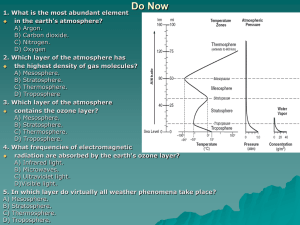
Composition of the Atmosphere The atmosphere is a mixture of gases surrounding Earth. Nitrogen (78%), the most common atmospheric gas, is released when dead plants and dead animals break down and also when volcanoes erupt. Oxygen (21%), the second most common atmospheric gas, is made by phytoplankton and plants. The remaining 1% of the atmosphere is made up of argon, carbon dioxide, water vapor and other gases. Air Pressure (Atmospheric Pressure) Gravity pulls gas molecules toward Earth, causing Air Pressure, which is the force with which air molecules push on a surface. Strongest at Earth’s surface Air Pressure decreases as altitude increseses Temperature Also changes as altitude increases The composition of atmospheric layers affect their temperature. The temperature differences result from the amount of gases present in each layer that absorb solar energy As the amount of gases that absorb solar energy increases, the temperature increases Layers of the Atmosphere The Earth’s atmosphere is divided into five layers based on their composition. The Silly Mouse Took Ex-lax R O P O S P H E R E T R A T O S P H E R E E S O S P H E R E H E R M O S P H E R E X O S P H E R E Troposphere Lowest layer of the atmosphere, lying next to Earth’s surface. Temperature decreases with altitude. Contains almost 90% of the atmosphere’s mass. Nearly all weather occurs in this layer. Water vapor, clouds, air pollution, and organisms are also found here. Stratosphere The atmospheric layer above the troposphere. Contains little moisture Lower stratosphere is extremely cold, but temperature increases as altitude increases in the stratosphere. The Ozone Layer- The upper layer of the Stratosphere. it absorbs UV radiation from the sun, warming the air protects life on Earth. Mesosphere The middle layer of the atmosphere. Coldest layer Temperature decreases as altitude increases, just like the troposphere. The upper layer of the Mesosphere (lower portion of the Thermosohere) is called the Ionosphere Ionosphere The lower part of the thermosphere is considered the Ionosphere. As a result of N2 atoms and O2 atoms absorbing the radiation, temperature in the thermosphere rises, and gas particles become electrically charged ions. Ions within the ionosphere can radiate energy as shimmering lights called auroras, a.k.a. the Northern and Southern Lights. Thermosphere Uppermost atmospheric layer. Temperature again increases steadily with altitude because nitrogen and oxygen atoms absorb solar radiation. This releases thermal energy. No data to determine its upper boundary. Blends with the vacuum of space (exosphere). Exosphere The last layer of the atmosphere. Very difficult to determine where it stops and space begins Very few atoms in this layer of the atmosphere Videos Antarctica Auroras Aurora Northern Lights as seen from Space