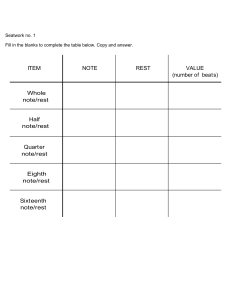
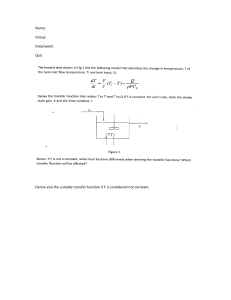
COURSE CODE : CE 33 COURSE TITLE : THEORY OF DETERMINATE STRUCTURES PRE-REQUISITE(S): CREDIT UNITS MATH 21 INTEGRAL CALCULUS ES 23 ENGINEERING MECHANICS I: STATICS : 4 UNITS (Lecture–3 units/Seatwork–1 unit) Number of Contact Hours per Week: Lecture–3hours/Seatwork=3 hours COURSE DESCRIPTION: The course covers the different types of structural systems, loads and its combinations and placement, applicable codes and specifications, and methods of analysis for statically determinate structures. LEARNING OUTCOMES (LO): (Description of knowledge and skills the students are expected to demonstrate. On completion of the subject, the student is expected to be able/will be able to do the following: SU-IGO PROGRAM OUTCOMES PO-A: Apply knowledge of mathematics and science to solve complex engineering problems Creative and Critical Thinking PO-B: Design and conduct experiment as well as to analyze and interpret data. PO-C: Design a system or process to meet desired needs within realistic constraints in accordance with standards; PO-E: Identify, formulate, and solve complex civil engineering problems. LEARNING OUTCOMES (LO) LO1: 1.Know the history of structural engineering, identify various types of structural systems, appreciate the importance of codes and specifications and decide the appropriate loads to apply into the structures; LO2: Idealize real structures to obtain analytical models; identify the state of determinacy and stability of structures; to know the various structural analysis theorems and principles; LO3: Apply the equations of static equilibrium to analyze the trusses, beams, frames, cables and arches; LO4: Develop intuition on deflected shapes of structures under loading; LO5: Analyze moving loads on highway and railway bridges using influence lines; Transformative Christian Witness PO-D: Function in multi-disciplinary and multi-cultural teams. PO-F: Understand professional and ethical responsibility; PO-H: Understand the impact of civil engineering solutions in a global, economic, environmental and social context; Effective Communicator PO-G: Communicate effectively civil engineering activities with the engineering community and with society at large PO-J: Know contemporary issues. LO6: Reflect on the consequences of analysis results to life and safety of people; LO7: Develop ethnical responsibility to their clients to produce strong and safe structures. LO8. Share /discuss their solutions of their seatworks /boardworks and other issues with their classmates using English language.- horizontal learning. PO-I: Recognize the need for, and engage in life-long learning; Independent, Reflective Life – Long Learner PO-K : Use techniques, skills and modern engineering tools necessary for civil engineering practice; LO9: Develop confidence in structural analysis in preparation for design courses; PO-L : Know and understand engineering and management principle as member and leader of a team, and to manage projects in multidisciplinary environment; PO-M : Understand at least one specialized field of civil engineering practice. STUDENT COURSE OUTPUTS: As evidence of attaining the above learning outcomes, the student is required to do and submit the following during the indicated date of term. LEARNING OUTCOME LO1 – LO8 REQUIRED OUTPUT Problem Sets (Plates) DUE DATE See Learning Plan Schedule Plates are composed of problem sets which are the supplementary activities for the students to apply the theory, principles and tools of determinate structures in various problems. To help the students appreciate the relevance of the analysis of determinate structures in real world problems. Some problems may represent ideal real structures. Collaborative work in plates is not discouraged but each student should complete the plates individually. Plates of each topic must be submitted before its respective Long Quiz. Plate No. 1 (LO1-LO2) Determinacy and Stability/Application of the Equation of equilibrium Plate No. 2 (LO3) Analysis of Trusses Plate No. 3 (LO3) Shear and Moment Functions & Diagrams: Beams & Frames Plate No. 4( LO4) Cables and Arches Plate No. 5 (LO5) Influence Lines Plate No. 6 (LO3-LO4)Approximate Method: Trusses, Beams & Frames RUBRICS FOR ASSESSMENT OF THE PROBLEM SETS (for projects, presentations or assessments other than exams): CRITERIA ANALYSIS & APPLICATION OF THEORY (60%) COMPUTATION AND PROCEDURE ( 40%) EXCELLENT 4 The problem is analyzed correctly and the theory and principles used are correct. (50-60 points) SATISFACTORY 3 The problem is analyzed correctly but some theory and principles used are not correct. (40-50 pts) DEVELOPING 2 The problem is analyzed incorrectly but some theory and principles used are correct. (30-40pts) BEGINNING 1 The problem is analyzed incorrectly and the theory and principles used are incorrect. (0-30 pts) The procedure is correct & numerical values are computed accurately with correct units (30-40pts) The procedure is correct with minor numerical errors. Some values are computed with incorrect units Major mistakes in the procedure and computation. Some values with incorrect units. (10-20 pts) Incorrect procedure. Basic computations incorrect. Incorrect units. (0-10 pts) (20-30%) TOTAL: OTHER REQUIREMENTS AND ASSESSMENTS: (proficiency examinations, seatworks, etc). LEARNING OUTCOME ASSESSMENT DUE DATE LO1 –LO2 Seatwork No. 1 Long Quiz No.1 3rd week LO3 Seatwork No. 2 Long Quiz No.2 Seatwork No. 3 Long Quiz No.3 Midterm Exam 6th week Seatwork No. 4 Long Quiz No.4 10th week LO3 LO3 8th week RATING LO4 Seatwork No. 5 Long Quiz No.5 12th week LO3 Seatwork No. 6 Long Quiz No.6 15th week GRADING SYSTEM: (Components of the final grade consisting the above-mentioned assessment and their corresponding weights or percentages). Quiz Average 35% Midterm Exam 20% Final Exam 30% Assignment, seat work, board work, etc. 5% Project 10% Total: 100% TEACHING METHODS/STRATEGIES: LEARNING PLAN: (Course contents to be covered). LEARNING OUTCOME LO1 LO2 TOPIC 1.Introduction to Structural Engineering 1.1 History of Structural Engineering Analysis and design of process; 1.2 Classification of structures 1.3 Loading conditions and building Materials 2.Analysis of Statically determinate Structures Idealized Structure Equations of Structure Determinacy and Stability Application of the Equation of equilibrium RESOU R-CES LEARNING ACTIVITIES WEE K NO. 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 2.1 2.3 2.4 2.5 lecture lcd presentation seatworks 1-2 lecture lcd presentation groupwork (seatworks and discussion) and then presentation 3-4 Seatwork1/Exam1 LO3 3.Analysis of Statically Determinate Trusses 3.1 Common type of Trusses 3.2 Classification of Coplanar Trusses 3.3 Method of joints 3.4 Zero Force Members 3.5 Method of Sections 3.6 Compound Trusses 3.7 Complex Trusses 3.8 Space Trusses 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 lecture lcd presentation groupwork (seatworks and discussion) and then presentation 4-5 Seatwork2/Exam2 LO4 4.Internal Loadings developed in Structural Members 4.1 Internal Loading at a specified point 4.2 Shear and Moment functions 4.3 Shear and Moment Diagrams for Beams 4.4 Shear and Moment Diagrams for Frames 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 lecture lcd presentation groupwork (seatworks and discussion) and then presentation 5-7 Seatwork3/Exam3 Midterm Exam Chapter 1-4 LO3 5.Cables & Arches 5.1 Cables 5.1.1 Cables subjected to concentrated Load 5.1.2 Cables Subjected to Uniformly Distributed Load 5.2 Arches 5.2.1 Three-hinged Arch 5.1 5.2 5.3 lecture lcd presentation 5.4 5.5 groupwork (seatworks and discussion) and then presentation 7-9 Seatwork4/Exam4 LO5 LO3 6. Influence Lines for statically Determinate Structures 6.1 Influence Lines 6.2 Influence lines for Beams 6.3 Qualitative Influence Lines 6.4 Influence Lines for Girders 6.5 Influence Lines for Trusses 6.6 Maximum Influence Due to a Series of concentrated Loads 6.7 Absolute Maximum Shear and Moment 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 lecture lcd presentation Seatwork5/Exam5 7. Analysis of statically indeterminate structures by Approximate method 7.1 7. lecture lcd presentation Seatwork6/Exam6 Final Exam :Chapter 1-7 groupwork (seatworks and discussion) and then presentation groupwork (seatworks and discussion) and then presentation REFERENCES:(List of books and other references in APA style). 10-12 13--15 Textbooks 1. Structural Analysis, 8th Ed, Prentice Hall 2012., N.J. By: HibbEler, R. C. 2. National Structural Code of the Philippines,7th ed.Association of Structural Engineers of the Philippines, Manila 2015 by Association of Structural Engineers of the Philippines. References: 1. Structural Analysis, 5th Ed, Prentice Hall 2003., N.J. By: Hibbeler, R. C. 2. Elementary Structural Analysis, 4th ed.McGraw-Hill Inc. N.Y. 1991 by Utku, Senol, Norris C.H. and Wilbur, J.B. 3. The National Building Code of the Philippines and its Implementing Rules and Regulations, Philippine Law Gazette, Manila, 2000 by Foz, V.B. ed 4. Introduction to Engineering Analysis, Prentice Hall, New Jersey, 2001 by Hagen, K.D. 5. Introduction to Structural Analysis and Design, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York, 2001 by Rajan, S.D. 6. Structural Analysis, A Unified Classical and Matrix Approach, 4th ed. E&FN Spon, London 1997 by Gahli, A. And Neville A.M. 7. Theory of Structures, Vol. 11, Tata McGraw-Hill PublishingCo. Ltd., New Delhi, 1999 by Gupta, S.P., Pandit, G.S., and Gupta, R. 8. Structural Concepts and Systems for Architects and Engineers, 1981 by Lin, T.Y. and Stotesbury, S.D. 9. Structural Analysis, 2nd Ed, Brooks/Cole Publishing Company, 1999 by Kassimali, A. 10 Structural Analysis, A Classical and Matrix Approach,_1997 by McCormac, J.C. and Nelson J.C. 11 Fundamentals of Structural Analysis,_1993,_John Wiley by West, H. ONLINE RESOURCES: (List of websites and electronic media resources where the course content can also be found).