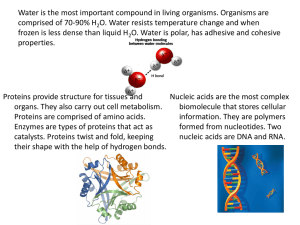
I These contain nucieic all genetic acids information This macromolecule has four, proteins structural levels. For this proteins polymer, form = function. biomolecules, Describe the organelles, cells, biological hierarchy, starting with tissues, organs, organ systems, biomolecules and ending with organism. organism I I DNA/RNA nucieic are examples adds of These are the carbohydrates main source of energy. These L primarily store energy. ipids These control proteins reaction (specifically enzymes!) rates. I Glucose is monosaccharide an example of (simple sugar) a Cellulose is polysaccharide (complex sugar/carbohydrate) an example of a Enzymes are examples of proteins Steroids are ipids examples of I r Where do you eel wall carbohydrates in the cell? (plants only!) Where do you find proteins ribosomes find in the cell? Where do plasma you find lipids membrane in the cell? Where do you in the nucleus find nucleic acids in the cell? (DNA!) I What is a monosaccharide carbohydrate (simple sugar) monomer? What is a protein amino acid monomer? What is a two types: fatty acid and glycerol lipid monomer? What is a nucleotide nucleic acid monomer? I What 6 elements make carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and up all living things? sulfur(CHNOPS!) What is another word for biomolecule/polymer macromolecule? All polymers are made up of smaller subunits monomers called Name the four types of biomolecules. carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids I Amino acid is to protein as is to nucleic acid. Fatty acid is to lipid as is to nucleotide monosaccharide polysaccharide. Give two amino acids, examples of nucleotides, fatty acids, glycerol, monomers. monosaccharides Give two examples of polymers sugars/carbohydrates/polysaccharides, fats/lipids, proteins/polypeptides, nucleic acids t I r Name the monomer that glucose (type of monosaccharide) feeds your brain. Name the polymer that has hydrophobic tails and a hydrophilic head. LI