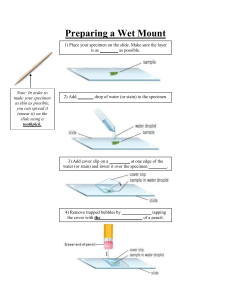
Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials SCOPE 1. These test methods cover the tension testing of metallic materials in any form at room temperature. (10-38 C or 50 to 100 F) determine yield strength yield point elongation tensile strength elongation reduction of area 2. The gauge lengths for most round specimens are required to be 4D for E8 and 5D for E8M 3. The values stated in metric units are to be regarded as separate from meter/gram unit. Significance and Use Tension test provide information on strength and ductility of materials under tensile stresses. This information may be useful in comparisons of materials, alloy development, quality control, and design under certain circumstances. Testing Machine Apparatus Gripping Device Dimension-Measur Devices Extensometer Testing Machine Universal Testing Machine is capable of applying tensile load at a controlled rate of deformation or load Gripping Device A gripping device, used to transmit the load from the testing machine to the test. Dimension-Measure Devices vernier caliper & Micrometer Used to measure th edimensions of the sppecmen Extensometer Extensometer used to measure the deformation of the specimens TEST SPECIMENS When preparing the specimen, that should be free of cold work, notches, chatter marks, grooves, gouges, burrs, rough surface or edges, overheating or other condition which can deleteriously affect the properties to be measured Specimens Dimension FIG. 1 Rectangular Tension Test Specimens Sheet and Plate types Procedure 1.Measure and record thee specimen dimension necessary to determine the cross-sectional area at the smallest point. the original cross sectional area is used for all engineer. 2 . Use ink and a scribe or punch to place gauge marks on the test specimen at the appropriate gauge length. The distance between the gauge mark after the specimen is broken is used to determine the percent elongation at break. (To accurately compare elongation value between tests ,the gauge length must be same) 3. Zero the testing machine without the specimen inserted in the grips. The install the specimen in the specimen in the grips and start loading the sample. The speed of testing is generally specified in one of three manner a) the rate of straining of the specimen is 0.015±o.006 mm/mm/min (0.5 in/in of the gauge length per minute ) b) the rate of stressing of the specimen is 1.15-11.5 MaP c) the rate of separation of the crossheads is 0.015±0.003 mm/mm/min In addition, the test rate is to remain constant through yield ultimate tensile strength and elongation at break. 4. Run the test until specimen failure or fracture. Remove the broken sample from the machine and fit the fractured ends together. (Measure the distance between the gauge marks to the nearest o.05 millimeter) Analysis and Results Plot the stress versus strain curve. Determining the yield strength using offset method Determining the modulus of elasticity using Hooke's law σ=E where: E =Modulus of elasticity σ =stress in proportional limit ε= corresponding strain, mm/mm(in./in.) FIG. 2 Stress-Straincurve Calculate the tensile strength σ max = P max /Ao FIG. 3 Stress-Strain curve for Determination of Yield Strength where: σ max =tensile strength/ ultimate strength ,in MPa(psi) P max=maximum load carried by the specimen during tension test, N(Ib) Ao= original cross- sectional area of the specimen, mm^2(in)^2 Calculate the elongation FIG. 4 Stress-Strain Diagram Showing Yield Point Elongation. Percent elongation = [(Ls-Lo)/Lo) x 100] where: Ls = gauge length after rupture, mm(in.) Lo = original gauge length, mm(in.) For elongation > 3.0 percent, fit the ends of the fractured specimen together and measure Ls as the distance between two gauge marks. For elongation < or equal 3.0 percent, fit the fractured ends together and apply an end load along the axis of the specimen sufficient to close the fractured ends together, then measure Ls as the distance between gauge marks. Calculate the reduction of cross-sectional area percent reduction in cross-sectional area =[ (Ao-As)/Ao ) x 100 ] where: Ao = original cross - sectional area of the specimen, mm^2(in.)^2 As = cross- sectional area after rupture, mm^2(in.)^2 Report 1 Test information on materials not covered by a product specification should be reported in accordance with 8.2 or both 8.2 and 8.3. 2 Test information to be reported shall include the follow- ing when applicable: Reference to the standard used, i.e. E8 or E8M. 8.2.2 Material and sample identification 3 Specimen type. Yield strength and the method used to determine yield. Yield point elongation . Tensile Strength (also known as Ultimate Tensile Strength) . Elongation (report original gauge length, percentage increase, and method used to determine elongation; i.e. at fracture or after fracture) 3 Test information to be available on request shall include. Specimen test section dimension(s). Equation used to calculate cross-sectional area of rectangular specimens taken from large-diameter tubular prod- ucts. Speed and method used to determine speed of testing . Method used for rounding of test results. Reasons for replacement specimens THANKS. MEMBER Mr.Napat Potisan ID 6331112002 Mr.Arthiwat Yatyuklai ID 6331112019 Mr.Si Thu Wai