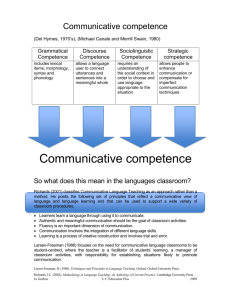
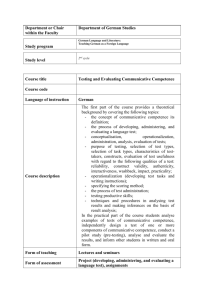
Lesson Types Traditionally lesson is viewed as a unit of teaching knowledge, forming skills and habits, and controlling results. According to this traditional organizational framework three big lesson types can be distinguished. The first type aims at habit formation, where some new language material is introduced, presented and trained. For example, new vocabulary presentation lessons where lexical (receptive/productive) habit formation is in focus; new grammar presentation lessons where grammatical (receptive/productive) habit formation is in focus. The second type aims at skills development where speech practice prevails. For example, lessons of speaking and listening development; speaking and reading; reading and writing; integrated lessons and so on. The third type is a mixed type of lesson, which is very usual in ELT. These lessons contain both habit formation and skills development activities. They aim at practicing language and speech skills. However, new tendencies in instruction organization have proved the effectiveness of the model of teaching which deepens the best sides of the model mentioned above and is known as interactive one. Interaction is understood, according to Douglas H. Brown, as the collaborative exchange of thoughts, feelings or ideas between two or more people resulting in reciprocal effect on each other. Cooperative character of this kind of teaching is evident, which in its turn seems the most effective in acquisition of communicative competence nowadays. We are sure that interactive teaching needs special lesson organization where communication is a must to meet the innovative character of the model of teaching. Thus, a modern concept of lesson, which draws teacher’s attention to learners, to their fruitful interaction, can best serve the purpose of interactive model of teaching and effective acquisition of communicative competence. The concept views lesson as a unit of organized cognitive activity of learners and subscribes to the ideas of learner-based teaching. The lesson type within the view depends on what components of communicative competence are chosen as the objective: linguistic, pragmatic, cognitive or informative. A mixed type of lesson is a balanced teaching unit, in which all components of teaching communicative competence are present. Linguistic component depends on linguistic exercises. Their aim is to create in learners the idea of the language and the semi-skills of language use. The formation of the pragmatic (practical) component of the communicative competence depends on the interactive exercises in using speech functions. Elementary role play is an example. Cognitive component of the communicative competence is formed with the help of the cognitive (thought-activating) exercises like interpreting, sequencing, choosing, classifying, identifying, imagining, digesting, critical thinking, deducing, summarizing, and others. Information exercises create background knowledge and include casestudying, project-writing, surveying, etc. Task 1 Use the information from the text to complete the network. Lesson Types 1 2 3 Add some more information to describe each lesson type.