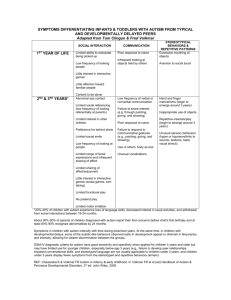
GILLIAMAUTISMRATINGSCALE• THIRDEDITION(GARS-3) The GARS-3 is a norm-referenced screening instrument that is designed to identify individual's ages 3 through 22 years of age who have severe behavioral problems that may be indicative of autism. The GARS-3 is divided into six subscales that describe specific, observable, and measurable behaviors. These behaviors are related to the Autism Society's (2012) definition of autism spectrum disorder and based on the diagnostic criteria for autistic disorder published in the DSM-5. Two Autism Indexes may be computed: Autism Index 6 based on all six subscales, or Autism Index 4 based on four subscales. The resulting Autism Index is a standard score with a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 15. The higher the Autism Index score, the greater is the probability that the person has autism spectrum disorder and the more severe the autistic behaviors. GARS-3 Subscales Parent %ile Ranks Scaled Scores Teacher %ile Ranks Scaled Scores Restricted/Repetitive Behaviors Social Interaction Social Communication Emotional Responses Cognitive Style Maladaptive Speech AUTISMINDEX (4 SCORES) AUTISMINDEX (6 SCORES) For children who are nonverbal or whose communication skills are severely impaired, the four-subscale composite 1s used. On the GARS-3, the larger the scaled score, the more severe the autistic behavior it represents. Results of ratings from 's teacher reveal notably elevated scaled scores in the subscale areas of . Restricted/Repetitive Behaviors may include stereotyped behaviors, or fixated interests, routines, or rituals. Social Interactions refer to social behavior such as showing little or no interest in others people, not initiating conversations with others, and showing minimal expressed pleasure with peers or others. Cognitive Style measures idiosyncratic fixated interests, characteristics and cognitive abilities. The Maladaptive Speech subscale consists of items that describe deficits and idiosyncrasies in verbal communication. Teacher ratings reveal that is demonstrating behaviors associated with the Autism Spectrum Disorder at levels in the school setting, and that these behaviors are limiting academic and social interactions. Results include an Autism Index standard score of For Stereotyped Behaviors the parents indicated that is frequently observed whirls, turns in circles, making rapid lunging, and darting movement when moving from place to place, he/she makes high-pitched sounds or other vocalizations for self-stimulation, and slaps, hits, or bites self or attempts to injure self in other ways. The parent reports that he/she is sometimes observed spinning objects not designed for spinning. The teacher does not report any stereotyped behaviors in the sometimes to frequently observed range, but did note that at times she notices him/her avoids establishing eye contact, looks away when eye contact is made, rocks back and forth while seated or standing, and makes rapid lunging, darting movements when moving from place to place. For Communication Behaviors the parents indicated that Student is sometimes observed repeating words or phrases over and over, uses pronouns inappropriately, repeats unintelligible sounds over and over; and inappropriately answers questions about a statement or brief story. The teacher did not report any communication behaviors in the sometimes to frequently observed range. For Social Interaction Behaviors the parent indicated that Student is frequently observed becoming upset when routines are changed. The reported that Student is sometimes observed avoiding eye contact; looks away when someone looks at him/her; does not imitate other people when imitation is required or desirable, such as in games or learning activities; withdraws, remains aloof, or acts standoffish in group situations; laughs, giggles, cries inappropriately; and responds negatively or with temper tantrums when given commands, requests, or directions. The teacher did not report any social interaction behaviors in the sometimes to frequently observed range. The parent did indicate that Student did reach out or prepare to be picked up when the parent attempted to lift the child; didn't use single words by 16 months of age; didn't use meaningful, communicative phrases by age 2; didn't develop normally in terms of language (i.e.: cooing, babbling, and speaking without any interruption or regression); and didn't follow directions. The following observations of abnormal functioning during the first three years of life were reported by the parent didn't cry when approached by unfamiliar persons during the first year, didn't engaged in imitative play before age 3, didn't indicate (show facial concern) when a parent or sibling cried or was distressed, didn't pretend he/she was someone else, didn't pretend that he/she had an imaginary friend or animal, and didn't play with dolls pretending that they were real persons • Restricted/Repetitive Behaviors may include stereotyped behaviors, or fixated interests, routines, or rituals. o Stares at hands, objects, or items in the environment for at least 5 seconds. o Flicks fingers rapidly in front of eyes for periods of 5 seconds or more o Does certain things repetitively, ritualistically o Engages in stereotyped behaviors when playing with toys or objects o Shows unusual interest in sensory aspects of play materials, body parts or objects. • Social Interactions refer to social behavior such as showing little or no interest in others people, not initiating conversations with others, and showing minimal expressed pleasure with peers or others. o Does not initiate conversations with peers or others o Shows minimal expressed pleasure when interacting with others o Doesn't' try to make friends with other people o Shows little or no interest in other people • Social Communication measures the individual's responses to social situations and understanding of the intent of social interaction and communication. o Has difficulty understanding jokes o Has difficulty understanding when someone is teasing o Fails to predict probable consequences in social events o Doesn't' seem to understand that the other person doesn't know something • Emotional Responses measures extreme emotional responses to everyday situations. o Needs an excessive amount of reassurance if things are changed or go wrong o Becomes upset when routines are changed o Has an extreme reaction (e.g. cries, screams, tantrums) in response to loud, unexpected noise. • Cognitive Style measures idiosyncratic fixated interests, characteristics and cognitive abilities. o Uses exceptionally precise speech o Talks about a single subject excessively o Shows an intense, obsessive interest in specific intellectual subjects. • The Maladaptive Speech subscale consists of items that describe deficits and idiosyncrasies in verbal communication. o Repeats (echoes) words or phrases verbally or with signs o Speaks (or signs) with flat tone, affect o Utters idiosyncratic words or phrases that have no meaning to others Based on the GARS-3 the teacher and parent scores were inconsistent and the probability that these behaviors are characteristics of Autism is . Additional assessment instruments, interviews, and observations need to be used to determine if displays characteristics that are related autism spectrum disorder. However does display some behaviors that may need additional follow-up. It is important to clarify that this is not a medical diagnosis, but rather assessment to determine if qualifies to receive special education services.