Chemistry Calculations Worksheet: Yield, Mass, Formulas
advertisement

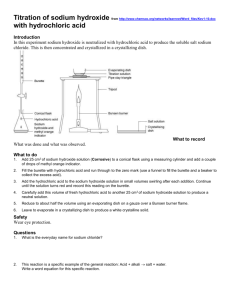
Questions Q1. Lead nitrate solution reacts with sodium iodide solution to form solid lead iodide and sodium nitrate solution. In an experiment, lead nitrate solution was reacted with sodium iodide solution to produce lead iodide. (i) The yield of lead iodide from this experiment was 3.5 g. The theoretical yield of lead iodide for this experiment was 5.0 g. Calculate the percentage yield of lead iodide in this experiment. (2) ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. percentage yield = ........................................................... % (ii) State two reasons why the percentage yields of experiments are often less than 100%. (2) reason 1 ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. reason 2 ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. (Total for question = 4 marks) Q2. Calculate the relative formula mass of iron chloride, FeCl3. (Relative formula masses: Cl = 35.5, Fe = 56) (2) .................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... ...................... .................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... ...................... .................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... ...................... answer........................................... Q3. The simplest ratio of aluminium atoms to chlorine atoms in aluminium chloride is 1 : 3. The empirical formula of aluminium chloride is AlCl3. The simplest ratio of aluminium atoms to oxygen atoms in aluminium oxide is 2 : 3. Give the empirical formula of aluminium oxide. (1) ........................................................... (Total for question = 1 mark) Q4. Zinc oxide is formed by decomposition of zinc carbonate (i) In an experiment to decompose some zinc carbonate, the actual yield of zinc oxide was 7.2 g. The theoretical yield of zinc oxide for this experiment is 9.0 g. Calculate the percentage yield of zinc oxide. (2) ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. percentage yield = ........................................................... % (ii) Explain why the actual yield of a product in an experiment is usually lower than the theoretical yield. (2) ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. (iii) Calculate the percentage by mass of zinc in zinc oxide, ZnO. (relative atomic masses: O = 16, Zn = 65 relative formula mass of ZnO = 81) (2) ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. percentage by mass of zinc = ........................................................... % (Total for question = 6 marks) Q5. Complete the sentence by putting a cross ( ) in the box next to your answer. (1) Magnesium reacts with sulfur to form magnesium sulfide In magnesium sulfide 24 g of magnesium are combined with 32 g of sulfur. The ratio of magnesium atoms to sulfur atoms in magnesium sulfide is (relative atomic masses: Mg = 24, S = 32) (Total for question = 1 mark) Q6. Calculate the relative formula mass of calcium carbonate, CaCO3. (relative atomic masses: C = 12, O = 16, Ca = 40) (1) ............................................................................................................................................. relative formula mass = ........................................................... (Total for question = 1 mark) Q7. Compounds (a) (i) Balance the equation for the reaction between sodium and chlorine to produce sodium chloride by putting numbers in the spaces provided. (2) .................. Na + Cl2 → .................. NaCl (ii) In an experiment to make sodium chloride, the yield is 2.5 g. The theoretical yield of sodium chloride for this experiment is 4.0 g. Calculate the percentage yield of sodium chloride in this experiment. (2) ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. percentage yield = ........................................................... % (iii) Sodium chloride has a high melting point. Sodium chloride does not conduct electricity when solid but does conduct electricity when molten. Complete the sentence by putting a cross ( ) in the box next to your answer. These properties show that the structure of sodium chloride is (1) A ionic B giant molecular, covalent C simple molecular, covalent D metallic (iv) Calculate the relative formula mass of sodium chloride, NaCl. (relative atomic masses: Na = 23, Cl = 35.5) (1) ............................................................................................................................................. relative formula mass = ........................................................... (b) Calculate the percentage by mass of magnesium in magnesium sulfate, MgSO4. (relative atomic masses: O = 16, Mg = 24, S = 32 relative formula mass: MgSO4 = 120) (2) ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. percentage of magnesium = ........................................................... % (c) The formula of a molecule of ethane is C2H6. (i) Give the empirical formula of ethane. (1) ........................................................... (ii) Ethane is a simple molecular, covalent compound. Ethane has a low boiling point. Explain, in terms of particles it contains, why ethane has a low boiling point. (2) ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. (Total for question = 11 marks) Q8. The answers shown are the molecular formulae of four hydrocarbons. What is the molecular formula of the hydrocarbon with the empirical formula CH2? Put a cross in the box ( ) next to your answer. (1) A CH4 B C2 H6 C C2H4 D C3H8 (Total for question = 1 mark) Q9. Lead nitrate solution reacts with sodium iodide solution to form solid lead iodide and sodium nitrate solution. (i) Complete the sentence by putting a cross ( ) in the box next to your answer. (1) This reaction is an example of A combustion B separation C neutralisation D precipitation (ii) The balanced equation for this reaction is shown. Complete the equation by filling in the state symbols for the products. (2) Pb(NO3)2(aq) + 2NaI(aq) → PbI2(...................) + 2NaNO3(...................) (iii) Calculate the relative formula mass of sodium nitrate, NaNO3. (relative atomic masses: Na = 23, N = 14, O = 16) (1) ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. relative formula mass = ........................................................... (iv) The formula of lead iodide is PbI2 . Calculate, using this formula, the percentage by mass of lead in lead iodide. (relative atomic masses: Pb = 207, I = 127; relative formula mass of PbI2 = 461) (2) ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. percentage by mass = ........................................................... % (Total for question = 6 marks) Q10. (a) An acid can be reacted with a base in a titration experiment. (i) State the name of the type of reaction when an acid reacts with a base. (1) ............................................................................................................................................. (ii) Complete the sentence by putting a cross ( ) in the box next to your answer. The general equation for the reaction of an acid with a base is (1) A acid + base → alkali + water B acid + base → salt + carbon dioxide C acid + base → salt + water + hydrogen D acid + base → salt + water (b) A solution of sodium hydroxide is prepared. The The The The mass of a container with solid sodium hydroxide is determined. sodium hydroxide is transferred to a flask. mass of the empty container is determined. sodium hydroxide is dissolved in water and the volume made up to 2 dm3. The results are mass of container + solid sodium hydroxide = 17.12g mass of empty container = 7.02g The results are used to calculate the concentration of the sodium hydroxide solution. (i) Calculate the mass of solid sodium hydroxide transferred to the flask. (1) ............................................................................................................................................. mass of solid sodium hydroxide = ........................................................... g (ii) Calculate the concentration of the sodium hydroxide solution in g dm−3. (1) ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. concentration of sodium hydroxide solution = ........................................................... g dm−3 Q11. In an experiment, 25.0 cm3 samples of a solution of sodium hydroxide, NaOH, were titrated with 0.095 mol dm–3 hydrochloric acid, HCl. NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O 18.5 cm3 of the hydrochloric acid neutralised 25.0 cm3 of the sodium hydroxide solution. Calculate the concentration of the sodium hydroxide solution, NaOH, in mol dm–3. (2) ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. concentration of sodium hydroxide solution = ........................................................... mol dm–3 (Total for question = 2 marks) Q12. In an experiment 25.0 cm3 of 0.0100 mol dm–3 ethanoic acid, CH3COOH, was titrated with 0.0200 mol dm–3 sodium hydroxide solution, NaOH. CH3COOH + NaOH → CH3COONa + H2O Calculate the volume, in cm3, of 0.0200 mol dm–3 sodium hydroxide solution needed to neutralise the ethanoic acid in this experiment. (3) ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. volume of sodium hydroxide solution needed = ........................................................... cm3 (Total for question = 3 marks) Q13. Titration can be used to determine the exact amount of hydrochloric acid that reacts with a given amount of sodium hydroxide solution. HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O Sodium hydroxide solution is titrated with dilute hydrochloric acid. The results of the experiment are volume of sodium hydroxide solution = 25.0 cm3 volume of 0.100 mol dm–3 hydrochloric acid used (i) State the volume of hydrochloric acid that must be used to calculate the concentration of sodium hydroxide solution. (1) volume of hydrochloric acid =. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .cm3 (ii) In a different experiment, 25.0 cm3 of sodium hydroxide solution reacted with 23.2 cm3 of 0.100 mol dm–3 hydrochloric acid, HCl. Calculate the concentration of this sodium hydroxide solution, NaOH, in mol dm–3. (3) NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O ............................................................................. ...................... ............................................................................. ...................... ............................................................................. ...................... ............................................................................. ...................... ............................................................................. ...................... ............................................................................. ...................... ............................................................................. ...................... ............................................................................. ...................... concentration of sodium hydroxide solution = . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .mol dm–3 Q14. A solution is made by dissolving calcium chloride in water. 11.1 g of calcium chloride are dissolved in water. The volume of the solution is made up to 500 cm3. Calculate the concentration, in mol dm−3, of calcium chloride, CaCl2, in this solution. (relative atomic masses: Cl = 35.5, Ca = 40.0) (3) ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. concentration = ...........................................................mol dm−3 Q15. Dilute nitric acid is placed in a beaker. A few drops of indicator are added. Sodium hydroxide solution is added until the indicator changes colour. Universal indicator is not a suitable indicator for this experiment. Suggest the name of a suitable indicator and state the colour change. (2) name of indicator ............................................................................................................................................. colour change from .................................................................... to .................................................................... (Total for question = 2 marks) Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)