistor with resistance series. . Finally, the . The potential difference across the is equal to since the components are in A capacitor made of two parallel plates separated by air is charged using a battery. While the battery remains connected, the plates are moved farther apart. How does the magnitude of the final charge on each plate and the energy stored in the capacitor compare to those same quantities before the capacitor plates were moved? AP Physics 2 Page 11 of 15 Scoring Guide Unit 4 Progress Check: MCQ Part A Charge Energy Stored (A) Greater Charge Greater Energy Stored (B) Greater Charge The same Energy Stored (C) Less Charge The same Energy Stored (D) Less Page 12 of 15 AP Physics 2 Less Scoring Guide Unit 4 Progress Check: MCQ Part A 17. Four lightbulbs are connected in series to a battery, as shown above. The resistances of the lightbulbs and three currents are labeled. Which of the following is a correct expression of conservation of energy in the circuit? Select two answers. (A) (B) (C) (D) AP Physics 2 Page 13 of 15 Scoring Guide Unit 4 Progress Check: MCQ Part A 18. A student has various metal rods of known dimensions and wants to determine whether the rods are made of the same metal by determining their resistivities. The student plans to connect the circuit shown above, record the potential difference of the power source, and use the meters to measure the potential difference across the resistor and the current. Will the measurement allow the student to determine whether the rods have the same resistivity, and why or why not? (A) No, because the voltmeter is not measuring the potential difference across the rod. (B) No, because the rods must have the same dimensions to compare their resistivities. (C) Yes, because the power source can be set to any arbitrary potential difference. (D) Yes, because the potential difference across the rod can be calculated and used with the current to determine the resistance of the rod. 19. A student has two cylindrical resistors that are made of the same material. The student connects each resistor to a power supply and varies the potential difference across each resistor. The potential difference across the resistor and . The graphs above show the data for each resistor. the current through it are measured until the current reaches Which of the following single differences in the resistors could account for the data? Page 14 of 15 AP Physics 2 Scoring Guide Unit 4 Progress Check: MCQ Part A (A) The length of resistor is greater than the length of resistor . (B) The radius of resistor is greater than the radius of resistor . (C) The resistivity of resistor is greater than the resistivity of resistor . (D) No single difference can be determined because the range of current is the same in both cases. 20. A student has four identical resistors and needs the largest possible resistance for a branch of a circuit. How should the student arrange the resistors to get the largest possible effective resistance? (A) Connect all the resistors in series (B) Connect all the resistors in parallel (C) Connect two of the resistors in parallel and then connect the parallel pair in series with the other two resistors (D) Connect three of the resistors in parallel and then connect the parallel set in series with the remaining resistor AP Physics 2 Page 15 of 15