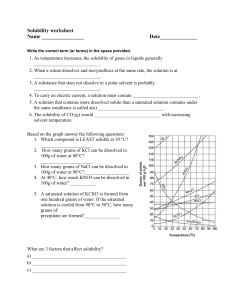
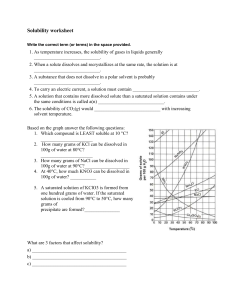
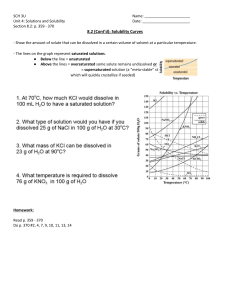
AKS 5a - Develop a model to illustrate the process of dissolving in terms of solvation versus dissociation (covalent vs. ionic). 1. What is the relationship between solutes and solvents? A solute is the substance that is being dissolved into the solvent 2. For the following - identify which is the solute and which is the solvent: a. MgCl2 and water b. water and CO2 In both situations water is the solvent. 3. What is the difference between dissociation and solvation? Dissociation is the breakdown of a substance into atoms or ions, and solvation is the interaction of solvent with dissolved molecules. 4. Describe how an ionic salt, such as KBr, goes into solution. This would be dissociate due to the ionic crystals, and they would separate from the other ions and the ions would be surrounded by the water molecules. 5. Describe how a covalent compound, like alcohol, would go into solution. The water molecules would interact with polar molecules and surround them(only surrounding particles and do not break apart molecules) ON YOUR OWN: Answer the following questions. 1. Draw a picture illustrating the process by which NaCl would dissolve in water. What is the process called? The process is dissociation 2. Draw a picture illustrating the process by which sugar would dissolve in water. What is the process called? Solvation because sugar is polar 3. For the two illustrations above, does either act as an electrolyte? Explain your answer. NaCl would act as an electrolyte because it is ionic. Solution that can conduct electricity due to the inon in the solution 4. Suppose you are given an aqueous KI solution. What is the solute? What is the solvent? KI would be the solute because it is getting dissolved and water(H2O) would be the solvent CHEMISTRY, Unit 8 Review, page 2 AKS 5b - Plan and carry out an investigation to evaluate the factors that affect the rate at which a solute (solid or gas) dissolves in a specific solvent. 1. What is the difference between soluble and insoluble? Soluble= can be dissolved insoluble=can not be dissolved 2. What is the difference between miscible and immiscible? When are these terms used? miscible=two liquids that are soluble in each other immiscible= two liquids that are not soluble in each other 3. What does the expression “like dissolves like” mean? Give two examples illustrating this concept. The expression means substances with similar chemical characteristics such as polar solvents will dissolve polar solutes and vise versa with nonpolar solvents and solutes. 4. What three factors affect the rate of solvation of a solid in a liquid? Agitation (shaking), temperature, surface area (breaking apart to increase surface area) 5. What factors affect the rate of solvation of a gas in a liquid? Temperature and pressure ON YOUR OWN: Answer the following questions. 1. Why is the best time to sweeten your tea or coffee when it is fresh brewed? While it is still hot because heat affects the rate in which solutes dissolve. 2. Why is it better to use granulated sugar rather than sugar cubes to sweeten your tea? Because there is more surface area on granulated sugar compared to sugar cubes. 3. Why does a soda go flat when it is left out on the counter with the top off for several hours? Because it is losing pressure and trying to create equilibrium with the environment 4. Fish breathe oxygen dissolved in the water they live in through their gills. What conditions are necessary to ensure that the fish in your fish tank have plenty of oxygen to breathe? Make sure the water cool as heat will make the oxygen rise out of the fish tank. 5. Fish kills can occur in very hot summers. Why would that happen? The water gets warmer and thus there is less oxygen for the fish to breath. AKS 5c - Use mathematics and computational thinking to evaluate commercial products (examples may include: saline, glucose, vinegar) in terms of their concentrations (i.e., molarity and percent by mass). 1. What is the concentration of NaCl solution if 1.5 moles of NaCl are used to make 2.25 L of solution? 1.5/2.25= 0.666 2. What is the molarity of an aqueous solution containing 75 grams of sodium hydroxide, NaOH, in 0.50 L of solution? 75 g/39.997 = 1.875 mol NaOH 1.875 mol NaOH/0.5 L =3.75 M CHEMISTRY, Unit 8 Review, page 3 3. How many grams of potassium sulfate, K2SO4, would be dissolved in 2.0 L of a 1.5 M solution? 1.5 M= X/2 1.5x2=3 3 mol X 174.259 = 522.777 4. What volume of a 0.85 M KBr solution would you make if you used 1.5 moles of KBr? 0.85 M= 1.5/X 1.5/0.85= 1.76 mol 5. Calculate the molarity of 200 mL of a solution containing 100 grams of nitric acid, HNO3. 100/63.01= 1.587 1.587/0.2= 7.935 M ON YOUR OWN: Solve the following molarity problems. 1. What is the concentration of a KCl solution made from 2.2 moles of KCl in 1.75 L of solution? 2.2 / 1.75= 1.257 2. What is the molarity of a 5.5 L solution made with 38 grams of potassium nitrate, KNO3? 38g/ 101.103 = 0.376 mol 0.376 mol / 5.5 L =0.068 M 3. How many grams of AgNO3 are needed to make 750 mL of a 2.8 M solution? 2.8 X .75= 2.1 2.1 mol X 169.87= 356.72 4. What volume of a 1.25 M HCl solution would you make if you used 2.75 moles of HCl? 2.75/1.25=2.2L 5. What is the molarity of 800 mL of a solution containing 130 g of LiSO4? 130g/103.00= 1.26 mol 1.26 mol/ .8 L= 1.56 M AKS 5d - Communicate scientific and technical information on how to prepare and properly label solutions of specified molar concentration. 1. Explain how you would prepare a 1.0 L solution of 2.5 M KNO3. a. How many grams of KNO3 would you need to dissolve into the solution? 2.5 mol x 101.103 =252.76 g b. How much water will you add? Enough to fill to the 1 L mark c. What would be on the correct label for the solution? KNO3 CHEMISTRY, Unit 8 Review, page 4 ON YOUR OWN: Solve this solution problem. 1. How would you prepare a 0.500 L solution of 2.0 M NH4Cl? a. How many grams of NH4Cl will you need to make the solution? 2 X 0.5=1 1 mol X 53.49= 53.49 g b. How much water will you add? 0.5 litters c. What will be on the correct label for the solution? NH4Cl AKS 5e - Develop and use a model to explain the effects of a solute on boiling point and freezing point. 1. Colligative properties depend on the __amount___ of solute particles but not _solvent___. 2. What are the two colligative properties that are affected by the solute? Boiling and freezing point 3. Which colligative property decreases by adding more solute to a solution? Freezing point 4. Which colligative property increases by adding more solute to a solution? Boiling point 5. Would a covalent or an ionic compound create more solute particles in a solution at the same molarity? Give examples to explain your answer. Ionic compounds. Nacl is ionic so 1 mol= 2 mol and the same for K2S 1mol= 3 mol 6. How many solute particles would MgCl2 produce when it goes into solution? 3 solute particles ON YOUR OWN: Answer the following questions about colligative properties. 1. How many solute particles would AlCl3 produce when it goes into solution? 4 solute particles 2. Which substance would have a greater effect on a solution’s boiling point: NaCl or CaCl2? Why? CaCl2 has 3 dissolved particles while NaCl only has 2 3. The boiling point of pure water is 100oC. What would most likely happen to the boiling point if 15 grams of KCl were added to a beaker containing 500 grams of water? Explain why this happens. The freezing point would increase 4. What would most likely happen to the freezing point if 25 grams of salt was added to a closed container of 1.0 L of water? The freezing point would become lower CHEMISTRY, Unit 8 Review, page 5 AKS 5f - Construct a solubility curve and interpret it based on saturated and unsaturated solutions to explain the relationship between solubility and temperature. 1. What is the correct relationship between the solubility of a gas in a liquid and its temperature? As the temperature increases the solubility of a gas will decrease 2. What is the correct relationship between the solubility of a solid in a liquid and its temperature? As temperature increases the solubility of a solid increases. 3. Us the solubility curve graph below to answer the following questions: a. Which substance is the least soluble in 100g of water at 90oC? Ce2(SO4)3 b. If a saturated solution of potassium nitrate, KNO3, in 100g of water is cooled from 70oC to 40oC, how much precipitate will form? 70 g of precipitate will form c. How many grams of ammonium chloride, NH4Cl, can be dissolved in 100g of water at 50oC? 50 g d. Will sodium nitrate, NaNO3, be saturated or unsaturated if 60 grams are placed in 100g of water at 40oC? Unsaturated e. An unsaturated solution of potassium chloride, KCl, at 80oC has 20 grams of solute dissolved in 100 g of water. How many more grams of solute must be added to saturate the solution? 30 more grams must be added to make it saturated f. Name a compound that shows a decrease in solubility from 0oC to 100oC. Explain why this occurs. Ce2(SO4)3 this is because it is a gas, as temperature increases the solubility of a gas decreases. CHEMISTRY, Unit 8 Review, page 6 ON YOUR OWN: Answer the following questions about the solubility curve graph. 1. Which substance is the most soluble at 10oC? Kl 2. How many grams of potassium nitrate, KNO3, can be dissolved in 100g of water at 70oC? 130 g 3. Will ammonium chloride, NH4Cl, be saturated or unsaturated if 60 grams are placed in 100g of water at 70oC? Saturated 4. Which compounds are gases? How do you know? Ce2(SO4)3 and NH3 because as temperature increases the solubility of gases decreases 5. An unsaturated solution of KNO3 at 50oC has 50 grams of solute dissolved in 100g of water. How many more grams of solute must be added to make it a saturated solution? 30 g 6. If a saturated solution of potassium chloride, KCl, in 100g of water is cooled from 80oC to 10oC, how much precipitate will form? 20 g