Managerial Economics reviewer
advertisement

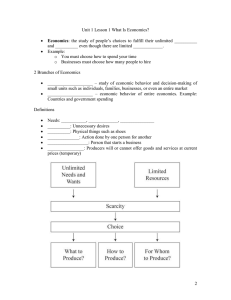
ECONOMICS VS. MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS ECONOMICS – is a science that deals with the activities of man in obtaining wealth for the satisfaction of human wants From the Latin word “oikonomous” where oiko means house/household and nomous means management. Economics is a household management ELEMENTS OF ECONOMIC ACTIVITIES 1) Human wants – insatiable desire of things, goods, and services. 2) Resources – things that are used to produce goods 3) Technology – technique of production ECONOMIC SYSTEM MODEL i. Father of Economics: Adam Smith WHY STUDY ECONOMICS? To study society Social Sciences: Studies human behaviour and interrelated discipline To study global affairs Economics: Studies human life ECONOMIC ACTIVITIES Is an interaction among economic units involved in: o Production o Distribution o Consumption o Exchange of goods and services Goods – Anything that satisfy human wants Services – Labor or work of expertise. Capitalism – factors of production and distribution is owned and managed by private individuals. Referred as, “Market Economy” FACTORS OF PRODUCTION 1) 2) 3) 4) Land – Labor – Capital – Entrepreneurship – CHARACTERISTICS OF CAPITALISM ii. iii. Private property Economic freedom Free competition Profit motive Communism – Command Economy Socialism – Mixed Economy o Major strategic industries owned by state/government o Minor industries owned by private individual/ sectors Managerial Economics Integration of economic theory with business practice for the purpose of facilitating decision-making and forward planning by management. Study of application of managerial skills in economics. It helps in anticipating, determining and resolving in problems. These problems may pertain to cost, prices or forecasting future market. It is a science dealing with effective use of scarce resources. It guides the managers in taking decisions relating to the firm’s customers, competitors, suppliers as well as relating to the internal functioning of firms. Managerial Decisions Applications of analytical tools (mathematical and statistical). Application of Economic concept, theories. DIFFERENCE ECONOMICS MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS Meaning Framing economic principle to solve economic problems Application of economic principles in solving economic problems Character Microeconomic and macroeconomic Microeconomic Main Task Fulfilment of the needs of individuals and entity Proper decision making Nature Positive and normative Normative Scope Wider Narrow Managerial Economics Applied branch of Economics Concerned with Theories from production, consumption and distribution Profit theory Analysis Involved Macro-level: growth, inflation and employment Micro-level: demand, supply and profit Economic aspects Economic and non-economic Based on certain assumptions Some assumptions become invalid when applied Branches Concentration Validity of Assumption ROLE OF MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS Studies business environment Production Scheduling Control Cost Set Prices Bring coordination Investment Analysis Factor of productions: Capital Resources Land Physiological needs: Food Clothing Shelter Barter Exchange of goods and services without using money