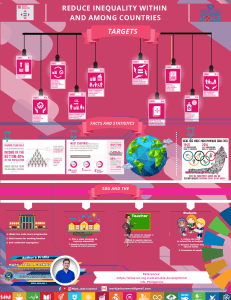
Sustainable Development Varsha Jogalekar What is Sustainable Development Complex concept – new catch phrase Used by all from World Bank to UNICEF Based on the idea that our planet has limits and they need to be respected Became popular in the late 1980s Refers to the process economic development where resources are used judiciously to satisfy needs of not only present generation but also to conserve them for the use of future generations Evolution World Commission for Environment and Development established in 1983 - the main agenda to propose global solution for the environmental concerns of the world Chaired by former Norwegian Prime Minister Gro Harlem Brundtland and referred to as the Brundtland Commission Published the report “Our Common Future,” also known as the “Brundtland Report,” in 1987 Milestone in triggering international awareness on the importance of global sustainable development In 1992, the UN Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED), or the "Earth Summit", in Rio de Janeiro, agreed on a Declaration setting out 27 principles supporting sustainable development A plan of action called Agenda 21, was agreed upon and recommended to all countries Definition First formal definition as per Brutland Report "Sustainable development is development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.” SD is an approach to development which uses resources in a way that allows them (the resources) to continue to exist for others (Mohieldin, 2017) Includes two concepts The concept of needs, in particular the essential needs of the world's poor, to which overriding priority should be given; and The idea of limitations imposed by the state of technology and social organization on the ability of the environment to meet present and future needs. Understanding the concept Development for us means –economic and social progress Sustainable Development emphasizes the link between develpoment and environmental problems and promotes political and economic change at all levels – local, national and international to tackle this problem Aims at achieving social progress, environmental equilibrium and economic growth Includes programs, initiatives and actions aimed at the preservation of resources Pillars of Sustainable Development Three interconnected spheres of sustainability Pillars of Sustainable Development 1. Economic Sustainability - a system of production that satisfies present consumption levels without compromising future needs Strategies that promote the utilization of socio-economic resources to their best advantage Involves making sure the business makes a profit, but also that business operations don’t create social or environmental issues Activities that fit under the economic pillar include compliance, proper governance and risk management Pillars of Sustainable Development 2. Social Sustainability – is the ability of a social system, such as a country, family, or organization, to function at a defined level of social well-being and harmony indefinitely Focuses on balancing the needs of the individual with the needs of the group Refers to, in broad terms, public policies that support social issues like healthcare, education, housing, employment, etc Problems like war, endemic poverty, widespread injustice, and low education rate are symptoms of a system that is socially unsustainable Pillars of Sustainable Development 3. Environmental Sustainability - ability of the environment to support a defined level of environmental quality and natural resource extraction rates indefinitely Occurs when processes, systems and activities reduce the environmental impact of an organizations facilities, products and operations This pillar refers to the laws, regulations, and other policy mechanisms concerning environmental issues Considered as world's biggest actual problem Triple Bottom Line In traditional business accounting and common usage, the "bottom line" refers to either the "profit" or "loss", which is recorded at the very bottom line on a statement of revenue and expenses Triple bottom line (TBL) accounting expands the traditional reporting framework to take into account social and environmental performance in addition to financial performance TBL dimensions are also commonly called the three Ps: people, planet and profits Difficulty lies in measuring them Sustainable Development Goals to transform our world Also known as Global Goals Adopted by all United Nations Member States at UN General Assembly Summit in September 2015 17 integrated goals – action in one are will affect outcome in other Based on the principle – Leave no one behind "A blueprint to achieve a better and more sustainable future for all by 2030“ – Mission Statement Aims to achieve many zeros – poverty, hunger…. #Envision2030: 17 goals to transform the world for persons with disabilities Sustainable Development Goals to transform our world 1 : No Poverty. 2: Zero Hunger. 3: Good Health and Well-being. 4: Quality Education. 5: Gender Equality. 6: Clean Water and Sanitation. 7: Affordable and Clean Energy. 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure 10: Reducing inequalities Sustainable Development Goals to transform our world 10: Reducing inequalities 11:Sustainable cities and communities 12:Responsible Consumption and Production 13: Climate Action 14: Life below Water 15: Life on Land 16: Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions 17: Partnership for the goals SDG Targets and Indicators Each of the goals has 6 – 8 targets to be achieved and some indicators The goals include a list of 169 SDG Targets Progress towards these Targets is tracked by 232 unique Indicators SDG 1 NO POVERTY End poverty in all its forms everywhere SDG 1 No Poverty- Targets The goal has seven targets and 13 Outcome Targets – Eradicating extreme poverty, Reduction of all poverty by half Implementation of social protection system Ensuring equal rights to ownership, basic services, technology and economic resources Building of resilience to environmental, economic and social disasters “Means of achieving” Targets mobilization of resources to end poverty establishment of poverty eradication policy frameworks at all levels SDG 1 NO POVERTY Greatest challenge Despite all efforts the world is far from achieving the target 10 percent -700 million people lived in extreme poverty in 2015 An Overseas Development Institute (ODI) assessment (September 2019) finds that 430 million people will still live in extreme poverty by 2030 Covid has further added millions of people living in extreme poverty SDG 2 Zero Hunger End hunger Achieve food security and improved nutrition and Promote sustainable agriculture SDG 2 Zero Hunger Nearly 690 million people are hungry or 8.9 percent of the world population Majority of the world’s undernourished – 381 million – are still found in Asia -- More than 250 million live in Africa World not on track to achieve Zero Hunger by 2030 In 2019, close to 750 million – nearly one in ten people in the world – were exposed to severe levels of food insecurity As per estimates number of people affected by hunger would surpass 840 million by 2030 As per the World Food Programme, 135 million suffer from acute hunger Covid is expected to double this number SDG 2 Targets UN has defined 8 targets and 13 indicators Universal access to safe and nutritious food Ends all forms of malnutrition Double the productivity and incomes of small-scale food producers Sustainable food production and resilient agricultural practices Maintain the genetic diversity in food production Invest in rural infrastructure, agricultural research, technology and gene banks Prevent agricultural trade restrictions, market distortions and export subsidies Ensure stable food commodity markets and timely access to information SDG 3 Good Health and Well Being “Ensure healthy lives and promote wellbeing for all at all ages” Targets of SDG3 Reduce the global maternal mortality ratio to less than 70 per 100 000 live birth End preventable deaths of newborns and children under 5 years of age End the epidemics of AIDS, tuberculosis, malaria and neglected tropical diseases Reduce by one third premature mortality from non-communicable disease Strengthen the prevention and treatment of substance abuse Halve the number of global deaths and injuries from road traffic accidents Achieve universal health coverage, including financial risk protection Reduce illnesses and deaths from hazardous chemicals and pollution Implement the WHO framework convention on tobacco control Support research, development and universal access to affordable vaccines and medicines Increase health financing and support health workforce in developing countries Improve early warning systems for global health risks SDG 4 Quality Education Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all Targets Ten targets which are measured by 11 indicators Free primary and secondary education Equal access to quality pre-primary education Equal access to affordable technical, vocational and higher education Increase the number of people with relevant skills for financial success Eliminate all discrimination in education Universal literacy and numeracy Education for sustainable development and global citizenship Build and upgrade inclusive and safe schools Expand higher education scholarships for developing countries Increase the supply of qualified teachers in developing countries SDG 4 Enrollment in primary education in developing countries has reached 91 percent Still, 57 million primary-aged children remain out of school, more than half of them in sub-Saharan Africa In developing countries one in four girls is not in school 103 million youth worldwide lack basic literacy skills, and more than 60 percent of them are women 6 out of 10 children and adolescents are not achieving a minimum level of proficiency in reading and math SDG 5 Gender Equality Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls SDG 5 Targets Equal rights to economic resources, property ownership and financial services Promote empowerment of women through technology Adopt and strengthen policies and legislation for gender equality SDG 6 Clean Water and Sanitation Ensure availability and Sustainable management of water and sanitation for all 2.2 billion people around the world still lack safely managed drinking water including 785 million without basic drinking SDG 6 Targets Achieve universal and equitable access to safe and affordable drinking water for all End open defecation and provide access to sanitation and hygiene Improve water quality, wastewater treatment and safe reuse Increase water-use efficiency and ensure freshwater supplies Implement IWRM Integrated Water Protect and restore water-related ecosystems Expand water and sanitation support to developing countries Support local engagement in water and sanitation management SDG 6 3 in 10 people lack access to safely managed drinking water services 6 in 10 people lack access to safely managed sanitation facilities.. Women and girls are responsible for water collection in 80 per cent of households without access to water on premises. Water scarcity affects more than 40 per cent of the global population and is projected to rise. 2.4 billion people lack access to basic sanitation services, such as toilets or latrines More than 80 per cent of wastewater resulting from human activities is discharged into rivers or sea without any pollution removal Each day, nearly 1,000 children die due to preventable water and sanitation-related diarrheal diseases SDG 7 Affordable and Clean Energy Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all SDG 7 Energy is central to nearly every major challenge and opportunity the world faces today - security, climate change, food production, jobs Energy access constitutes a core component of the sustainable development 13% of the world do not have access to electricity 40% - 3 billion people of the world do not have access to clean fuels for cooking – leading to indoor pollution and diseases Per capita energy consumption varies more than 10-fold across the world - average US citizen still consumes more than ten times the energy of the average Indian Low-income households lack access to electricity and clean fuels SDG 7 aims at ensuring everyone has access to affordable, reliable, and modern energy services by the year 2030 SDG 7 Targets SDG 8 Decent Work and Economic Growth Promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all SDG 8 Eradicating poverty will only be possible through stable and well paid employment After 2009 global work productivity began to increase and unemployment rates improved However in 2019 the world economy achieved its lowest growth rate, which was further affected by the pandemic According to a Report on Progress with Compliance with the SDGs (2020) World is heading for the biggest increase in global unemployment since the Second World War. SDG 8 Targets Sustainable Economic Growth – Minimum 7% GDP per annum in least developed countries Diversify, innovate and upgrade for economic productivity Promote policies to support job creation and growing enterprises Improve resource efficiency in consumption and production Full and productive employment and decent work with equal pay Promote youth employment, education and training End modern slavery, trafficking, and child labour Promote beneficial and sustainable tourism Universal access to banking, insurance and financial services Increase aid for trade support Develop a global youth employment strategy SDG 9 Industry, innovation and infrastructure Build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and foster innovation SDG 9 Infrastructure and innovation are crucial drivers of economic growth and development Interlinked with many other SDGs Technological progress is essential for solutions to economic and environmental challenges Failing to improve infrastructure and promote technological innovation results into poor health care, inadequate sanitation and limited access to education. More than 4 billion people still do not have access to the Internet The manufacturing industry which was already declining due to tariffs and trade tensions has been severely hit by the pandemic SDG 9 Targets Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure Promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization Increase access to financial services and markets Upgrade all industries and infrastructures for sustainability Enhance research and upgrade industrial technologies Facilitate sustainable infrastructure development for developing countries Support domestic technology development and industrial diversification Universal access to information and communications technology SDG 10 Reduced Inequalities Reduce inequality within and among countries SDG 10 Inequalities is a growing concern Inequalities based on income, sex, age, disability, sexual orientation, race, class, ethnicity, religion and opportunity continue to persist 2 among 10 people reported of having experienced some kind of discrimination on at least one ground established by international human rights law Women, children, older people, refugees, migrants face discrimination, lack of opportunities and even health care Measuring inequality in its individual forms is a crucial component Gini Index/ Coefficient is used to measure socioeconomic equality SDG 10 Targets SDG 11 Sustainable Cities and Communities Make cities inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable SDG 11 The future we want includes cities of opportunities for all, with access to basic services, energy, housing, transportation and more. - UN Cities occupy just 3 percent of the Earth’s land but account for 60 to 80 percent of energy consumption and at least 70 percent of carbon emissions 90 percent of urban expansion will be in the developing world 828 million people are estimated to live in slums Cities generate about 80 percent of the global GDP. SDG 11 Targets 11.1Safe and affordable housing 2 Affordable and sustainable transport systems 3 Inclusive and sustainable urbanization 4 Protect the world's cultural and natural heritage 5 Reduce the adverse effects of natural disasters 6 Reduce the environmental impacts of cities 7 Provide access to safe and inclusive green and public spaces 11.a Strong national and regional development planning 11.b Implement policies for inclusion, resource efficiency and disaster risk reduction 11.c Support least developed countries in sustainable and resilient building SDG 12 Responsible Consumption and Production Ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns SDG 12 World continues with development which uses natural resources unsustainably Economic and social progress has resulted in environmental degradation Aims at ensuring sustainable consumption and production patterns Increasing welfare gains from economic activities by reducing resource use, degradation and pollution Reduce current global consumption rates in order to fit with the biophysical capacity If the global population reaches 9.6 billion by 2050, the equivalent of almost three planets could be required to provide the natural resources needed to sustain current lifestyles SDG 12 Targets 12.1 Implement the 10-year framework of programs on sustainable consumption and production (SCP pattern accepted in June 2012) 12.2 Achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources 12.3 Halve per capita global food waste at the retail and consumer levels 12.4 Achieve the environmentally sound management of chemicals and all wastes throughout their life cycle 12.5 Substantially reduce waste generation through prevention, reduction, recycling and reuse 12.6 Encourage companies to adopt sustainable practices and sustainability reporting 12.7 Promote public procurement practices that are sustainable 12.8 Promote universal understanding of sustainable lifestyles SDG 12 Targets 12.a: Support developing countries' scientific and technological capacity for sustainable consumption and production 12.b: Develop and implement tools to monitor sustainable tourism 12.c: Remove market distortions that encourage wasteful consumption SDG13 Climate Action Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts SDG 13 2019 was the second warmest year on record Carbon dioxide (CO2) levels greenhouse gases in the atmosphere rose to new records in 2019 Climate change is caused by anthropogenic emissions of CO2 and other greenhouse gasses Climate change is disrupting national economies and affecting lives Weather events are becoming more extreme Changing climate will seriously compromise food production Science indicates that we have just over a decade to avert climate disaster, and demands bold action. SDG 13 Targets 13.1: Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related disasters 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into policy and planning 13.3: Build knowledge and capacity to meet climate change 13.A: Implement then UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (Green Climate Fund mobilization of $100 billion) 13.B: Promote mechanisms to raise capacity for planning and management SDG 14 Life Below Water Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources for sustainable development SDG 14 Healthy oceans and seas are essential to our existence Marine biodiversity is currently in global decline – over fishing, ocean acidification, reduction of species 40 percent of the ocean is heavily affected by pollution, depleted fisheries, loss of coastal habitats and other human activities Ocean absorbs about 30 percent of carbon dioxide, buffering the impacts of global warming SDG 14 Targets 14.1 Reduce Marine Pollution 14.2 Protect and Restore Ecosystems 14.3 Reduce Ocean Acidification 14.4 Sustainable Fishing 14.5 Conserve Coastal and Marine Areas 14.6 End Subsidies Contributing to Overfishing 14.7 Increase the Economic Benefits from sustainable Use of Marine Resources 14.a Increase scientific knowledge, research and technology for ocean health 14.b Support small scale fishers 14.c Implement and enforce international sea law SDG 15 Life on land Protect, restore and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, sustainably manage forests, combat desertification, and halt and reverse land degradation and halt biodiversity loss. SDG 15 Land is the most important habitat is in grave danger Future of life is linked to the survival of this ecosystem Estimated 18 million acres (7.3 million hectares) of forest are lost every year 52% of the land used for agriculture is moderately or severely affected by soil degradation Degradation of drylands has led to the desertification of 3.6 billion hectares As per the IUCN 27 % evaluated species face extinction SDG 15 Targets 15.1: Conserve and restore terrestrial and freshwater ecosystems 15.2: End deforestation and restore degraded forests 15.3: End desertification and restore degraded land 15.4: Ensure conservation of mountain ecosystems 15.5: Protect biodiversity and natural habitats 15.6: Protect access to genetic resources and fair sharing of the benefits 15.7: Eliminate poaching and trafficking of protected species 15.8: Prevent invasive alien species on land and in water ecosystems 15.9: Integrate ecosystem and biodiversity in governmental planning SDG 15 Targets 15.a: Increase financial resources to conserve and sustainably use ecosystem and biodiversity 15.b: Finance and incentivize sustainable forest management 15.c: Combat global poaching and trafficking SDG 16 Peace Justice and Strong Institutions Promote peaceful and inclusive societies for sustainable development, provide access to justice for all and build effective, accountable and inclusive institutions at all levels SDG 16 This goal is dedicated to the promotion of peaceful and inclusive societies for sustainable development Violence is the most significant and destructive challenge to the development, growth and wellbeing Armed conflicts cause fatalities and mass human displacement Other forms of violence – crime and sexual and gender based violence also on a rise Sustainable development agenda for 2030 will begin with restoring security and human rights to individuals SDG 16 Targets 16.1: Significantly reduce violence everywhere 16.2 :End abuse, exploitation, trafficking and all forms of violence against and torture of children. 16.3: Promote the rule of law at the national and international levels and ensure equal access to justice for all. 16.4: By 2030, significantly reduce illicit financial and arms flows, strengthen the recovery and return of stolen assets and combat all forms of organised crime. 16.5: Substantially reduce corruption and bribery in all their forms. 16.6: Develop effective, accountable and transparent institutions at all levels. 16.7: Ensure responsive, inclusive, participatory and representative decision-making at all levels. SDG 16 Targets 16.8: Broaden and strengthen the participation of developing countries in the institutions of global governance. 16.9: By 2030, provide legal identity for all, including birth registration. 16.10: Ensure public access to information and protect fundamental freedoms, in accordance with national legislation and international agreements. 16.a Strengthen relevant national institutions, including through international co-operation, for building capacity at all levels, in particular in developing countries, to prevent violence and combat terrorism and crime. 16.b Promote and enforce non-discriminatory laws and policies for sustainable development SDG 17 Partnership for the Goals Strengthen the means of implementation and revitalize the global partnership for sustainable development SDG 17 Interconnected global development agenda requires a new global partnership Need for cross sector and cross country collaboration in pursuit of all the goals by the year 2030 Considered a vision for improved and more equitable trade, as well as coordinated investment initiatives to promote sustainable development Goal has 17 targets to be achieved by 2030, broken down into five categories - finance, technology, capacity building, trade and systemic issues SDG 17 Targets - Finance Strengthen domestic resource mobilization, including through international support to developing countries Implement all development assistance commitments Mobilize additional financial resources for developing countries from multiple sources Assist developing countries in attaining long-term debt sustainability through coordinated policies- debt financing, debt relief and debt restructuring Adopt and implement investment promotion regimes for least developed countries SDG 17 Targets – Technology & Capacity Building Knowledge sharing and cooperation for access to science, technology and innovation (Enhance North-South, SouthSouth and triangular regional and international cooperation) Promote the development, transfer, dissemination and diffusion of environmentally sound technologies to developing countries Strengthen the science, technology and innovation capacity for least-developed countries Enhanced SDG capacity in developing countries SDG 17 Targets – Trade Promote a universal rules-based, open, non-discriminatory and equitable trading system under the WTO Significantly increase the exports of developing countries,… doubling the least developed countries’ share of global exports Remove trade barriers for least-developed countries SDG 17 Targets - Systemic issues Enhance global macroeconomic stability, including through policy coordination and policy coherence Enhance policy coherence for sustainable development Respect each country’s policy space and leadership to establish and implement policies for poverty eradication and sustainable development Enhance the global partnership for sustainable development, complemented by multi-stakeholder partnerships that mobilize and share knowledge, expertise, technology and financial resources Encourage and promote effective public, public-private and civil society partnerships, building on the experience and resourcing strategies of partnerships Enhance availability of reliable data Further develop measurements of progress