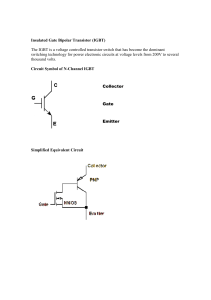
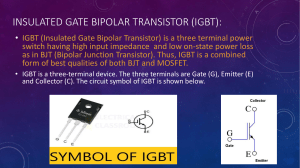
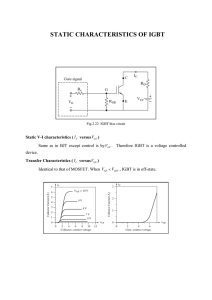
Bipolar transistor with isolated gate Kirill Gopenko Group K-22 M IGBT Cell A cross-section of a typical IGBT showing the internal connection of a MOSFET and a bipolar device The IGBT cell is constructed similarly to the n-channel vertical structure. A power MOSFET, except that the n+ drain is replaced by a p+ collector layer, thus forming a vertical bipolar PNP transient transistor. This additional p+ region creates a cascade connection of a PNP bipolar transient transistor with a surface n-channel. 2 What's new? A. Nakagawa invented the design concept of an IGBT device without fixation in 1984. The invention is characterized by a device design that sets the saturation current of the device below the fixation current, which triggers a parasitic thyristor. Static characteristic of IGBT In this invention, for the first time, complete suppression of the parasitic action of thyristors was realized, since the maximum collector current was limited by the saturation current and never exceeded the fixation current 3 Practical implementation of the device Successful attempts to suppress the fixation of a parasitic thyristor and scaling of the nominal voltage of devices in GE allowed the introduction of commercial devices in 1983.4 Once the lock-free capability was achieved in IGBTs, it was found that IGBTs have a very reliable and very large safe working area. Typical gate drive circuit for IGBT modules It was demonstrated that the product of the operating current density and collector 5 voltage exceeds the theoretical limit of bipolar transistors 2 ∙ 10 𝑊/с𝑚2 and 5 achieved 5 ∙ 10 𝑊/с𝑚2 4 Commercial Customized IGBT Modules 1. Commercial customized IGBTs available have a rated current of 200-400 A and a rated voltage of 1700 V. The rated voltage is predicted to be up to 2-3 kV. (The rated voltage of IGBTs is higher than that of BJTs, due to the small current gain of pnp BJT.) 2. For a 1 kV device, the operating voltage is 2-3 V at rated current. 3. The on and off time is less than 1 microsecond. 4. IGBTs are available in a module in which 4 to 6 separate IGBTs are connected in parallel. Therefore, the current nominal values are in the range from 1000 to 1500 A. 5 IGBT Operation Process The whole process of IGBT operation can be represented by two stages: as soon as a positive voltage is applied, a field-effect transistor opens between the gate and the source, that is, an n-channel is formed between the source and the drain. At the same time, charges begin to move from the n region to the p region, which entails the opening of a bipolar transistor, as a result of which a current rushes from the emitter to the collector. Simplified equivalent IGBT scheme The essence of his work is that a field-effect transistor controls a powerful bipolar. As a result, switching of a powerful load becomes possible at low power, since the control signal enters the gate of the field-effect transistor. 6 Modes of operation of the transistor 1. Inverse active mode. The amplifying properties in this mode are as bad as possible, so transistors in this mode are used very rarely. 2. Saturation mode. The main charge carriers of the collector and emitter "run" to the base, where they actively recombine with its main carriers. Due to the resulting redundancy of charge carriers, the resistance of the base and p-n junctions decreases. 3. Cut-off mode. The current of the main charge carriers between the emitter and the collector stops. Flows of non-primary charge carriers create only small and uncontrolled thermal currents of transitions. Due to the poverty of the base and transitions by charge carriers, their resistance increases greatly. 4. Barrier mode. In this mode, the base is directly or through a small resistance closed with the collector. A resistor is included in the collector or emitter circuit, which sets the current through the transistor. Thus, the equivalent of a diode circuit with a series-connected resistance is obtained. 7 Features and applications of IGBT. Distinctive qualities of IGBT: • Voltage-controlled (like any field-effect transistor); • Have low losses in the open state; • They can work at a temperature of more than 100°C; • They are capable of operating with a voltage of more than 1000 volts and capacities of more than 5 kilowatts. Install these devices in uninterruptible power supplies and in high-voltage networks. They can be found in the electronic circuits of washing machines, sewing machines and dishwashers, inverter air conditioners, pumps, electronic ignition systems of cars, power supply systems of server and telecommunication equipment. 8 Thanks for your attention 9