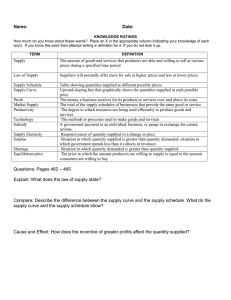
CHAPTER 5- SUPPLY Please answer the questions as you read. For any True-False questions (T/F)…if it is FALSE, make sure to replace what is underlined with the word/phrase that would make it a true statement. Section 1- What is Supply? (pages 128-135) 1. Define SUPPLY. The amount of a product offered for sale at all possible prices in the market 2. What is the LAW OF SUPPLY? Principle that more will be offered for higher prices than at lower prices… 3. What is a SUPPLY SCHEDULE? a table that shows the quantity supplied at different prices in the market; is a listing of the various quantities of a particular product supplied at all possible prices in the market 4. What is the variable/factor that gives producers incentive to produce more of their product? The goal is to make a profit so increased prices would give incentive for making more of the product 5. What is the SUPPLY CURVE? What “type” of slope do most supply curves have ( + or -)? Why? A supply curve is graph showing the various quantities supplied at all possible prices that might prevail in the market at any given time. All normal supply curves have a positive slope that goes up from the lower left-hand corner of the graph to the upper right-hand corner. This shows that if the price goes up, the quantity supplied will go up too. 6. How are we (humans…you, me, etc.) “suppliers”? Explain. We can be considered suppliers if we create something or add something to the world and/or other people’s lives, for example through services or producing goods. 7. What is a MARKET SUPPLY CURVE? the supply curve that shows the quantities offered at various prices by all firms that offer the product for sale in a given market 8. Define QUANTITY SUPPLIED. is the amount that producers bring to market at any given price. The amount of a good or service offered for sale at a specific price. Represented by a point on the supply curve. The higher the price; the larger the quantity produced 9. What is a CHANGE IN QUANTITY SUPPLIED? What is the main variable that causes the change? the change in amount offered for sale in response to a change in price 10. How do world oil prices impact the “supply” of oil? 11. How is a CHANGE IN SUPPLY different than a change in quantity supplied? A change in supply is a situation where suppliers offer different amounts of products for sale at all possible prices in the market. quantity changes even though the price remains the same Please read the “Global Economy and You”…what are some thing that are beyond our control that can influence the supply (and therefore the price) of coffee???? 12. When there is an overall increase in supply, the supply curve shifts to the _right_; if there is an overall decrease in the supply of something, the supply curve shifts to the _left_. The questions that follow deal with factors that will change overall supply (increases or decreases). If you see questions with blanks, the answer will be (increase or decrease; up or down, etc.). 13. If the cost of resources goes up, supply will _increase_; if the cost of resources drops, supply will _decrease_. 14. If a company’s productivity improves, supply will _increase_; if a company’s productivity decreases, supply will _decrease_. 15. Normally, the adoption of new technology will _decrease_ the cost of production and will therefore _increase_ supply. 16. Businesses almost always want taxes to _decrease_. 17. If business taxes are increased, overall supply is likely to _decrease_; if business taxes are decreased, overall supply is likely to _increase_. 18. What is a SUBSIDY? List some examples of people that get subsidies. A subsidy is a government payment to an individual, business, or other group to encourage or protect a certain type of economic activity 19. If subsidies to farmers increase, overall supply is likely to _increase_; if certain subsidies are repealed (or removed), overall supply is likely to _decrease_. 20. What is a regulation (not in the book, but you should know it)? ______________ a rule or directive made and maintained by an authority. 21. If there is a decrease in government regulations, overall costs go _down_, so supply will _up_. 22. If there is an increase in government regulations, overall costs go _up_, so supply will _down_. 23. What are some regulations/requirements that the government has implemented in the auto industry that have also resulted in increased production costs? 24. If an industry is shrinking, and businesses are closing, what happens to supply? _decreases_ 25. If an industry is growing, and businesses are opening, what happens to supply? _increases_ 26. What is SUPPLY ELASTICITY? is a measure of the way in which the quantity supplied responds to a change in price 27. I know you did this for demand, but please describe the following types of elasticity (this time with respect to SUPPLY). ELASTIC- large change in quantity supplied due to a change in price INELASTIC- small change in quantity supplied due to a change in price UNIT ELASTIC- proportional change in quantity supplied due to a change in price 28. If a company is able to quickly adjust to a new price change, is supply MORE or LESS elastic. (circle one) 29. Is nuclear power elastic or inelastic? Inelastic 30. For things that can be made easily and quickly (like candy, toys, etc.), are they more ELASTIC or INELASTIC when it comes to supply? Elastic 31. When it came to elasticity of demand, there were several things to consider. When it comes to elasticity of supply, what does a product’s elasticity depend on? Resources