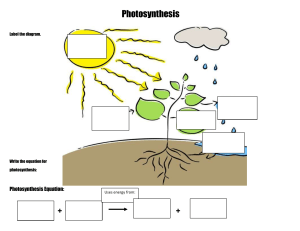
AP Biology Photosynthesis Lab Report Photosynthesis Introduction: Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Photosynthesis is important for both plant and animal’s lives. Photosynthesis provides the source of energy that drives all their metabolic functions and the oxygen required for respiration. The most important function of photosynthesis is to convert solar energy into chemical energy and then store that chemical energy for future use. For the most part, the planet's living systems are powered by this process. Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to see how does CO2 affect the rate of photosynthesis in a spinach leaf and when there are changes in the variables. The buoyancy of the leaf disk is actually an indirect measurement of the net rate of photosynthesis occurring in the leaf tissue. Spongy mesophyll layer of leaves are normally infused with gases, such as oxygen and carbon dioxide, which cause leaves to normally float in water. Hypothesis: If the spinach leaf is placed in the CO2 solution, the rate of photosynthesis will increase because photosynthesis depends on gas exchange, specifically CO2. Therefore, when the spinach leaf is placed in the CO2 solution, the rate of photosynthesis will increase due to gas diffusion. Data: Regular Spinach Lettuce (second trial) Time CO2 H2O Time CO2 H2O 1 2 0 1 0 0 2 5 0 2 0 0 3 6 0 3 0 0 4 8 0 4 0 0 5 9 0 5 0 0 6 9 0 6 0 0 7 10 0 7 0 0 8 10 0 8 0 0 9 10 0 9 0 0 10 10 0 10 0 0 20 Class data of regular spinach disk over time: 0 0 Soda amount 1 tb 1tb 1 tb 1 tb 1 tb 1 tb 1 tb 1 tb 1 tb 1 tb 1 tb 1 tb 1 tb 1 tb Time X mins H2O CO2 H2O CO2 H2 O CO2 H2O CO2 H2 O CO2 H2 O CO2 H2O CO2 Ave H2O Ave CO2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 5 0 0 0 0 0 3 0 0 0 9 1 1 3 6 0.57 2.71 10 0 1 0 0 0 7 0 0 0 10 1 1 3 10 0.57 4.14 15 0 7 0 0 0 7 1 1 0 10 3 6 4 10 1.14 5.85 20 0 10 0 0 0 7 1 4 0 10 5 9 4 10 1.42 7.14 Evidence: We stated earlier in the hypothesis that the solution with the greatest amount of baking soda would speed up the rate of photosynthesis. This is proved when the first cup , which had one spoon of baking soda, had its 9 leaf disks rise by only 5 minutes. And also all the 10 leafs disk rise within the 20 minutes. This happened because baking soda, or sodium bicarbonate, provides the solution with CO2. This carbon dioxide is one of he key factors in determining the rate of photosynthesis. CO2 is what begins the light reactions along with the solar energy provided by the light source. Therefore, because is contained the greatest amount of baking soda, it had the greatest amount of carbon dioxide. This made the rate of photosynthesis much greater than the cups containing less. However, if we were to continue the experiment with greater amounts of baking soda, it would level off. It may end up with more CO2 than other reactants. And if we were to graph out these results, the graph would level off, much like enzymes when it has an excess of substrate. On our graph you can see how the higher the number of the cup, the greater rate of photosynthesis is. But as we changed a variable ( spinach to lettuce) our results changed. Even in the cup with CO2 the leafs didn’t disk rise at all. Here were can say that different factors like changing the variables can also affect the rate of photosynthesynthesis. In this experiment time, amount of light and amount soda are the independent variables but the number of leafs disk rising is our dependent variable. Critique: In this experience source of error could be in many ways. The major mistake that could possibly be very common is not having similar light for both cups with the leafs inside. Maybe the light moved or the cup moved. Or another error within the experiment could be releasing all the oxygen within the syringe that is filled with the spinach discs and soap solution. Another possibility is that maybe the soda measurement wasn’t exact. So the whole data is based on false measurements. CER ( conclusion) We can conclude from the graph, that our hypothesis was correct. Our hypothesis stated that the cup with the greatest amount of baking soda would speed up the rate of photosynthesis. This data is taken over an interval of 20 minutes. Our data shows that Cup 2, didn't have any leaf disks rise in the 20 minutes that we observed. Cup 1 that had soda in it had all leaf disk rise at 10 minutes. In our second trial both our solution with and withour soda didn’t float at all. This could be because of the variable that was changed. Since there is not CO2 is water so the photosynthesis can’t happen. The graph and data table are set up accordingly and clearly support our hypothesis and claim. The only variable changed was the type of leaf in our experiment. Other variables that were kept constant were the temperature, amount of water, lighting, time, amount of soap, and number of leaf disks. We can also conclude from this lab that If light affects the rate of photosynthesis, then the more light there is, there will be a greater rate of photosynthesis.