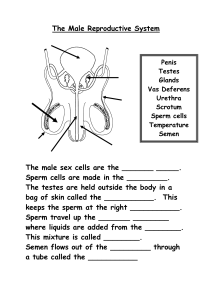
Male reproductive system Made by: Raneem Ahmed (1220556) Nadeen Hossam(1220545) Male reproductive anatomy Scrotum is like a sac, it is function to maintain the temperature of the body lower than body temperature by 2 degree Celsius to make it a suitable environment for sperm development, there is also a muscle that is responsible for the movement of the scrotum near or away from the tests according to the body temperature Testes (a pair of testicles), their main function is sperm formation, they consist of lobules, each lobule contains 1 to 3 seminiferous tubules (which is made up from lumen and wall) The sperm is formed under the influence of testosterone hormone. Testosterone is regulated by the anterior pituitary gland that releases LH (luteinizing hormone) and FSH (Follicle stimulating hormone) Epididymis is on the top of the tests, their function is to prepare the sperm become motile and mature for ejaculation Vas deferens (ductus deferens) used in transporting of sperms Urethra: extends from the urinary bladder and it is a path for both urine and semen (common tract between reproduction and urinary system) Seminal vesicles: produce about 60% of the semen. Semen is alkaline as the ph of the vagina is acidic so that the sperm can survive in these acidic conditions and neutralize it, it also contains fructose which acts as a supply of nourishment to the sperms so that it can survive up to 5 days in the female reproductive organs and it can be used as a source of energy in the form of ATP, semen also contains sticky yellowish proteins that can help the semen stick to the surface of the female cervix, it also contains prostaglandins , chemical that cause uterus to contract to help in propelling the sperms into the egg. Semen= sperms+ fluid Bulbourethral glands (Cowper’s glands): its main function is pre-ejaculatory is secreting alkaline fluid that clears any acidity found in urethra The human penis contains the urethra as well as three cylinders of spongy erectile tissue as corpus cavernosum and corpus spongiosum. During sexual arousal, the erectile tissue fills with blood from the arteries. As this tissue fills, the increasing pressure seals off the veins that drain the penis, causing it to engorge with blood. The main shaft of the penis is covered by relatively thick skin. The head, or glans, of the penis has a much thinner outer layer and is consequently more sensitive to stimulation. The human glans is surrounded by a fold of skin called the prepuce, or foreskin, which is removed if a male is circumcised Sympathetic and parasympathetic Parasympathetic which is responsible for erection that releases the nitrogen (NO) and that induces the production of the CGMP which is like ATP Erectile dysfunction: is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection suitable for sexual inter-course. ED may be caused by a number of factors, including poor blood flow, certain medications, and many illnesses. Medications for the treatment of erectile dysfunction inhibit the enzyme that breaks down cGMP, some of these medications can cause vision problems because the same enzyme occurs in the retina 400 million sperm in the 3.5 mL of semen expelled during ejaculation In older men, the prostate can enlarge and squeeze off the urethra, making urination painful and difficult. Hyperplasia is a form of benign prostate cancer which is non-metastatic cancer External reproductive organs as scrotum and penis Internal reproductive organs as the male gonads (testes) Accessory glands as seminal vesicles, prostate gland and bulbourethral (cowpers gland) Ducts as ejaculatory ducts Questions Testosterone is synthesized primarily by the A) sperm cells . B) hypothalamus . C) Leydig cells. D) anterior pituitary gland. E) seminiferous tubules. Human sperm cells first arise in the A) prostate gland. B) vas deferens. C) seminiferous tubules. D) epididymis. E) Sertoli cells. The surgical removal of the seminal vesicles would likely A) cause sterility because sperm would not be produced. B) cause sterility because sperm would not be able to exit the body. C) greatly reduce the volume of semen. D) enhance the fertilization potency of sperm in the uterus. E) cause the testes to migrate back into the abdominal cavity.