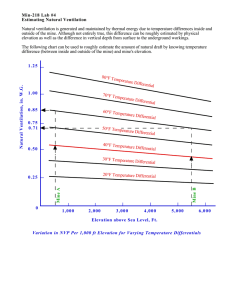
VENTILATION SYSTEM EM 165: Mine Ventilation MSU-IIT COE VENTILATION SYSTEM Every UG mine is unique Classification: Mine systems District systems Auxiliary ventilation systems VENTILATION SYSTEM: MINE SYSTEM Fresh air enters via downcast shafts or other surface connections. Air flows along intake airways to working areas where most pollutants are added. Contaminated air returns back through the system along return airways. The return air passes back up to the surface via upcast shafts or other surface return connections. VENTILATION SYSTEM: MINE SYSTEM Passive Device Area of Less Resistance Air Airflow Control Device Active Device Area of High Resistance Area usually needs ventilation VENTILATION SYSTEM: MINE SYSTEM Active Devices: adds energy to air to direct it to where it is needed Main Fan: primary means of producing and controlling the ventilation airflow; usually located near the surface Types of main fan systems: VENTILATION SYSTEM: MINE SYSTEM Active Devices: Main Fan Exhausting vs. Forcing Fan System Gas control (control during falls of barometer and fan stoppage favors exhausting) Transportation (selection depends on whether transporting mineral through intake or return airways) Fan maintenance (exhaust fan subjected to air carrying dust, warmer air, and water droplets, thus the combined effects of impaction and corrosion are greater than in forcing case) Fan performance (cooler air implies lower mass flow duty for a forcing fan and hence for a certain airflow, a reduced pressure and running costs). However, this effect is usually not great. VENTILATION SYSTEM: MINE SYSTEM Active Devices: Main Fan Push-Pull Fan System For metalliferous mine employing caving technique Employed in multi-shaft mines for better distribution of airflow, greater flexibility, better control over pressure and leakage, reduced operating cost. VENTILATION SYSTEM: MINE SYSTEM Active Devices: Main Fan Advantages: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Simpler Installation Simpler Testing Simpler Maintenance Easier Access Better Protection in Emergency Situation VENTILATION SYSTEM: MINE SYSTEM Active Devices: Main Fan VENTILATION SYSTEM: MINE SYSTEM Active Devices Booster Fan: employed when air flows through a ventilation network loses energy. Advantages: No need to upgrade existing main fan facilities, avoiding capital and operating cost increases; and Only a proportion of the whole mine airflow is boosted, saving operational costs compared to having to boost the whole mine airflow. VENTILATION SYSTEM: MINE SYSTEM Passive Devices: add resistance to flow routes to encourage the air to flow along other routes VENTILATION SYSTEM: MINE SYSTEM Passive Devices: add resistance to flow routes to encourage the air to flow along other routes VENTILATION SYSTEM: MINE SYSTEM Passive Devices: add resistance to flow routes to encourage the air to flow along other routes Air Doors and Airlocks: employed to minimize shortcircuiting of ventilation flow by increasing resistance of a potential shortcircuit route VENTILATION SYSTEM: MINE SYSTEM Passive Devices: add resistance to flow routes to encourage the air to flow along other routes Regulators: an air door fitted with an adjustable orifice for reduction of airflow in a particular section downstream to a defined airflow by increasing the resistance of the airway VENTILATION SYSTEM: MINE SYSTEM Passive Devices: Regulators VENTILATION SYSTEM: MINE SYSTEM Passive Devices: add resistance to flow routes to encourage the air to flow along other routes Air crossing: installed where intake and return airways need to cross over each other Forms: Natural Intersection Prefabricated VENTILATION SYSTEM: MINE SYSTEM Passive Devices: Air crossing Types: Overcast: roof is ripped over one of the galleries, two chambers constructed and one of the air currents, usually the return is made to go via top chamber. Undercast: the floor-dug up to make the two chamber, and one of the air currents, usually the return, is made to flow through the lower chamber. VENTILATION SYSTEM: MINE SYSTEM Passive Devices: Stoppings: blockage placed between intake and return airways which was previously used to provide quick access but no longer required Seals: constructed to prevent unwanted air loss from a ventilation system and to preclude oxygen from entering mined-out areas to prevent spontaneous combustion