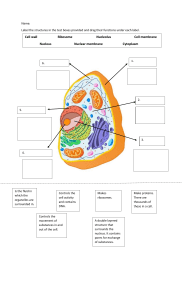
NUCLEUS Nucleolus it participants in the formation of signal recognition particles and play a role in the cell's response to stress Nuclear Envelope it surrounds the nucleus and encloses the genetic ,aterial that consisting two lipid bilayer membranes Nucleoplasm a type of protoplasm that makes up the cell nucleus Nuclear Pore double membrane surrounding the eukaryotic cell nucleus serve as a suspending substance for the organelles within a nucleus usually don't be with nuclear pores allowing large molecules LYSOSOME hydrolytiv enzyme mixture Hydrolytic enzymes the enzyme break down large molecules into small molecules lipid layer membrane Function : break down excess cell parts that contains digestive enzymes GOLGI APPARATUS Lumen Cisternae Incoming transport vesicle Cis face Outgoing transport vesicle Trans face 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. __________ __________ __________ __________ __________ __________ cisternae lumen incoming cis face trans face outgoing transport Function : modifies the proteins and transport to eventual transport CENTRIOLES Function : organizing microtubules that serves as the cell's skeletal system they help to determine the cocation of nucleus Why plant cells do not have centrioles? higher plants mitosis use nucleate microtubules instead of centriole 9 8 7 1. 2. 3 5 4 3. 1 2 4. DEFINITION 5. A collection of membranous structures involved in 6. transport within the cell. The main components of the 7. endomembrane system are __________, 8. __________ , __________ and __________ 9. and __________. endoplasmic reticulum golgi apparatues lysosomes vesicles The function of the endomembrane system includes: the system separates the cell into ________________________ ________________________ different compartments ________________________ ________________________ _______________________. near cell membrane presenting lipid forming cell - synthesis and store lipids - store proteins Anything else I should remember : in animal or plant cell ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________. __________ __________ __________ __________ __________ __________ __________ __________ __________ golgi apparatus lysosome secretory vesicle en doplasmic reticulum ribosomes nucleus pore nuclear envelope nucleus nucleus - ribosome - near cytoplasm ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM 6 - present in protein forming cell RIBOSOMES Function : RNA A ribosome is a ______ organelle. It functions proteins as a micro-machine for making ___________. Ribosomes Ribosomes were discovered by Robinson and Brown (1953) in plant cells and by Palade (1955) in animal cells. Function : membranebubbles found in cells. They Vacuoles are ______ animals and plant are found in both _____ _____ cells but are much larger in plant cells. Vacuoles might nutrient cell might store ____ food or any variety of _____a waste need to survive. They can even store _____ _____, products so the rest of the cell is protected from damage __________. VACUOLE In 1676, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, inventor of the microscope, discovered vacuoles. storage, animal, plant, food, nutrients, waste products, contamination single large vacuole permanent structure rarely comprise temporary structure storage store nutrient waste product mainly store water ATP synthase parficles granules mitochondria DNA cristae ribosome matrix inner membrane Word Bank outer membrane Cristae Inner Membrane inner membrane space Outer Membrane generate most of the chemical energy needed to power the cell's Mitochondrial DNA Function biochemical reactions Ribosome Matrix Maternal Mitochondria means Granule maintain the correct concentration of calcium ions Intermembrane space ATP Synthase DNA outer membrane Ribosome inner membrane Thylakoid Stroma Outer membrane Inner membrane Light reaction happen at thylakoid _____________. Dark reaction happen at outside the thylakoid _____________. DNA Ribosome Thylakoid Function : carry out a number of other functions stroma 3 4 8 2 13 1 7 5 PLASMA MEMBRANE 10 6 12 14 9 11 1 protein channel 2 globular protein 3 glycolipid carbonhydrate groups affached to protein 4 hydrophilic head contacting the fluad both inside and outside peripherial protein attached either to integral protein 5 6 7 8 9 filaments of cytoskelenton transport protein enzymes, transport molecules give the cell its shape and organize cell's part integral protein integrated into the membrane carbonhydrate allowing immanecells to differentate between cells cholesterol help to minimize the effectst temperature of fluidiby The cell membrane was discovered by Swiss botanist Carl Naegeli and C. Cramer in 1855. 3 4 8 2 13 1 7 5 PLASMA MEMBRANE 10 6 12 14 9 11 10 11 12 surface protein stick partcuy into membrane hydrophobic tails easily interact with other nonpalav molecule alpha-helic protein allows ions or other small molecules to pass 13 glycoprotein 14 phosholipid mdecule present on outer surface make up the basic fabric of plasnes membrane Function of the membrane : it protects and organize cells Why call it phospholipid bilayer?: it formed by these interactions makes a good barrier between the interior or exterior of the cell animal cells in living cells make up of lipid protective cover Dear Educators, At EduZvezda, we are proud to offer a platform to educators across the world to connect, collaborate, inspire and support all educators. Harvey’s Biology is EduZvezda’s first initiative, with a range of visually attractive worksheets which wil help learners remember key words and facts, giving them the foundation to deep dive into the wonders of Biology. Worksheets are suitable for the following curriculums: IGCSE, IB, GCSE Copyright Notice © 2020 EduZveda All rights reserved. All copies (including electronic) of this document shall include this copyright notice. You may not, except with the express permission of EduZvezda, commercial y exploit the content.