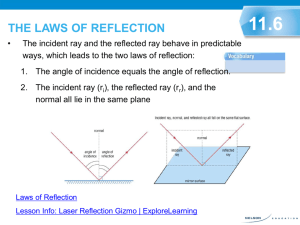
APPLICATION OF EM WAVES EM waves Applications/Uses • Radio waves - Radio and television communication • Microwaves - Satellite communication, terrestrial communications, RADAR, microwave oven • Infrared - Remote control, infrared scanner, night- vision google, autofocus camera, thermogram • Visible light - Photosynthesis, artificial lighting, optical fibers in medical uses, screen of electronic devices - Sterilization of water from drinking fountain, check signatures on a passbook, used to identify fake banknotes - Medical use, engineering applications - Medical treatment, radiotherapy, nuclear reactions • Ultraviolet Rays • X-rays • Gamma rays 1 2 Reflection - turning back of light rays when it hits a shiny surface like a mirror. LAW OF REFLECTION 3 • • The first law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. The second law states that the normal line, incident ray and reflected ray all lie in the same plane. The Two Kinds of Rays • Incident ray is the ray of light approaching the mirror. • Reflected ray is the ray of light which leaves the mirror. Normal Line - imaginary line that can be drawn perpendicular to the surface of the mirror and used as reference point in determining the angle of reflection and angle of incidence Plane mirrors - exhibits regular reflection where the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. - the type of image is virtual formed behind Virtual image is an image formed when an outgoing ray from an object always diverge - “Not Real” because it cannot be projected - Image only seems to be there! Lateral inversion - is a phenomenon wherein what is left on the object appears as right on the image and vice versa, This is due to the direction that light follows when it strikes a reflecting surface generally like a mirror. Real Image – Image is made from “real” light rays that converge at a real focal point so the image is real ¶ -Can be projected onto a screen because light actually passes through the point where the image appears -Always inverted curved mirror- is a reflecting surface in which its section is a section of a sphere. There are two kinds of curved mirrors, the concave and the convex. • Concave Mirrors - Curves inward - May be real or virtual image • concave mirror - called converging mirror because the parallel incident rays converge or meet/intersect at a focal point. 4