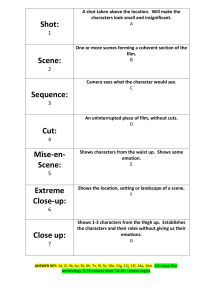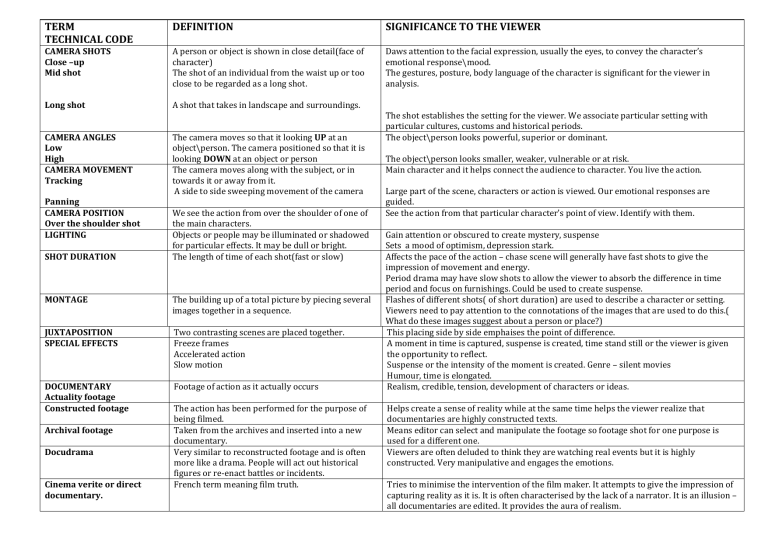
TERM TECHNICAL CODE DEFINITION SIGNIFICANCE TO THE VIEWER CAMERA SHOTS Close –up Mid shot A person or object is shown in close detail(face of character) The shot of an individual from the waist up or too close to be regarded as a long shot. Daws attention to the facial expression, usually the eyes, to convey the character’s emotional response\mood. The gestures, posture, body language of the character is significant for the viewer in analysis. Long shot A shot that takes in landscape and surroundings. CAMERA ANGLES Low High CAMERA MOVEMENT Tracking The camera moves so that it looking UP at an object\person. The camera positioned so that it is looking DOWN at an object or person The camera moves along with the subject, or in towards it or away from it. A side to side sweeping movement of the camera Panning CAMERA POSITION Over the shoulder shot LIGHTING SHOT DURATION We see the action from over the shoulder of one of the main characters. Objects or people may be illuminated or shadowed for particular effects. It may be dull or bright. The length of time of each shot(fast or slow) MONTAGE The building up of a total picture by piecing several images together in a sequence. JUXTAPOSITION SPECIAL EFFECTS Two contrasting scenes are placed together. Freeze frames Accelerated action Slow motion DOCUMENTARY Actuality footage Constructed footage Footage of action as it actually occurs Archival footage Docudrama Cinema verite or direct documentary. The action has been performed for the purpose of being filmed. Taken from the archives and inserted into a new documentary. Very similar to reconstructed footage and is often more like a drama. People will act out historical figures or re-enact battles or incidents. French term meaning film truth. The shot establishes the setting for the viewer. We associate particular setting with particular cultures, customs and historical periods. The object\person looks powerful, superior or dominant. The object\person looks smaller, weaker, vulnerable or at risk. Main character and it helps connect the audience to character. You live the action. Large part of the scene, characters or action is viewed. Our emotional responses are guided. See the action from that particular character’s point of view. Identify with them. Gain attention or obscured to create mystery, suspense Sets a mood of optimism, depression stark. Affects the pace of the action – chase scene will generally have fast shots to give the impression of movement and energy. Period drama may have slow shots to allow the viewer to absorb the difference in time period and focus on furnishings. Could be used to create suspense. Flashes of different shots( of short duration) are used to describe a character or setting. Viewers need to pay attention to the connotations of the images that are used to do this.( What do these images suggest about a person or place?) This placing side by side emphaises the point of difference. A moment in time is captured, suspense is created, time stand still or the viewer is given the opportunity to reflect. Suspense or the intensity of the moment is created. Genre – silent movies Humour, time is elongated. Realism, credible, tension, development of characters or ideas. Helps create a sense of reality while at the same time helps the viewer realize that documentaries are highly constructed texts. Means editor can select and manipulate the footage so footage shot for one purpose is used for a different one. Viewers are often deluded to think they are watching real events but it is highly constructed. Very manipulative and engages the emotions. Tries to minimise the intervention of the film maker. It attempts to give the impression of capturing reality as it is. It is often characterised by the lack of a narrator. It is an illusion – all documentaries are edited. It provides the aura of realism.