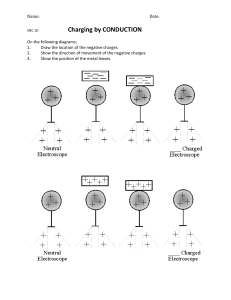
General Physics 2 12 Quarter 3 Self-Learning Module 2 Electric Charge For the Learner: Welcome to the General Physics 1 Self-Learning Module on Electric Charge! This module was designed to provide you with fun and meaningful opportunities for guided and independent learning at your own pace and time. You will be enabled to process the contents of the learning material while being an active learner. This module has the following parts and corresponding icons: Expectations - This points to the set of knowledge and skills that you will learn after completing the module. Pretest - This measures your prior knowledge about the lesson at hand. Recap - This part of the module provides a review of concepts and skills that you already know about a previous lesson. Lesson - This section discusses the topic in the module. Activities - This is a set of activities that you need to perform. Wrap-Up - This section summarizes the concepts and application of the lesson. Valuing - This part integrates a desirable moral value in the lesson. Posttest - This measures how much you have learned from the entire module. EXPECTATIONS The module is about electric charge and its properties. After going through this module, you are expected to: 1. describe charging by rubbing and charging by induction using ray diagram; 2. explain the role of electron transfer in electrostatic charging by rubbing; and 3. describe experiments to show electrostatic charging by induction. PRETEST Choose the letter of the BEST correct answer. Write the chosen letter in your notebook. 1. Two balls are repelling each other as they hang from the ceiling. What can you say about their charges? A. one is positive, the other one is negative B. both are positive C. both are negative D. both are positive or both are negative 2. A metal ball hangs from the ceiling by an insulating thread. The ball is attracted to a positive-charged rod heald near the ball. What must be the charge of the ball? A. positive B. negative C. neutral D. positive or negative 3. In which way is the electric force similar to the gravitational force? A. Electric force is proportional to the mass of the object. B. Electric force is similar in strength to gravitational force. C. Electric force is both attractive and repulsive. D. Electric force decreases in strength as the distance between the charges increases 4. Which activity does not produce the same results as the other three? A. sliding over a plastic-covers automobile seat B. walking across a woolen carpet C. scraping food from a metal bowl with a metal spoon D. brushing dry hair with a plastic comb 5. A negatively charged object is brought close to the surface of a conductor, whose opposite side is then grounded. What is this process of charging called? A. charging by contact B. charging by induction C. charging by conduction D. charging by polarization RECAP Atoms make up a matter consists of subatomic particles. Give some important details about these particles by completing the table below: - Value of charge Coulomb (C) -1.6 x 10 -19 C Mass in kilogram (kg) 9.11 x 10 -31 kg p + +1.6 x 10 -19 C 1.67 x 10 -27 kg n neutral 0 1.67 x 10 -27 kg Name of Particle Symbol Charge Electron e Proton Neutron LESSON Pairs of electrical charges have a force that acts between them. It is called the electric force. Unlike gravity which can only be an attractive force, the electric force can be either attractive or repulsive. Electrostatics deals with the interaction of electric charge at rest. But how do charges interact? Have you ever experience something in the parts of your body that you can’t explain where it came from? Like... Copyright © https://google/images receiving an electric shock while touching a doorknob? Copyright © https://google/images Copyright © https://google/images your hair following the movement of the balloon? or spark between you and your friend? These are examples of how charges transfer from one object to another. How do you think these objects acquire charges? How do we know the charge of an object? How does it transfer from one object to another? Try rubbing a balloon with a piece of cloth and place it near running water on your faucet... What do you observe? The water bends as the rubbed balloon moves closer to it Why do you think it happened? The process of supplying the electric charge to an object or losing an electric charge from an object is called charging. Electric charge is conserved. It can be transferred from one object to another by moving electrons but it can not be created nor destroyed. On your browser, copy this link to explore how charges transfer from one object to another https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/html/balloons-and-staticelectricity/latest/balloons-and-static-electricity_en.html As you can see, the balloon, the cloth, and the wall are neutrally charged, meaning they have equal numbers of protons and electrons. When you rub the balloon on the cloth, the negatively charged particles in the cloth are being attracted to the balloon. Making the cloth positively charged and the balloon negatively charged. The cloth becomes positively charged because it has a deficiency in electrons after rubbing. While the balloon becomes negatively charged because it has excess electrons. Positive charge: When an object has a positive charge, it means that it has more protons than electrons. Negative charge: When an object has a negative charge, it means that it has more electrons than protons. Neutral charge: When an object has an equal number of protons and electrons it means the object is neutrally charged. When you release the negatively charged balloon, it is being attracted to the positively charged cloth. But if you place the balloon near the wall, you can see that the negatively charged particles on the wall are being repelled by the negatively charged balloon. Thus we can say that unlike charges attract and like charges repel The law for electrostatic charge simply tells us that as charges repel and unlike charges attract. Process of Charging: Charging by Friction When two objects are rubbed against each other, charge transfer takes place. One of the objects loses electrons while the other object gains electrons. The object that loses electrons becomes positively charged and the object that gains electrons becomes negatively charged. Both the objects get charged due to friction and this method of charging is commonly known as electrification by friction. Charging by Conduction The method of charging an uncharged object by bringing it close and in contact with a charged object is known as charging by conduction. The charged conductor has an unequal number of protons and electrons, hence when an uncharged conductor is brought near it, it discharges electrons to stabilize itself. A conductor is an object or type of material that allows the flow of charge (electrical current) in one or more directions. Materials made of metal are common electrical conductors. Electrical current is generated by the flow of negatively charged electrons, positively charged holes, and positive or negative ions in some cases. Charging by Induction The process of charging an uncharged conductor by bringing it near a charged conductor without any physical contact is known as charging by induction. An electrical insulator is a material in which the electron does not flow freely or the atom of the insulator has tightly bound electrons whose internal electric charges do not flow freely; very little electric current will flow through it under the influence of an electric field. Some examples of conductors and insulators: https://www.toppr.com/ask/content/concept/classification-of-materials-conductors-and-insulators-209361/ ACTIVITIES Activity 1 – Determining Charge Determine the charge on the object and explain why it has this charge: Reference: https://studylib.net/doc/8476708/01.1-laws-of-electric-charge-worksheet Activity 2 – Law of Charges Describe what charge is on each object and the law of electric charge is applied. Reference: https://studylib.net/doc/8476708/01.1-laws-of-electric-charge-worksheet WRAP-UP Complete the table about what you have learned about electric charge: VALUING/APPLICATION EARTHING AND ITS ADVANTAGES: Connecting a charged object to the earth with the help of conducting wires or physical contact is called Earthing. The earth is considered to be a huge reservoir of electrons. Depending upon the charge on the object, the earth provides or accepts electrons from a charged object connected to it. Can you name some electrical appliances at home that needs to be grounded or Earthed? Reference: https://www.toppr.com/ask/content/concept/classification-ofmaterials-conductors-and-insulators-209361/ POSTTEST Choose the letter of the best answer. Write the chosen letter in your notebook. 1. When two dissimilar materials contact each other some of the electrons in one material will be drawn into the other material, this effect can be increased by rubbing the two surfaces together. What charging process is involved? A. charging by conduction B. charging by friction C. charging by induction D. all of the above 2. A student has a neutrally charged glass rod and a neutrally charged silk cloth. When the student rubs the silk cloth on the glass rod, the rod acquires a net positive charge. What is the charge on the silk cloth after the student performs this experiment? A. the silk has no charge B. the silk has a charge that is equal in magnitude to the glass rod’s charge, but it is negative C. the silk is positively charged and has a greater magnitude of charge than the glass rod D. the silk is negatively charged and has a smaller magnitude of charge than the glass rod 3. All matters are said to be neutral wherein the numbers of electron and protons are equal so once charges it do not stay for a long time because of the following factors except; A. amount of charge gain B. presence of polar molecules C. type of charge D. type of material 4. Rubber is a nonconducting material that is why it cannot easily conduct heat and electricity. Which is the best explanation for this situation?. A. it has excess electrons which are loosely bounded with its nuclei so it can free to move B. it has a deficiency in electrons which are tightly bounded with their nuclei so it can not move freely C. it has few electrons D. it has no electrons 5. A negatively charged object is brought close to the surface of a conductor, whose opposite side is then grounded. What kind of charge is left on the conductor’s surface? A. neutral B. negative C. positive D. both positive and negative REFERENCES Physics a First Course Teacher Resource CD-Rom, 2005. CPO Science. Tony Wayne. Physics Students Workbook. Creative Commons Noncommercial 3.0 United States License. Attribution- Faughn, J. S.; Serway, R. A. Holts Physics, Teacher’s Edition Textbook, 2006. Pages 160-163. Tom Strong. Honors Physics Review Notes. 2009. Mt. Lebanon High School Tony Wayne. Physics Students Workbook. Creative Commons Noncommercial 3.0 United States License. Attribution- Walker, James S., Physics, Fourth Edition. 2010. Lecture Outline, Chapter 7. Pearson Education, Inc. Acknowledgment: This module was collaborated and created by the Division of Pasig City.